Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Orthop. Apr 18, 2015; 6(3): 374-379
Published online Apr 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i3.374
Published online Apr 18, 2015. doi: 10.5312/wjo.v6.i3.374
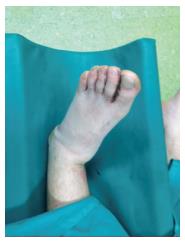
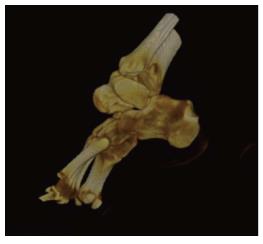
Figure 1 Photograph showing the calcaneus and the rest foot is displaced medially while tibiotalar joint maintain normal angulation.
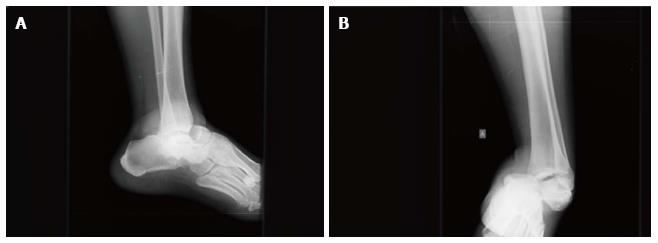
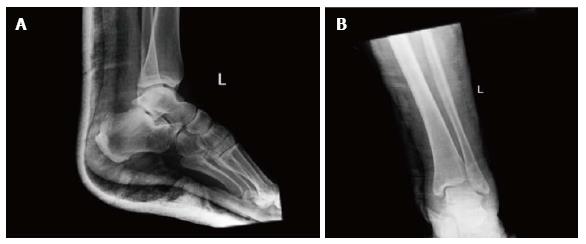
Figure 2 X-rays of the left ankle.
Dislocation of the talonavicular and talocalcaneal joints with no obvious fracture is shown. The calcaneus is displaced in medial position in the anteroposterior view. A: Lateral view; B: Anterior posterior view.
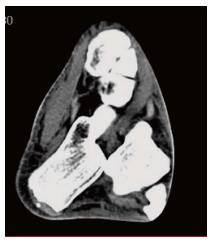
Figure 3 Transverse plane computed tomography image of the patient’s left ankle demonstrating the subtalar dislocation without any associated fracture.
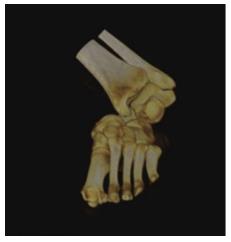
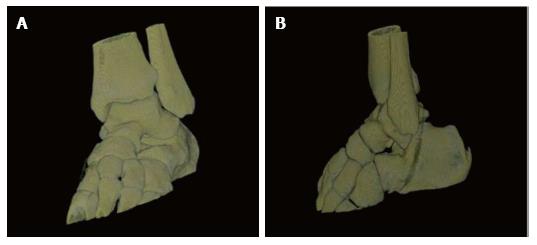
Figure 4 Computed tomography scan with 3D reconstruction image in the coronal plane showing the medial subtalar displacement of the calcaneus with the rest foot.
Figure 5 Computed tomography scan with 3D reconstruction image of the patient΄s ankle joint that demonstrates the dislocation of the talocalcaneus joint and the absence of a fracture.
Figure 6 Radiographs of the left ankle after reduction and immobilization with a posterior splint.
A: Lateral view; B: Anterior posterior view.
Figure 7 Computed tomography scan with 3D reconstruction images after reduction.
There are no intraarticular free bodies. A: Coronal plane; B: Sagittal plane.
- Citation: Giannoulis D, Papadopoulos DV, Lykissas MG, Koulouvaris P, Gkiatas I, Mavrodontidis A. Subtalar dislocation without associated fractures: Case report and review of literature. World J Orthop 2015; 6(3): 374-379
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2218-5836/full/v6/i3/374.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5312/wjo.v6.i3.374