Copyright
©2010 Baishideng.
World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. Jun 15, 2010; 1(2): 23-29
Published online Jun 15, 2010. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.23
Published online Jun 15, 2010. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.23
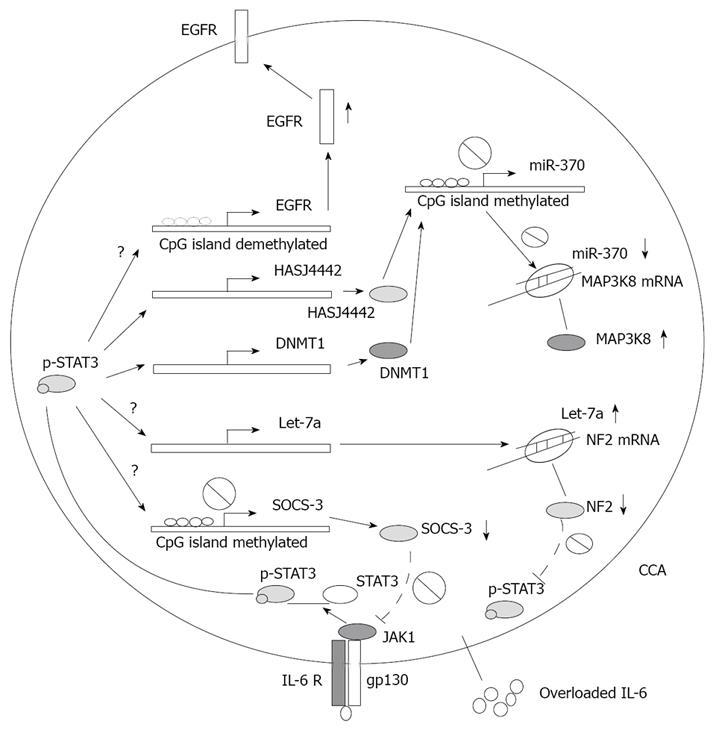
Figure 1 The role IL-6 signaling in CCA inflammation-related epigenetic regulation.
In CCA, the negative feedback of the IL-6 pathway is deficient owing to aberrant epigenetic silence of suppressors of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3), which is mediated by the IL-6/STAT3 pathway to maintain gene promoter hypermethylated. Up-regulation of EGFR expression through decreasing its promoter methylation level mediated by undefined mechanisms. Moreover, overloaded IL-6 also increased let-7a expression via an undetermined mechanism, resulting in suppression of neurofibromatosis 2 (NF2) and subsequently increasing phosphorylated STAT3. Overloaded IL-6 in CCA can up-regulate expressions of two DNA methyltransferases, DNMT1 and HASJ4442, which leading to hypermethylation of the miR-370 gene promoter and abrogating suppressing effect of miR-370 on oncogenic mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 8 (MAP3K8).
- Citation: Huang L, Frampton G, Liang LJ, DeMorrow S. Aberrant DNA methylation profile in cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2010; 1(2): 23-29
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2150-5330/full/v1/i2/23.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4291/wjgp.v1.i2.23