Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Sep 28, 2014; 6(9): 737-740
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i9.737
Published online Sep 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i9.737
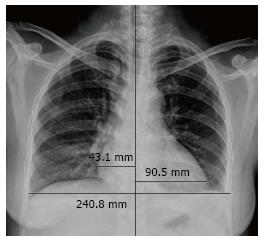
Figure 1 Posteroanterior chest radiograph showing an increased cardio-thoracic ratio [(43.
1+90.5)/240.8 > 0.5] demonstrating enlargement of the heart. Bilateral pleural effusion is also evident.
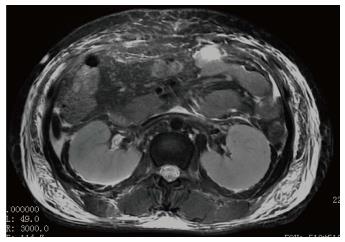
Figure 2 Axial Fat Suppressed T2 Weighted Periodically Rotated Overlapping Parallel Lines with Enhanced Reconstruction FSE image of the abdomen shows bilaterally enlarged kidneys with loss of corticomedullary differentiation.
Anterior, posterior renal fascia along with lateral coanal fascia is thickened. High signal intensity within the abdominal cavity represents ascites and those in abdominal soft tissue represent soft tissue edema.
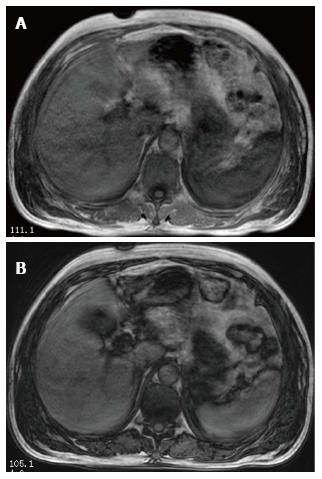
Figure 3 Axial LAVA-Flex T1 Weighted In-Phase image (A) and gradient echo T1 Weighted Out-of-Phase image (B) of the abdomen show decreased signal intensity of the spleen on In-Phase image (A) as compared to Out-of-Phase image (B).
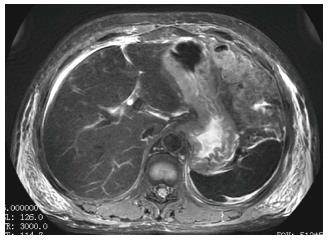
Figure 4 Axial Fat Suppressed T2 Weighted Periodically Rotated Overlapping Parallel Lines with Enhanced Reconstruction FSE image of the abdomen shows decreased signal intensity of the spleen as well as the liver as compared to that of paraspinal muscle.
- Citation: Das SK, Zeng LC, Li B, Niu XK, Wang JL, Bhetuwal A, Yang HF. Magnetic resonance imaging correlates of bee sting induced multiple organ dysfunction syndrome: A case report. World J Radiol 2014; 6(9): 737-740
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i9/737.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i9.737