Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Radiol. Oct 28, 2014; 6(10): 756-778
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.756
Published online Oct 28, 2014. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.756
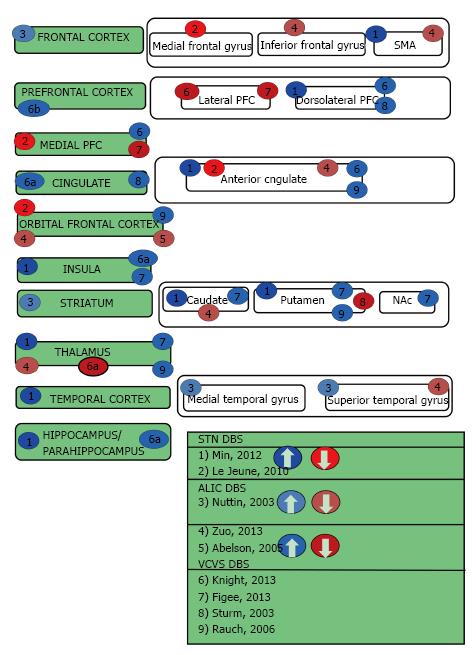
Figure 1 Obsessive compulsive disorder deep brain stimulation.
aAs stimulation voltage increased from 3 V 130 Hz to 5 V 130 Hz, the region of BOLD signal modulation increased; bAs stimulation voltage increased from 3 V 130 Hz to 5 V 130 Hz, the region of BOLD signal modulation decreased for n = 2 pigs. SMA: Supplementary motor area; NAc: Nucleus accumbens; PFC: Prefrontal cortex; BOLD: Blood oxygen level dependent.
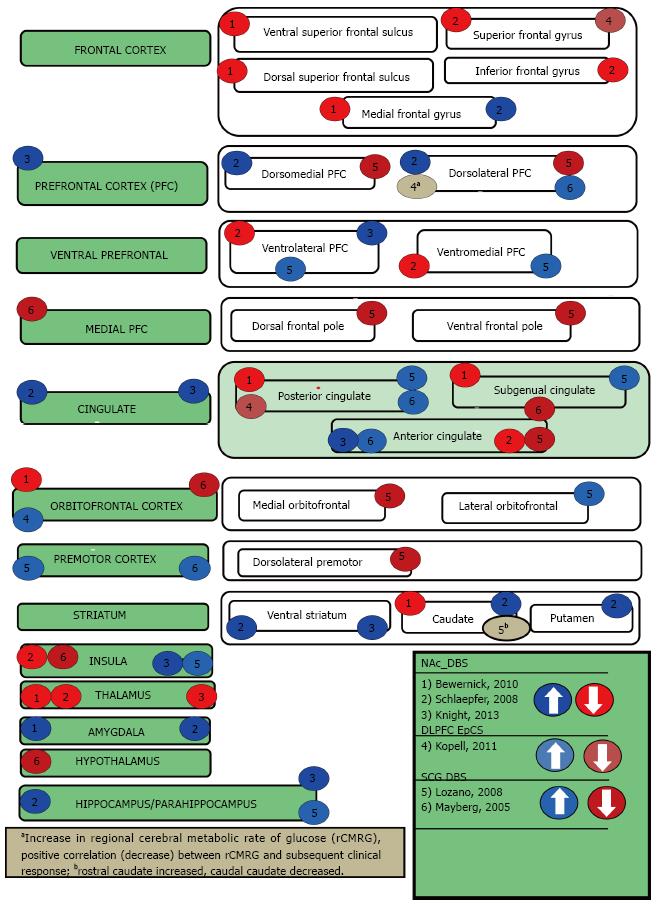
Figure 2 Treatment-resistant depression deep brain stimulation.
NAc: Nucleus accumbens; DLPFC: Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; EpCS: Epidural cortical stimulation; SCG: Subcallosal cingulate gyrus.
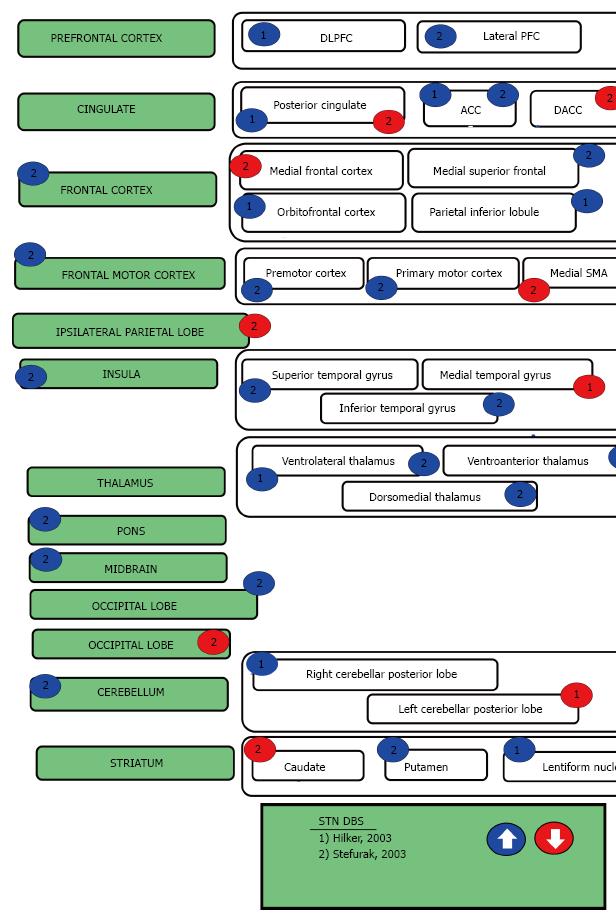
Figure 3 Parkinson’s disease deep brain stimulation.
DLPFC: Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; PFC: Prefrontal cortex; ACC: Anterior cingulate cortex; DACC: Dorsoanterior cingulate cortex; SMA: Supplementary motor area; STN: Subthalamic nucleus; DBS: Deep brain stimulation.
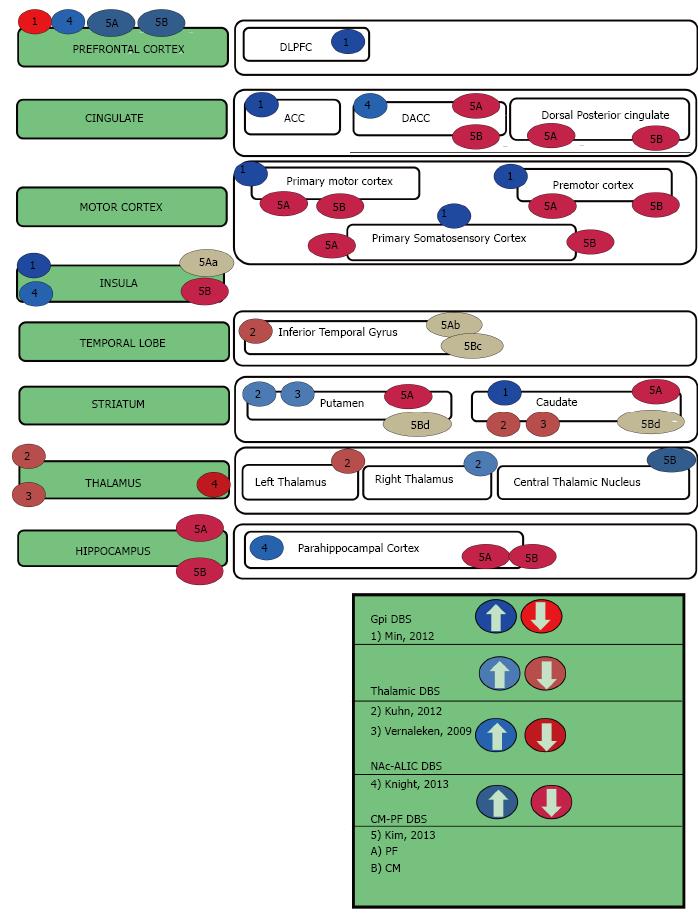
Figure 4 Tourette syndrome deep brain stimulation.
aResponse at 130 Hz 3V AND 60 Hz 3V decreased, but increased at 130 Hz 5V and 60 Hz 5V; bResponse decreased at 130 Hz 3V, but increased at 130 Hz 5V and 60 Hz 5V; cResponse decreased at 130 Hz 3v and 60 Hz 3V, but increased at 130 Hz 5V and 60 Hz 5V; dResponse increased at 130 Hz 3V, but decreased at 130 Hz 5V and 60 Hz 5V. GPi: Globus pallidus internus; NAc: Nucleus Accumbens; ALIC: Anterior limb of internal capsule; CM-PF: Centromedian-parafascicular nuclei complex; DLPFC: Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; ACC: Anterior cingulate cortex; DACC: Dorsal Anterior cingulate cortex; DBS: Deep brain stimulation.
- Citation: Williams NR, Taylor JJ, Lamb K, Hanlon CA, Short EB, George MS. Role of functional imaging in the development and refinement of invasive neuromodulation for psychiatric disorders. World J Radiol 2014; 6(10): 756-778
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v6/i10/756.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.756