Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Radiol. Aug 28, 2025; 17(8): 107732
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i8.107732
Published online Aug 28, 2025. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v17.i8.107732
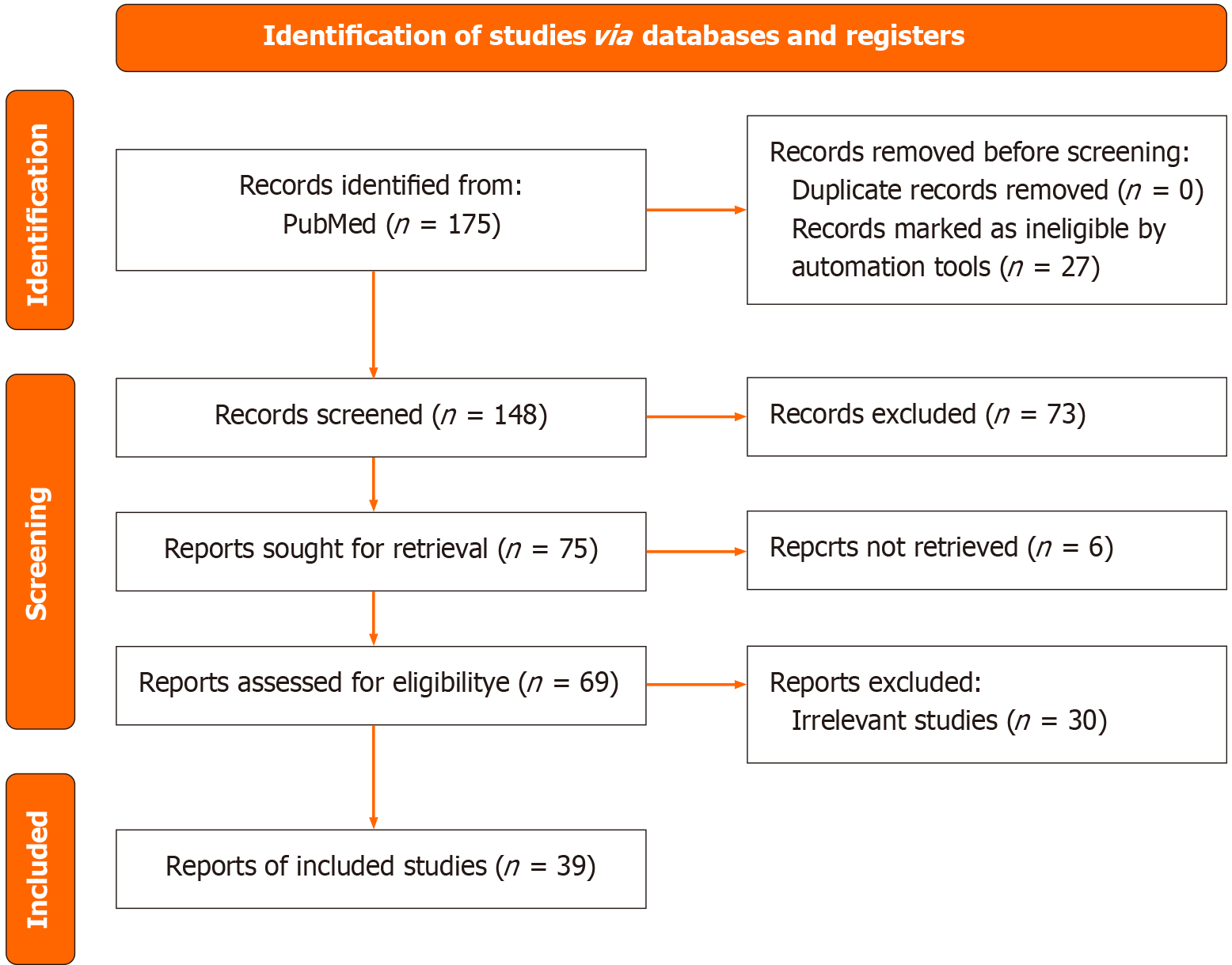
Figure 1
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses flow diagram outlining the study selection process for a systematic review of the applications of photon-counting detector CT in oncologic imaging.
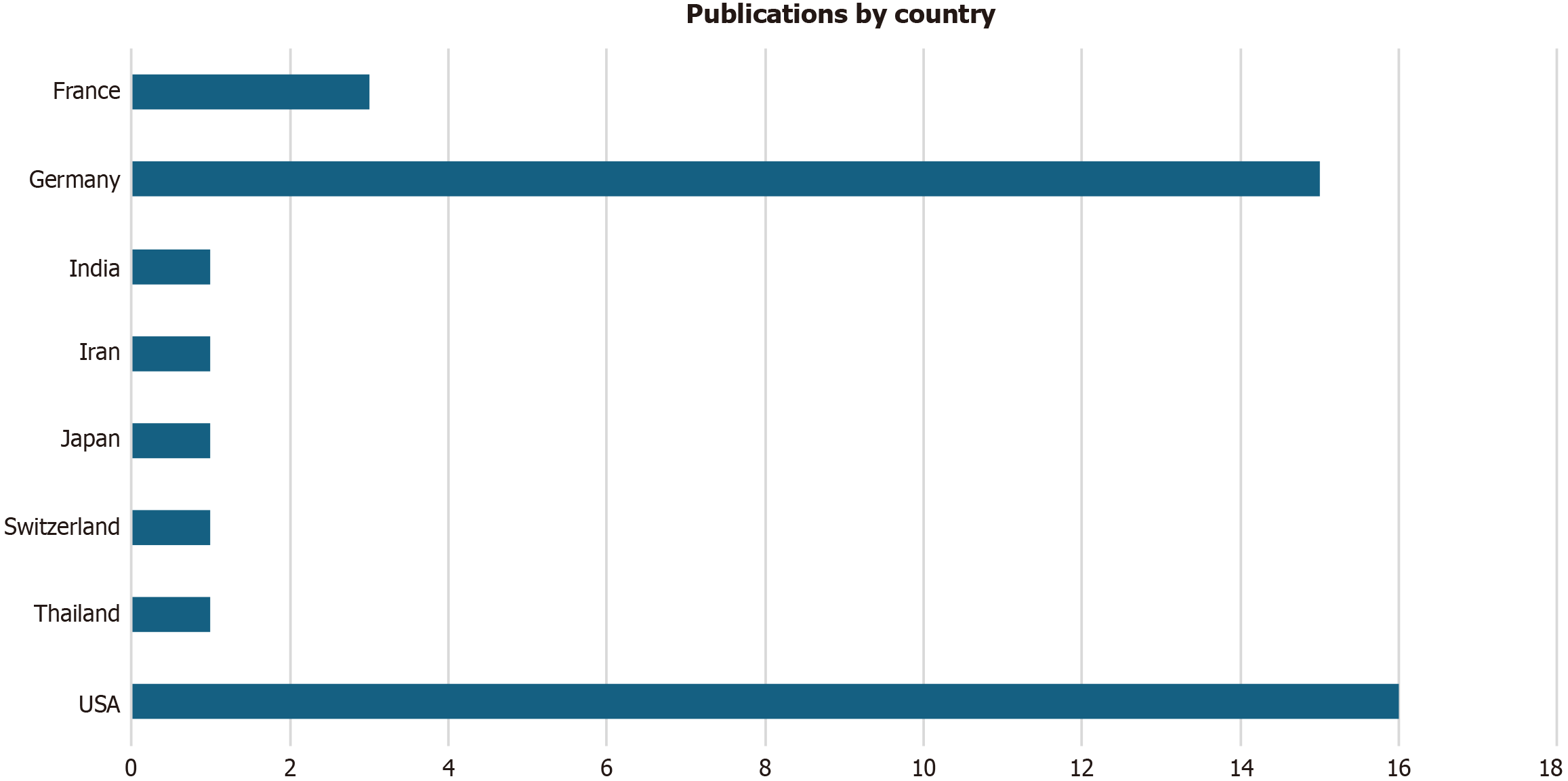
Figure 2 Number of publications by country.
USA: United States of America.
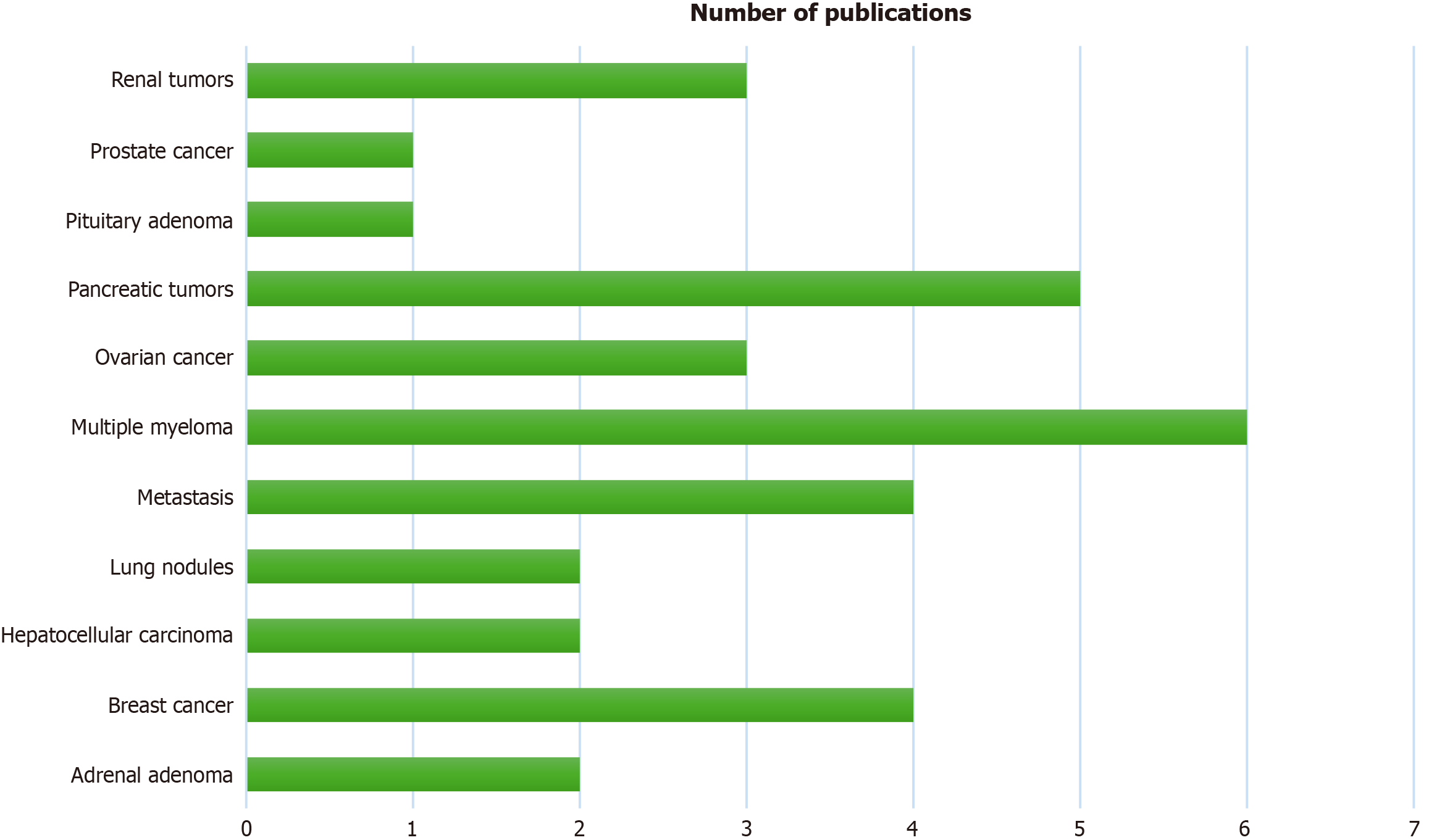
Figure 3
Types of tumors assessed by photon-counting detector CT and the relative number of publications.
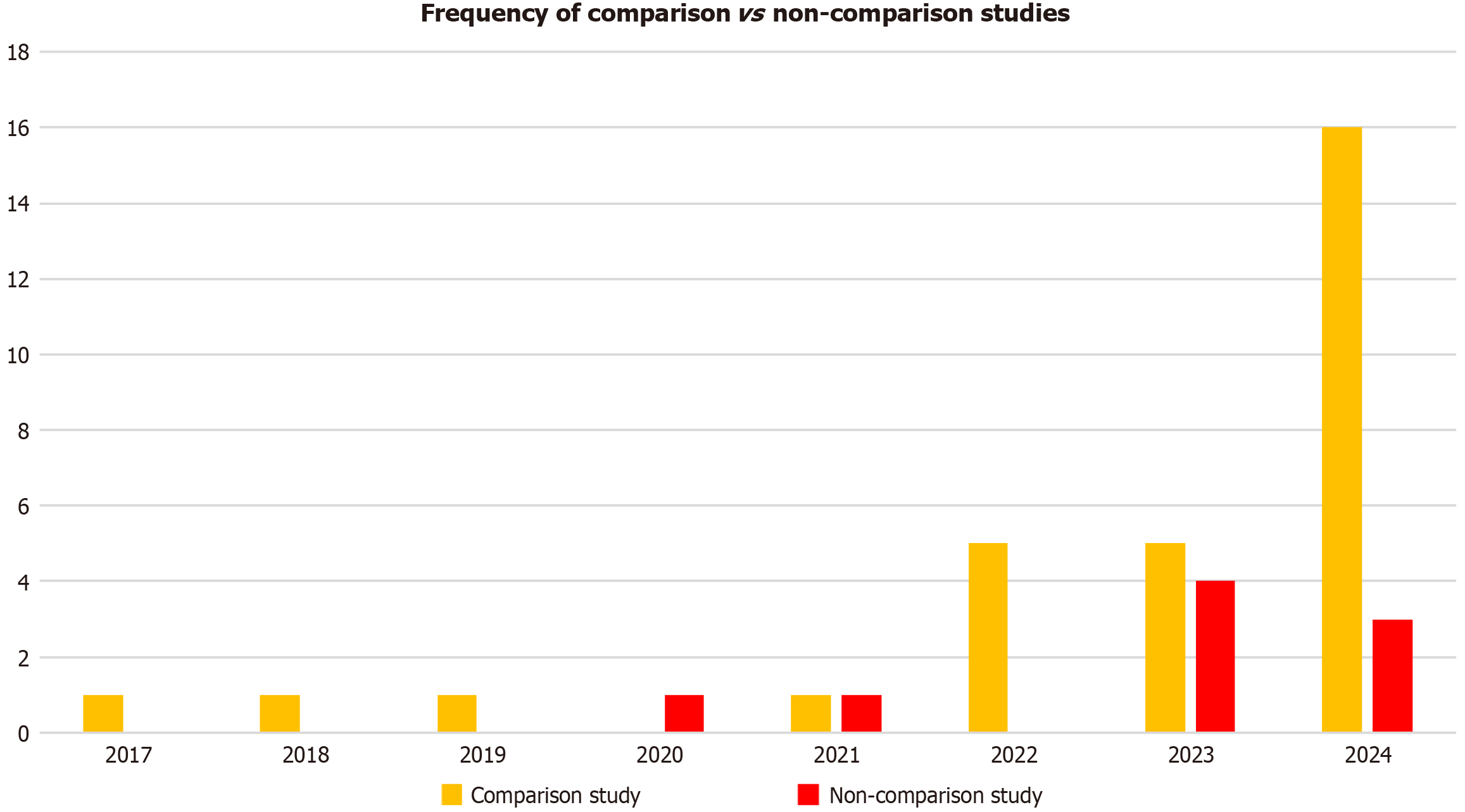
Figure 4
Frequency of comparison studies vs non-comparison studies in each year from 2017-2024.
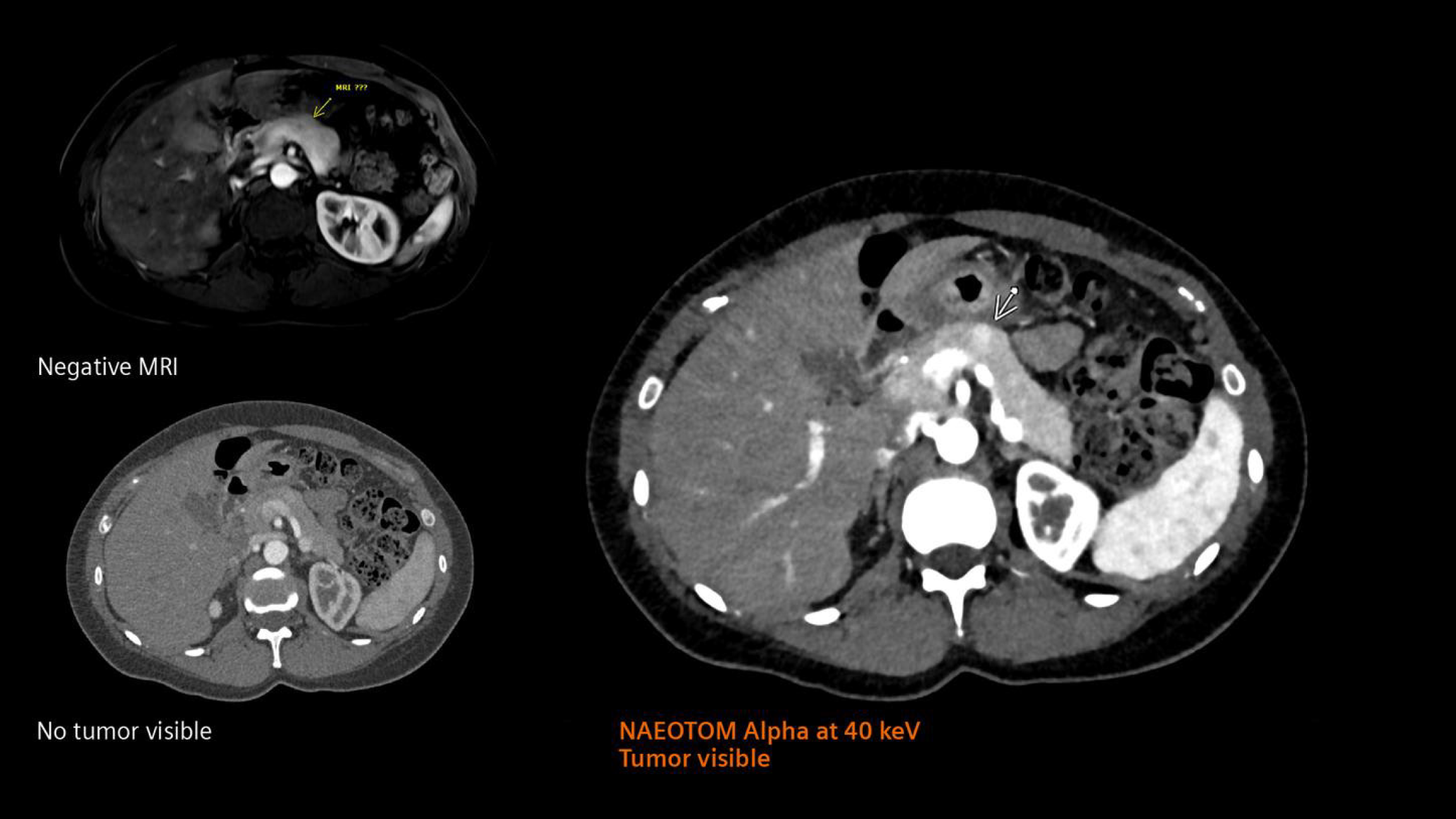
Figure 5 Combination of high resolution and spectral information obtained with photon-counting detector CT.
NAEOTOM Alpha allows the high-precision visualization of a pancreatic insulinoma with high precision when compared with conventional CT and magnetic resonance imaging[19]. Citation: Siemens Healthineers. The NAEOTOM Alpha class. Available from: https://www.siemens-healthineers.com/computed-tomography/naeotom. Copyright ©Siemens Healthineers AG 2024. The authors have obtained the permission (Supplementary material). MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging.
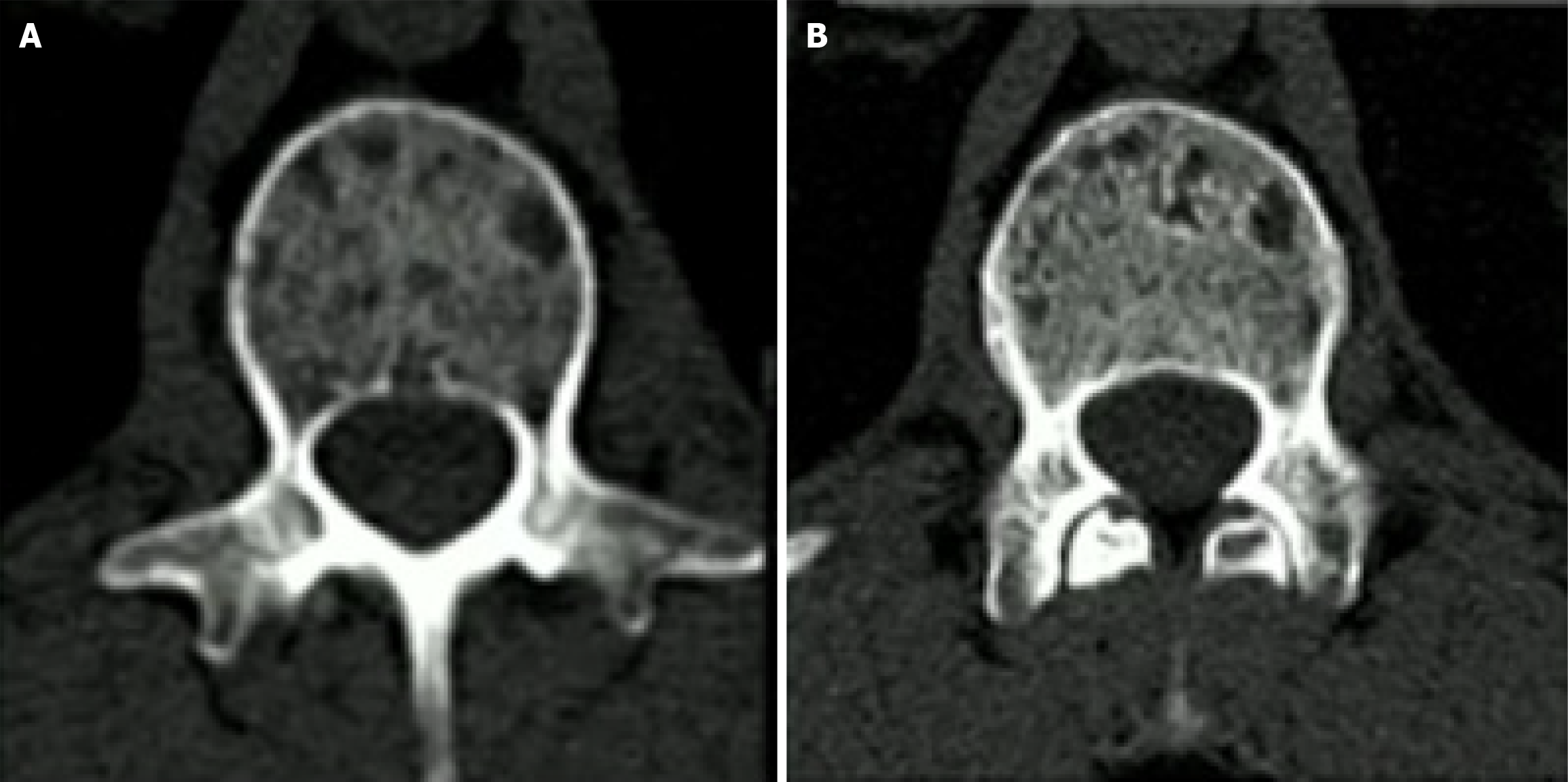
Figure 6 Comparison between second generation dual energy CT and photon-counting detector CT.
The images were obtained from the vertebra of a 56-year-old patient with multiple myeloma[19]. Note the improvement in spatial resolution in the photon-counting detector CT image with a better depiction of trabeculae and osteolysis. A: Second generation dual energy CT; B: Photon-counting detector CT. Citation: Siemens Healthineers. The NAEOTOM Alpha class. Available from: https://www.siemens-healthineers.com/computed-tomography/naeotom. Copyright ©Siemens Healthineers AG 2024. The authors have obtained the permission (Supplementary material).
- Citation: Perera Molligoda Arachchige AS, Dashiell A, Jesuraj AS, D’Urso AI, Fiore B, Cattaneo M, Pierzynska E, Szydelko S, Centini FR, Verma Y. Applications of photon-counting CT in oncologic imaging: A systematic review. World J Radiol 2025; 17(8): 107732
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v17/i8/107732.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v17.i8.107732