Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Radiol. Jul 28, 2024; 16(7): 265-273
Published online Jul 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i7.265
Published online Jul 28, 2024. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v16.i7.265
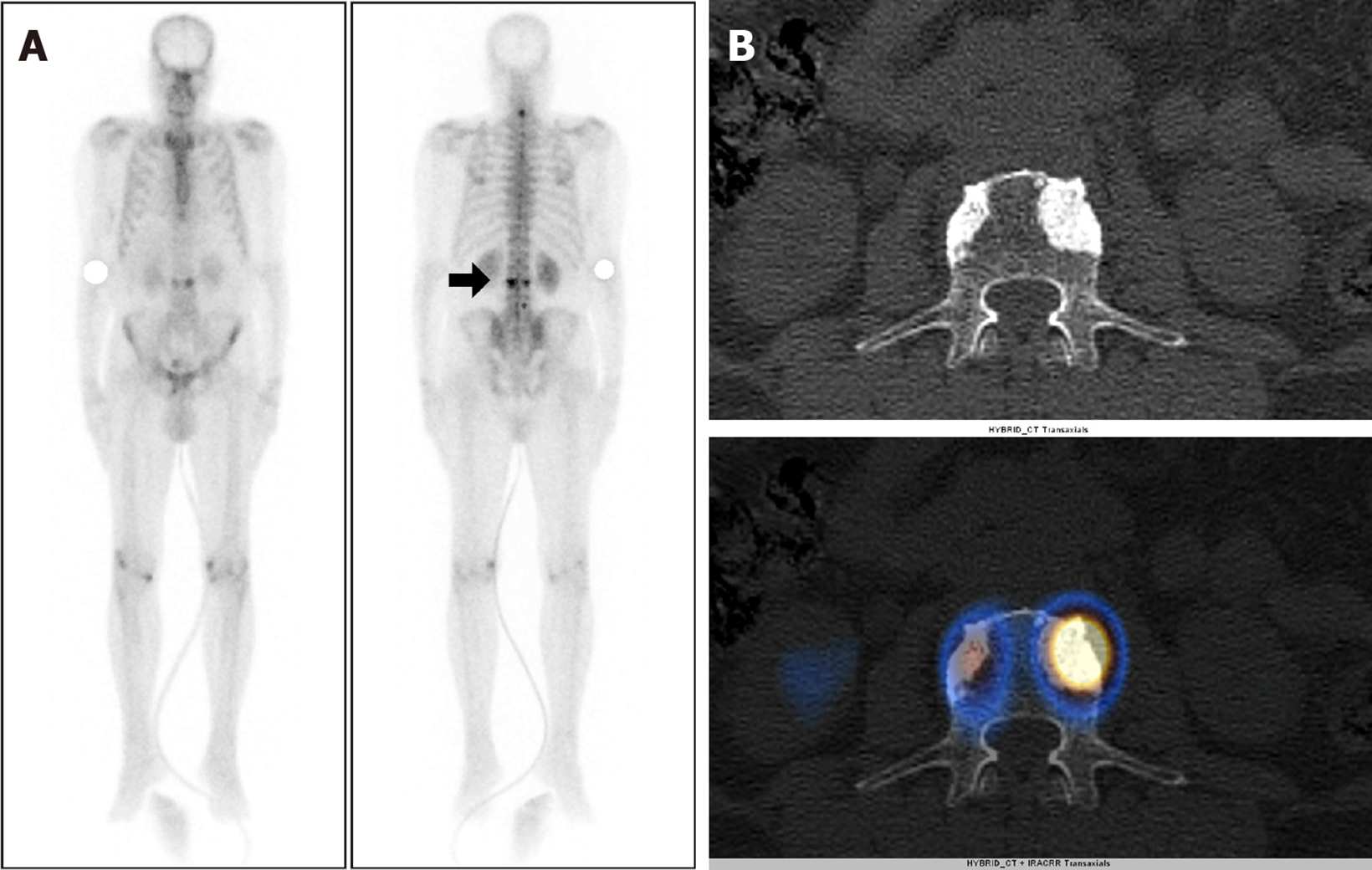
Figure 1 A 74-year-old male, with a newly diagnosed case of carcinoma of the prostate [Gleason’s Score 7 (4 + 3)] with serum prostate-specific antigen level 491 ng/mL and underwent whole body bone scintigraphy.
A: 99mTc methylene diphosphonate Whole body planar images show focal increased tracer uptake involving the cervical and lumbar vertebrae (arrow) raising the suspicion of metastatic disease; B: Axial computed tomography (CT) and fused single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)-CT images show tracer localization to sclerotic lesion involving L3 vertebrae suggestive of metastatic disease. No metastatic disease was seen in pelvic bones on SPECT-CT.
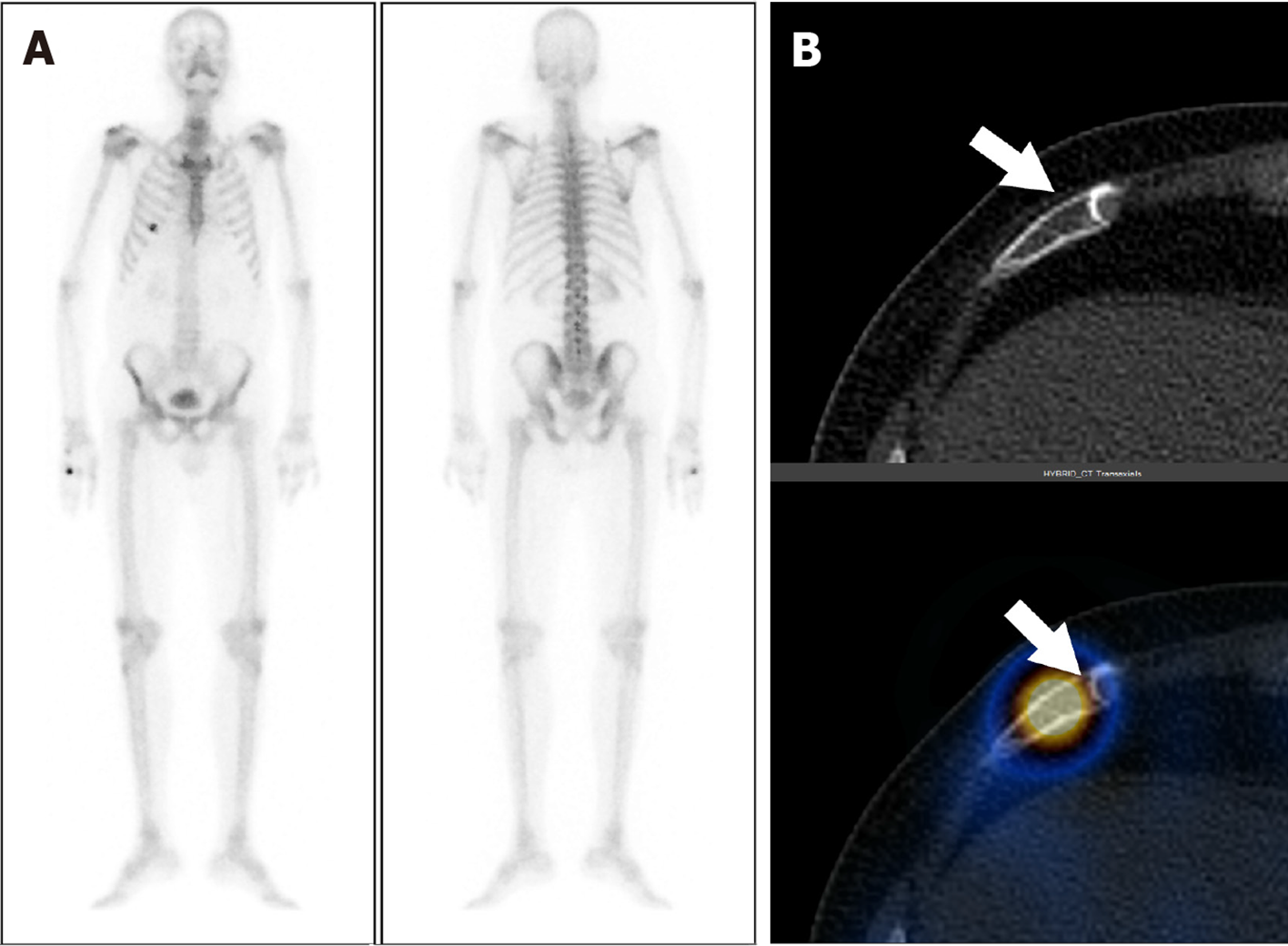
Figure 2 A 66-year-old male with carcinoma of the prostate and serum prostate-specific antigen of 23.
3 ng/mL. A: Staging with whole body bone scintigraphy show focal areas of increased tracer uptake involving the right 6th rib; B: Axial computed tomography (CT) and fused single photon emission computed tomography-CT images show tracer localization to the right 6th rib anteriorly with a fracture line (arrow). The uptake was thus secondary to rib fracture post traumatic. There was no other abnormal uptake anywhere in the bones on whole body study.
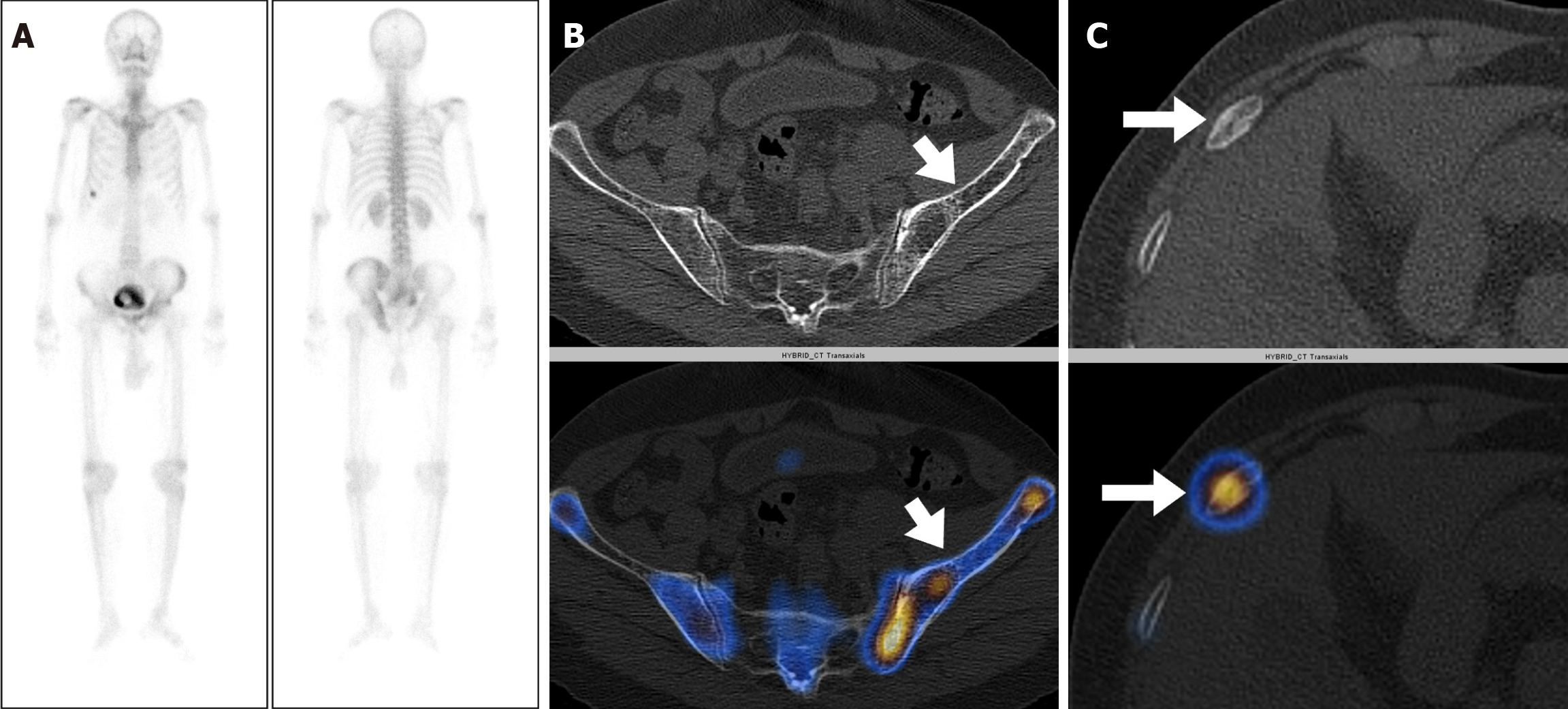
Figure 3 A 77-year-old male with carcinoma of the prostate and a Gleason’s Score 8 (4 + 4) and serum prostate-specific antigen level of 100 ng/mL.
A: Staging whole body bone scintigraphy show heterogeneously increased tracer uptake involving the left hemipelvis and focal areas of increased tracer uptake involving the right 8th rib raising the suspicion of metastatic disease; B and C: Axial computed tomography (CT) and fused single photon emission computed tomography-CT images localizes the tracer to the left iliac bone with cortical thickening and bony expansion consistent with Paget’s disease (arrow in B) and to the right 8th rib anteriorly with a fracture line (arrow in C).
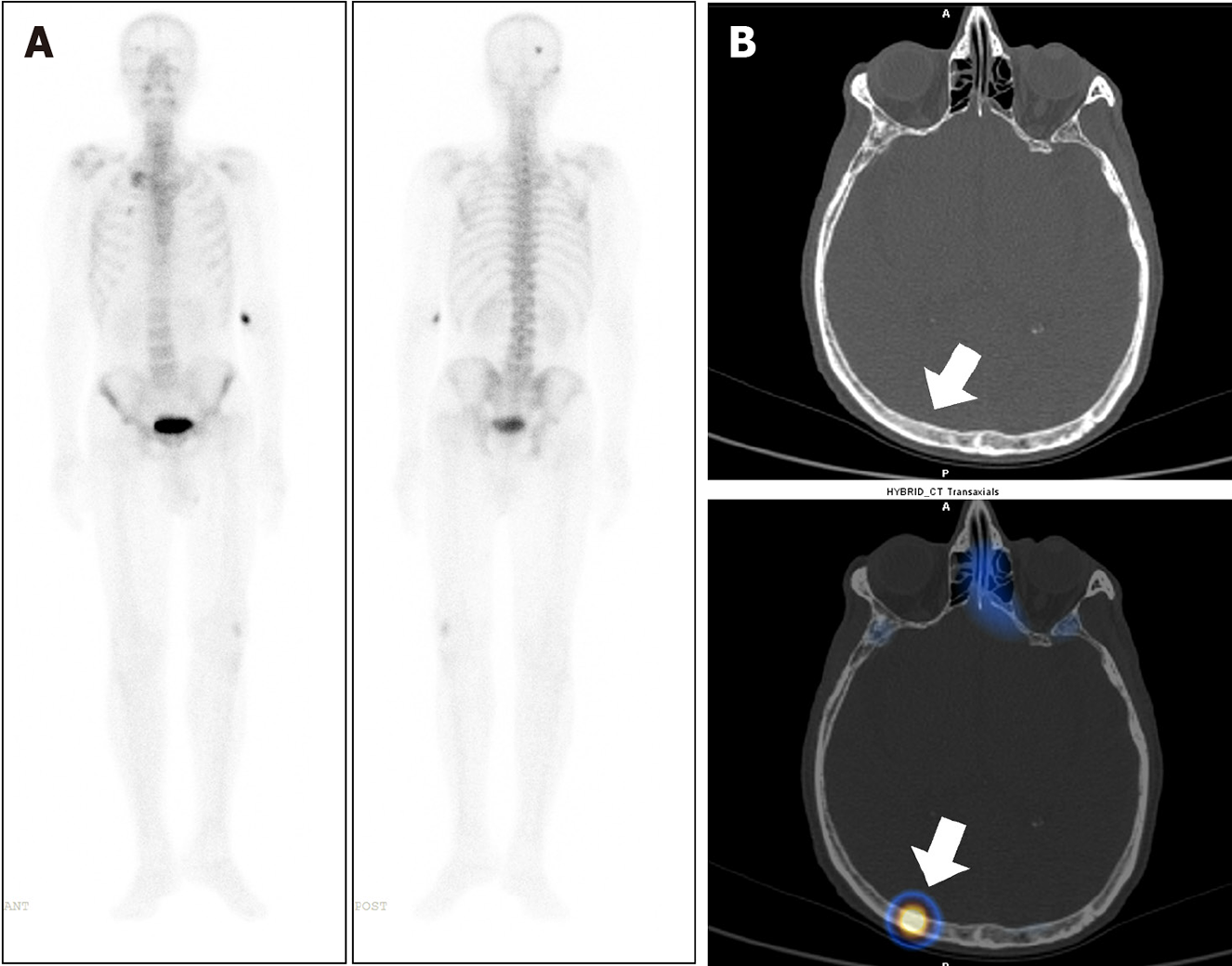
Figure 4 A 76-year-old male, with a newly diagnosed case of carcinoma of the prostate underwent whole body bone scintigraphy.
A: 99mTc methylene diphosphonate Whole body planar images show solitary focal area of increased tracer uptake involving skull bone on the right side; B: Axial computed tomography (CT) and fused single photon emission computed tomography-CT images show tracer localization to the right parietal bone (arrow) with no significant CT abnormality to suggest of metastatic disease involvement. The lesion was thus considered indeterminate.
- Citation: Singh P, Agrawal K, Rahman A, Singhal T, Parida GK, Gnanasegaran G. Incidence of exclusive extrapelvic skeletal metastasis in prostate carcinoma on bone scintigraphy. World J Radiol 2024; 16(7): 265-273
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1949-8470/full/v16/i7/265.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v16.i7.265