Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Aug 27, 2025; 17(8): 105112
Published online Aug 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i8.105112
Published online Aug 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i8.105112
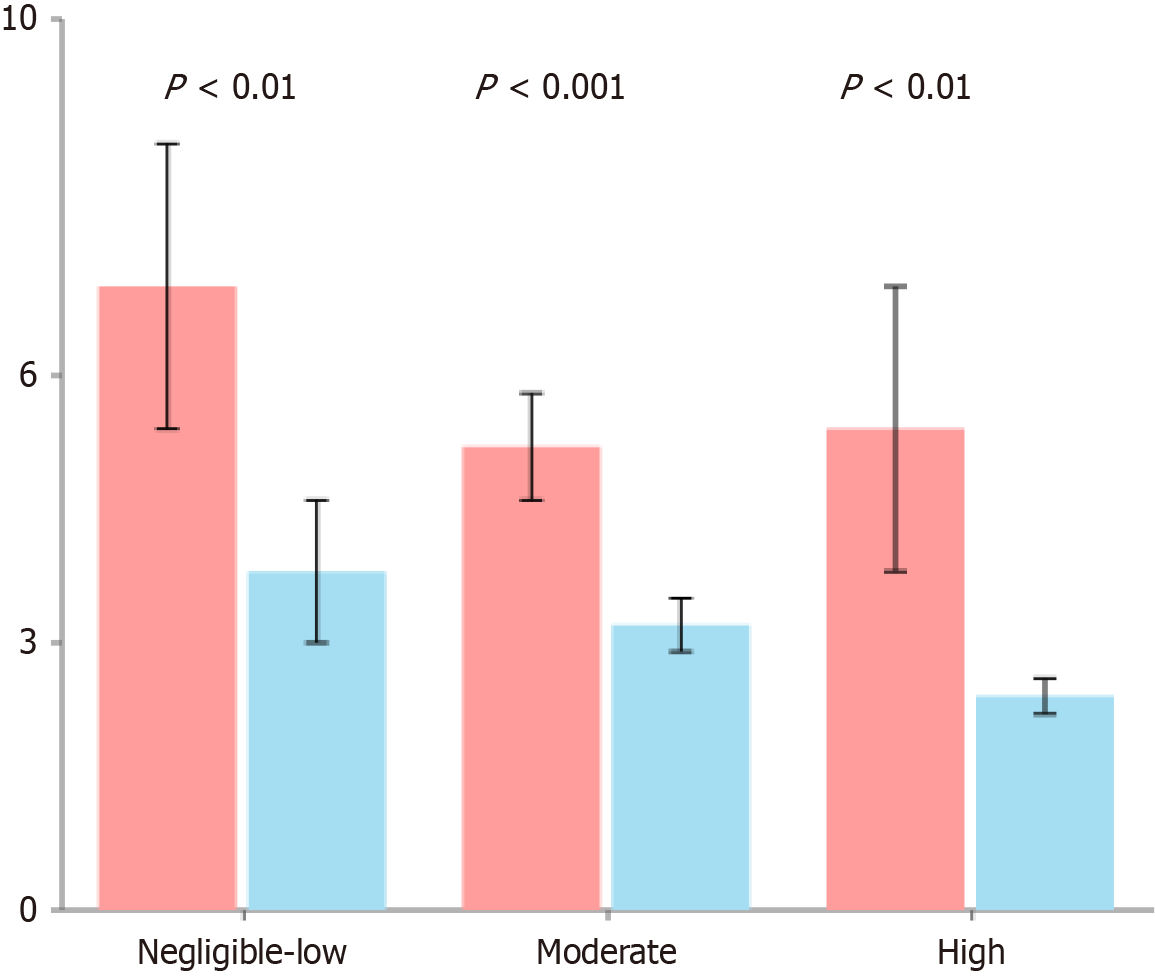
Figure 1 Predictive effect of preoperative inflammatory data, interleukin-17A, and fluid load on post pancreatectomy acute pancreatitis.
Preoperative interleukin-17A (IL-17a) concentrations were significantly elevated in patients who developed post pancreatectomy acute pancreatitis (PPAP) compared to those who did not, regardless of their fistula risk score (FRS) classification (P < 0.01). This consistent IL-17a elevation across all FRS risk categories suggests its potential role as a biomarker for PPAP following pancreaticoduodenectomy.
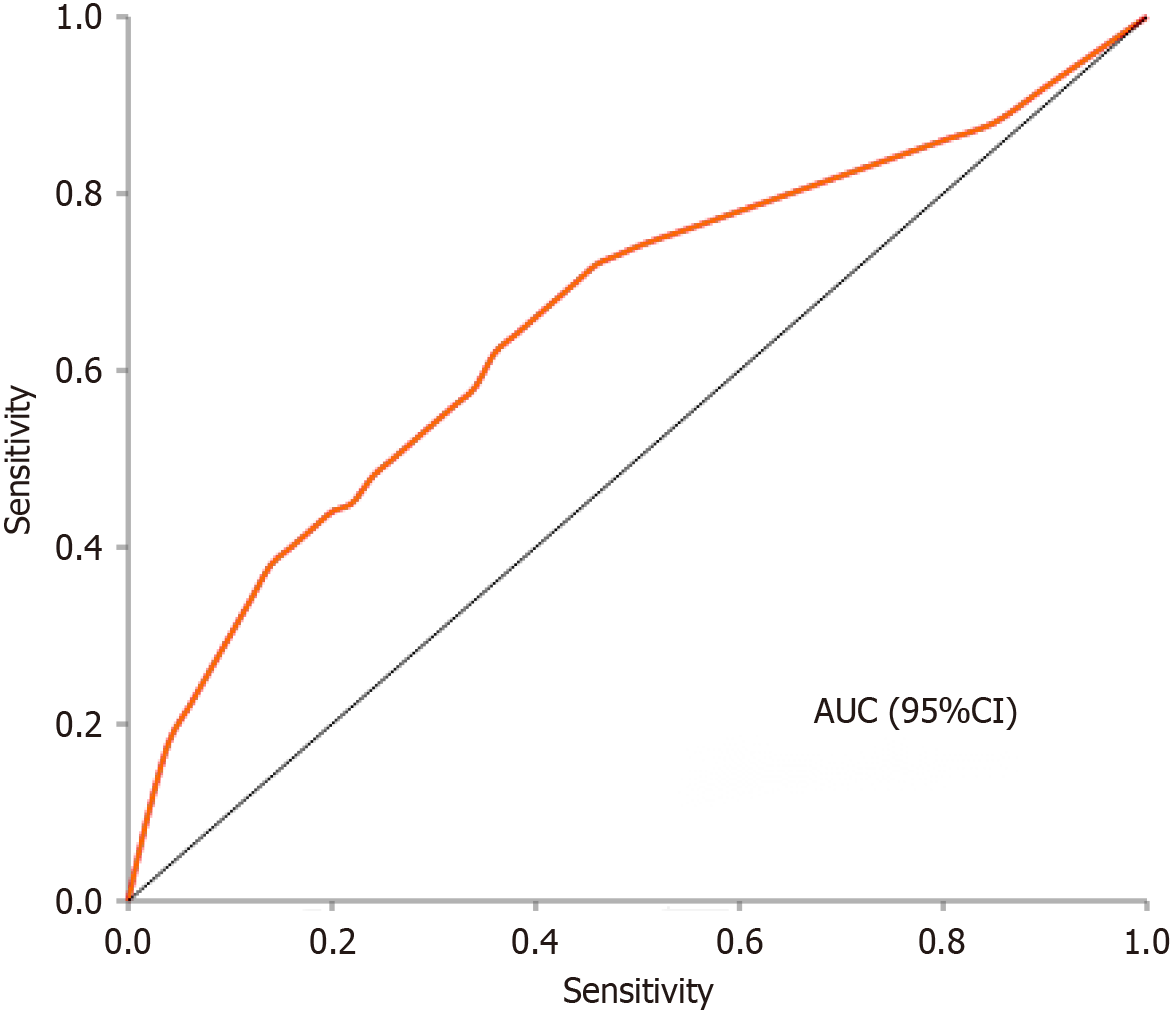
Figure 2 Analysis of receiver operating characteristic curves.
Preoperative interleukin-17A (IL-17a) as a moderate predictor of post pancreatectomy acute pancreatitis (PPAP) following pancreaticoduodenectomy, with an area under the curve of 0.71 (95%CI: 0.65-0.77). At the optimal threshold determined by Youden index, IL-17a demonstrated good sensitivity (0.805) but modest specificity (0.553) for PPAP prediction. AUC: Area under the curve.
- Citation: Zheng J, Ye WK, Wang J, Zhou YN, Yu TT. Preoperative interleukin-17a as a predictor of acute pancreatitis after pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(8): 105112
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i8/105112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i8.105112