Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Surg. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 105007
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.105007
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.105007
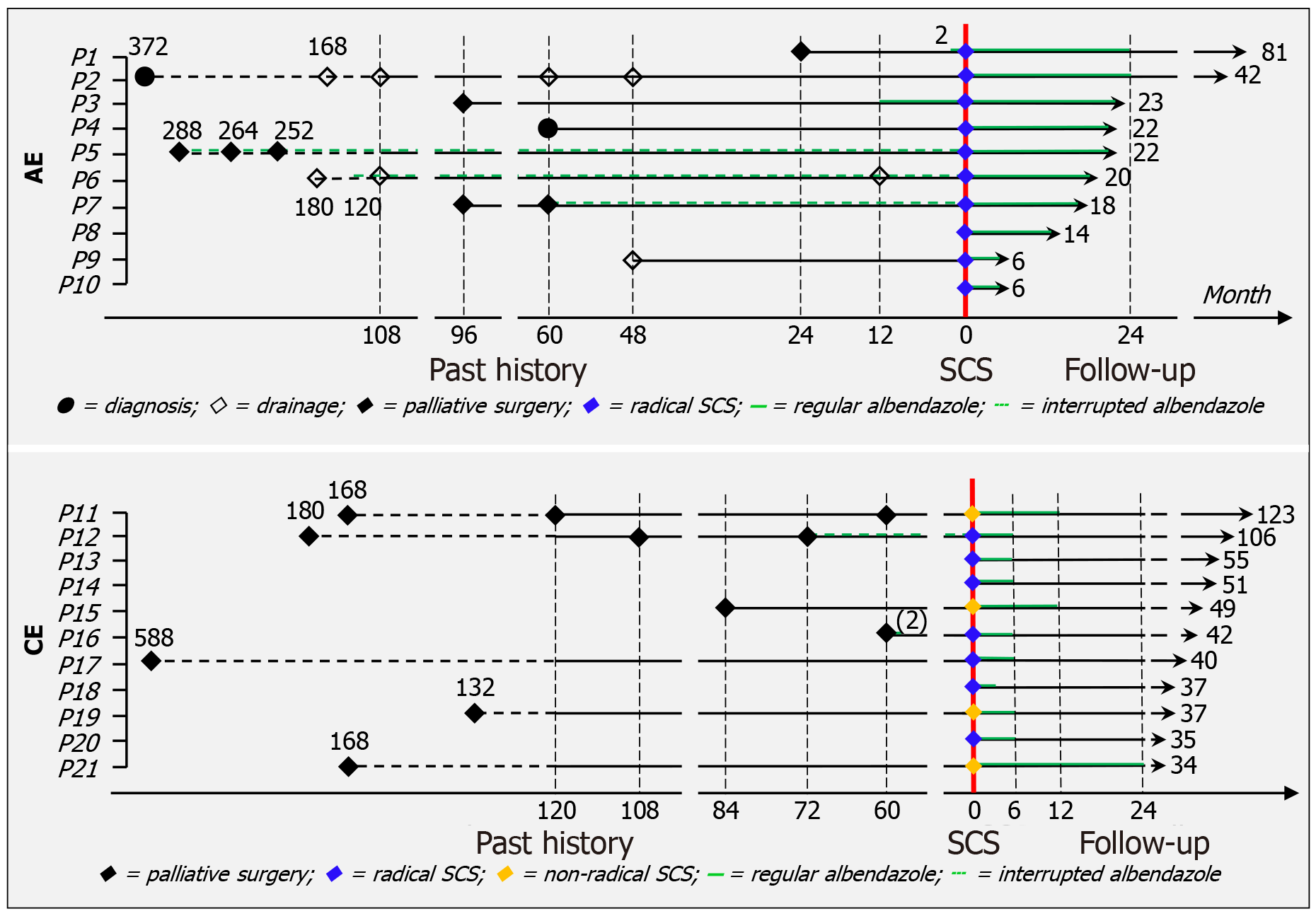
Figure 1 Treatment timelines.
The majority of patients with alveolar echinococcosis (AE) underwent multiple palliative interventions prior to presentation. All AE patients were deemed suitable for radical simultaneous combined surgery (SCS). Postoperatively, all AE cases adhered to expert consensus guidelines and achieved cure. Conversely, two patients with cystic echinococcosis (CE) received repetitive palliative surgeries, and five others experienced recurrence following a single surgical procedure. Radical SCS was feasible in only seven CE patients. Nonetheless, all CE patients achieved clinical cure. AE: Alveolar echinococcosis; CE: Cystic echinococcosis; SCS: Simultaneous combined surgery.
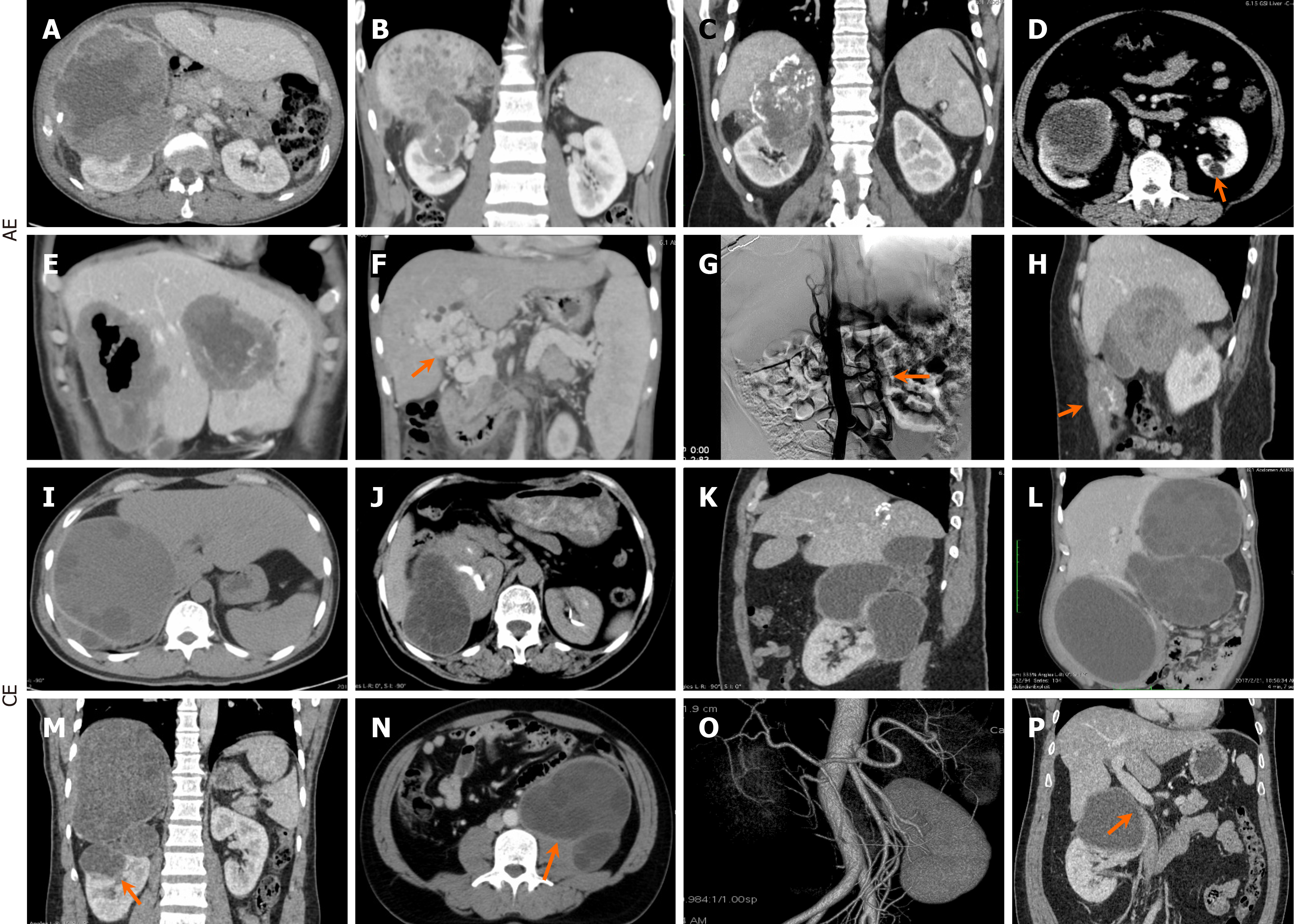
Figure 2 Radiological findings.
A-C: Right-sided hepatorenal alveolar echinococcosis (AE) lesion involvement was prevalent in AE cases; D and E: Isolated single lesions were observed in the left kidney (D) and the left lateral lobe of the liver (E); F-H: AE comorbidities included portal vein cavernous transformation (F), bilateral collateral circulation (G) secondary to severe inferior vena cava (IVC) involvement, and abdominal wall invasion (H); I-M: In contrast, cystic echinococcosis (CE) presented with solitary and multiple large cysts bilaterally; N-P: CE comorbidities included psoas muscle invasion (N), renal function impairment (O), and IVC involvement (P). AE: Alveolar echinococcosis; CE: Cystic echinococcosis.
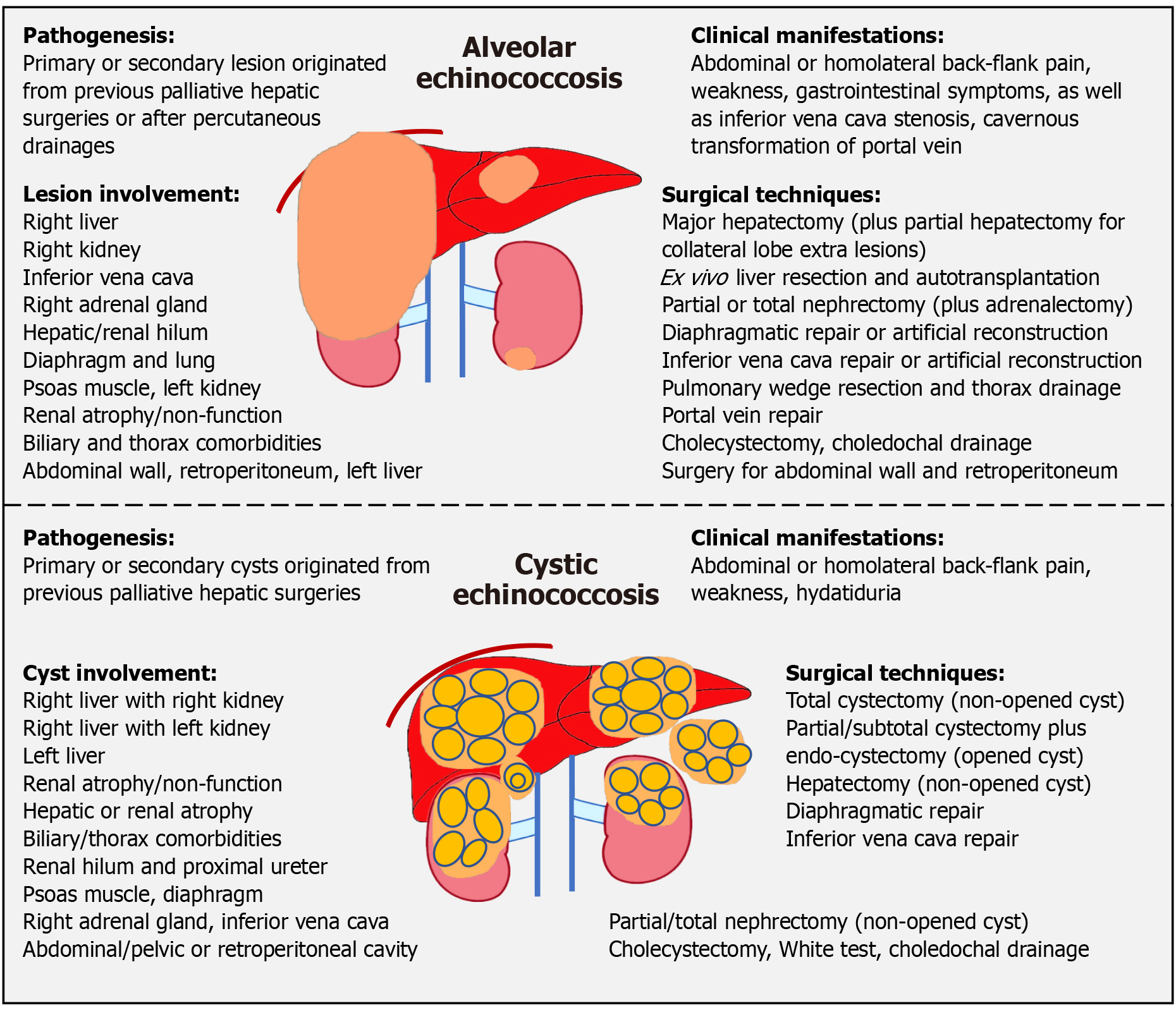
Figure 3 Study summary.
The upper and lower panels depict the pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, lesion/cyst involvement, and corresponding surgical techniques for alveolar echinococcosis and cystic echinococcosis patients, respectively.
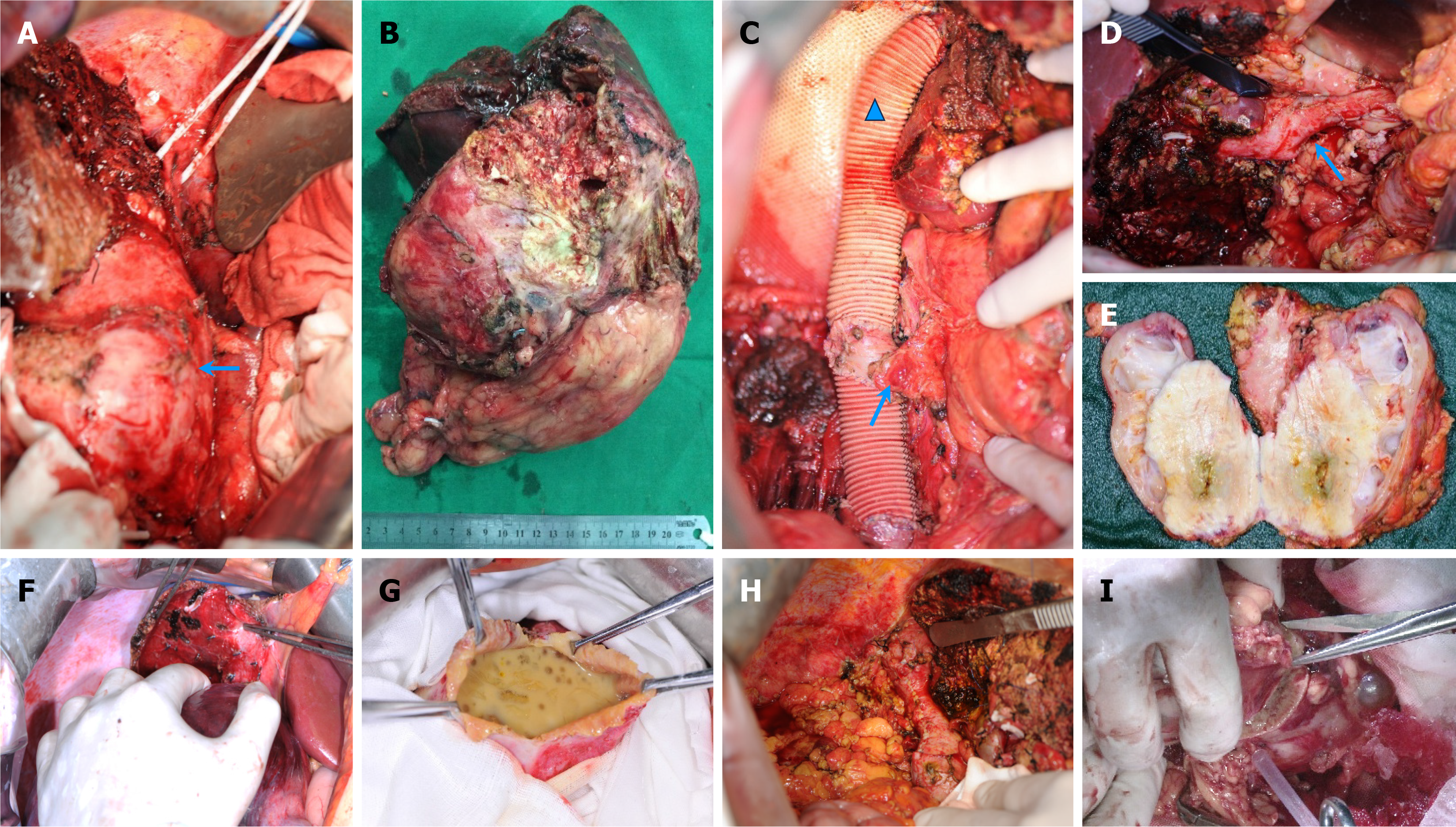
Figure 4 Surgical observations.
A-E: En bloc resection of the right hemiliver and right kidney (arrow) (A and B), extended prosthetic replacement of the diseased inferior vena cava, sutured and repaired blood vessels (arrow) and artificial blood vessels (triangle) (C) or repair via sutures (D), and (E) near-complete occupation of renal tissue were observed in alveolar echinococcosis cases; F and G: Total cystectomy (F) and open cystectomy (G) were predominantly employed in cystic echinococcosis (CE) subjects; H and I: Additionally, procedures such as inferior vena cava (arrow) repair with sutures (H) and partial nephrectomy (I) were required in select CE cases.
- Citation: Tulahong A, Zhu DL, Liu C, Jiang TM, Zhang RQ, Tuergan T, Aji T, Shao YM. Simultaneous combined surgery for hepatic-renal double organ alveolar or cystic echinococcosis: A retrospective study. World J Gastrointest Surg 2025; 17(6): 105007
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9366/full/v17/i6/105007.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4240/wjgs.v17.i6.105007