Published online Dec 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.1969
Peer-review started: December 14, 2021
First decision: December 15, 2021
Revised: December 15, 2021
Accepted: December 15, 2021
Article in press: December 15, 2021
Published online: December 15, 2021
Processing time: 2 Days and 5.8 Hours
The 2021 online editorial board meeting of the World Journal of Diabetes (WJD) was held on November 9, 2021. Jin-Lei Wang, General Manager on behalf of the Baishideng Publishing Group, and Professor Islam, one of the Editors-in-Chiefs (EiCs) of the WJD, organized the meeting. Three EiCs and 18 Baishideng Publishing Group staff attended the meeting. The meeting goal was to brief the EiCs on the journal’s performance, discuss the issues of concern of the EiCs, and gather ideas for the journal’s development in 2022. As of November 8, the WJD had received 287 manuscripts since the year’s start, among which 122 met the criteria for publication. These numbers represent an increase of 117.4% for submissions and 110.3% for publications compared to those in 2020. However, how to effectively control the academic quality of manuscripts and attract high-quality original article submissions remain a challenge. The EiCs provided feedback and suggestions centered on three topics: (1) Who should and how to control the academic quality of the manuscripts; (2) How the EiCs perform their responsibilities; and (3) The distinctive and shared responsibilities of the publisher and the EiCs.
Core Tip: The 2021 World Journal of Diabetes editorial board meeting was held on November 9, 2021. The meeting goal was to brief Editors-in-Chiefs (EiCs) on the journal’s performance, discuss issues of concerns of the EiCs, and gather ideas for the journal’s development in 2022. The discussion focused on: (1) Who should and how to control the academic quality of the manuscripts; (2) How the EiCs perform their responsibilities; and (3) The distinctive and shared responsibilities of the publisher and the EiCs.
- Citation: Wang JL, Yan JP, Li X, Islam MS, Xiao JB, Cai L, Ma N, Ma L, Ma LS. Meeting report of the chief editorial board meeting for World Journal of Diabetes 2021. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(12): 1969-1978
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i12/1969.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i12.1969
Since new Editors-in-Chiefs (EiCs) were appointed to the World Journal of Diabetes (WJD) in August 2021, Professor Islam, one of the EiCs, suggested to organize a meeting from the editorial office in order to understand the editorial process of the journal so that the EiCs may serve their role in an optimized manner. According to the EiCs’ suggestions, the WJD editorial office hosted the meeting on November 9, 2021 to review the journal’s performance, discuss issues of concerns of the EiCs, and gather ideas for the journal’s development in 2022. The meeting was moderated by Miss Na Ma, Company Vice-Editor-in-Chief. The first part of the meeting consisted of presentations on journal status review, and the second part consisted of open discussions with the EiCs to garner their feedback and suggestions.
This online meeting brought together three EiCs, namely Professor Jian-Bo Xiao, Professor Lu Cai, Professor Md Shahidul Islam, and 18 Editors (Na Ma, Jin-Lei Wang, Xiang Li, Ze-Mao Gong, Jia-Ping Yan, Ya-Juan Ma, Yun-XiaoJian Wu, Jia-Ru Fan, Chen-Chen Gao, Man Liu, Ji-Hong Liu, Yu-Jie Ma, Yan-Xia Xing, Yan-Liang Zhang, Kai-Le Chang, Jing-Jie Wang, Li-Li Wang, and Han Zhang) from Baishideng Publishing Group Inc (Figure 1).
Jin-Lei Wang began the meeting by offering an overview of the WJD’s journal statistics, status quo of the editorial board, publication process for manuscripts, etc.
Overview of the journal: The WJD is a high-quality, monthly, online, open-access, single-blind peer-reviewed journal. The WJD publishes articles based upon their academic quality, academic norms, academic ethics, and academic integrity, with an aim of disseminating academic research results to the world and leading the healthy development of the academic community. The WJD is now abstracted and indexed in Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE, also known as SciSearch®), Journal Citation Reports/Science Edition, Current Contents®/Clinical Medicine, Scopus, PubMed, and PubMed Central.
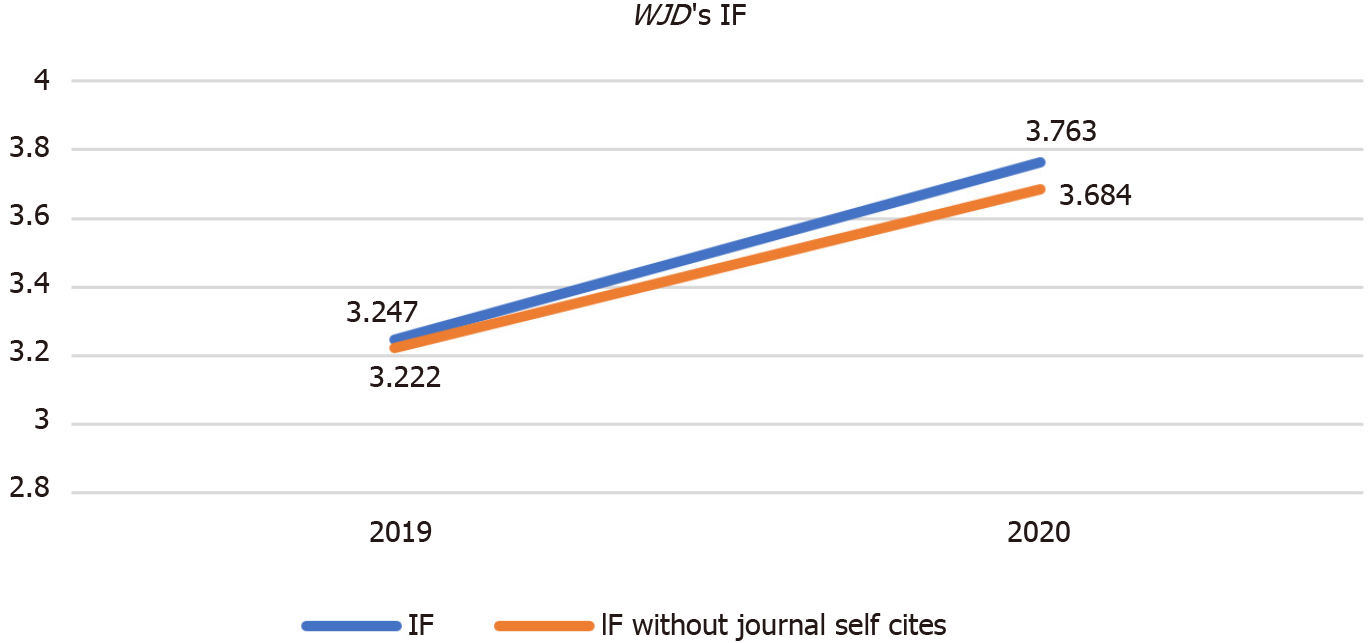
Journal metrics: The 2021 Edition of Journal Citation Reports® cites the 2020 impact factor (IF) for WJD as 3.763; IF without journal self cites: 3.684; 5-year IF: 7.348; Journal Citation Indicator: 0.64; Ranking: 83 among 146 journals in endocrinology and metabolism; and Quartile category: Q3.
The WJD was included in SCIE in 2019. The WJD’s first IF was 3.247 and the IF without journal self cites was 3.222 (in 2019). The IF in 2020 increased by 15.9% compared with the IF in 2019 (Figure 2).
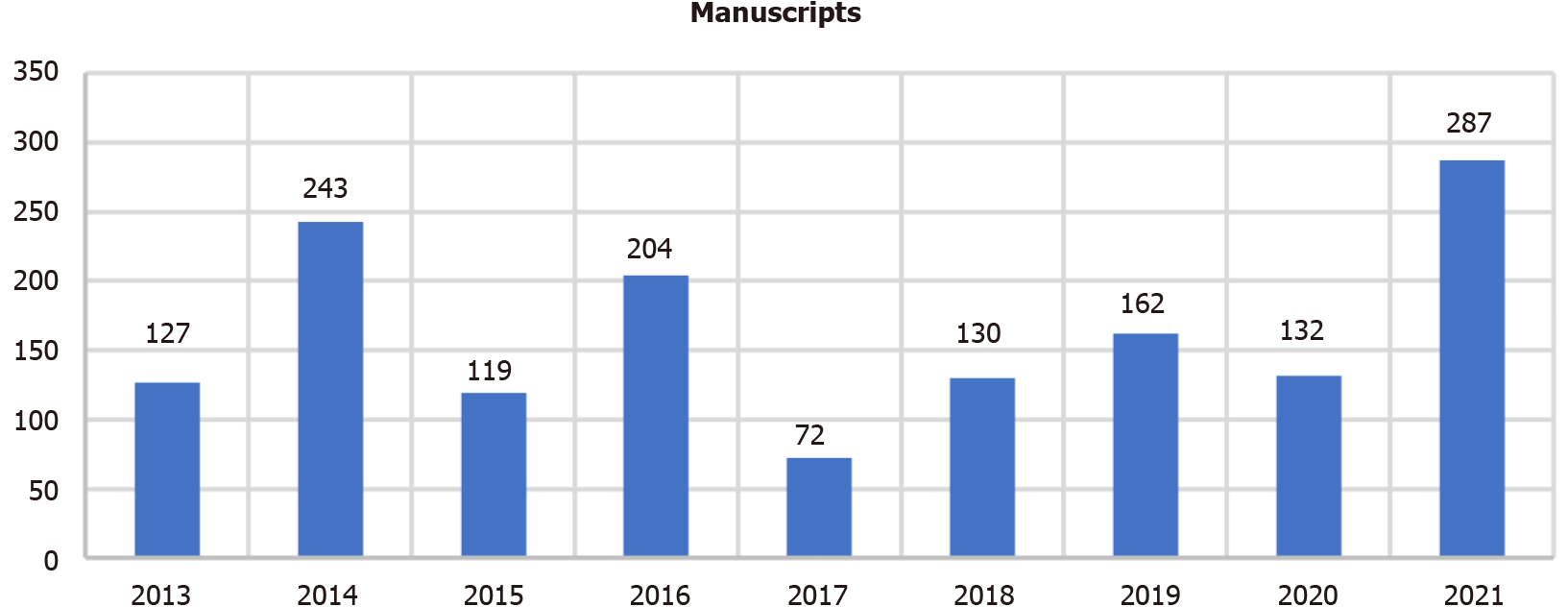
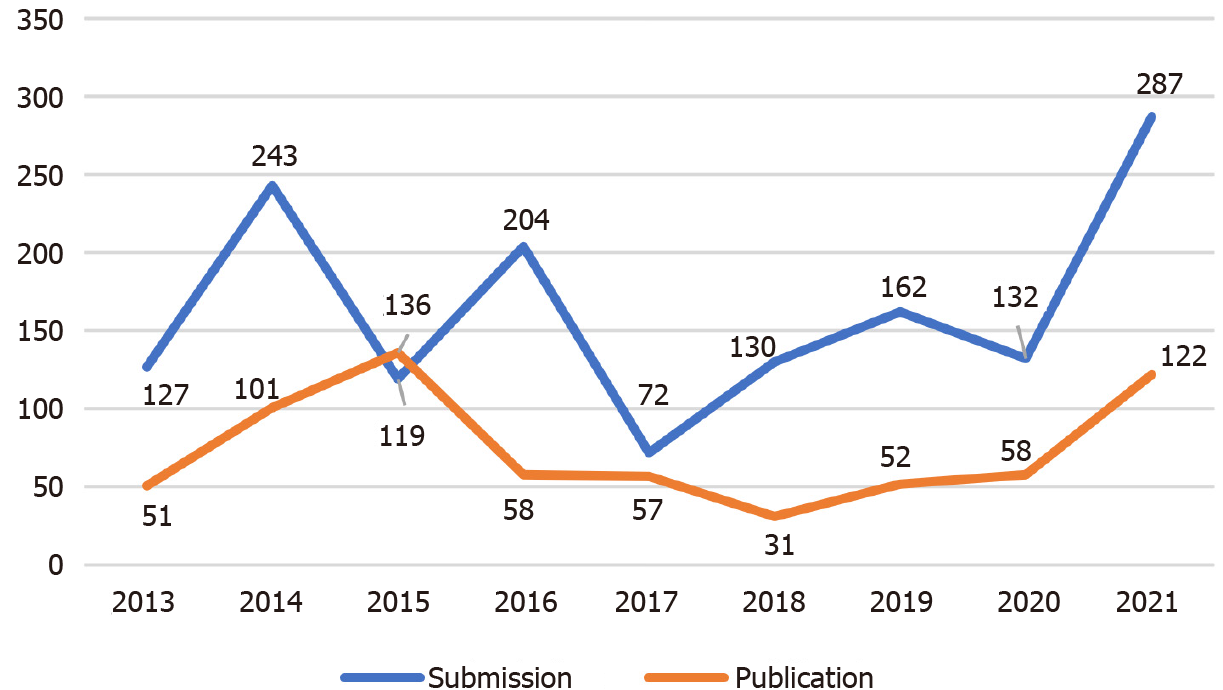
Number of submissions in recent years: From 2013 to 2021, the WJD received a total of 1476 manuscript submissions for consideration of publication, with an average number of submissions per year of 164 (Figure 3). As of November 8, 2021, the WJD had received 287 manuscript submissions since the beginning of the calendar year, whose authors were from 46 countries/territories.
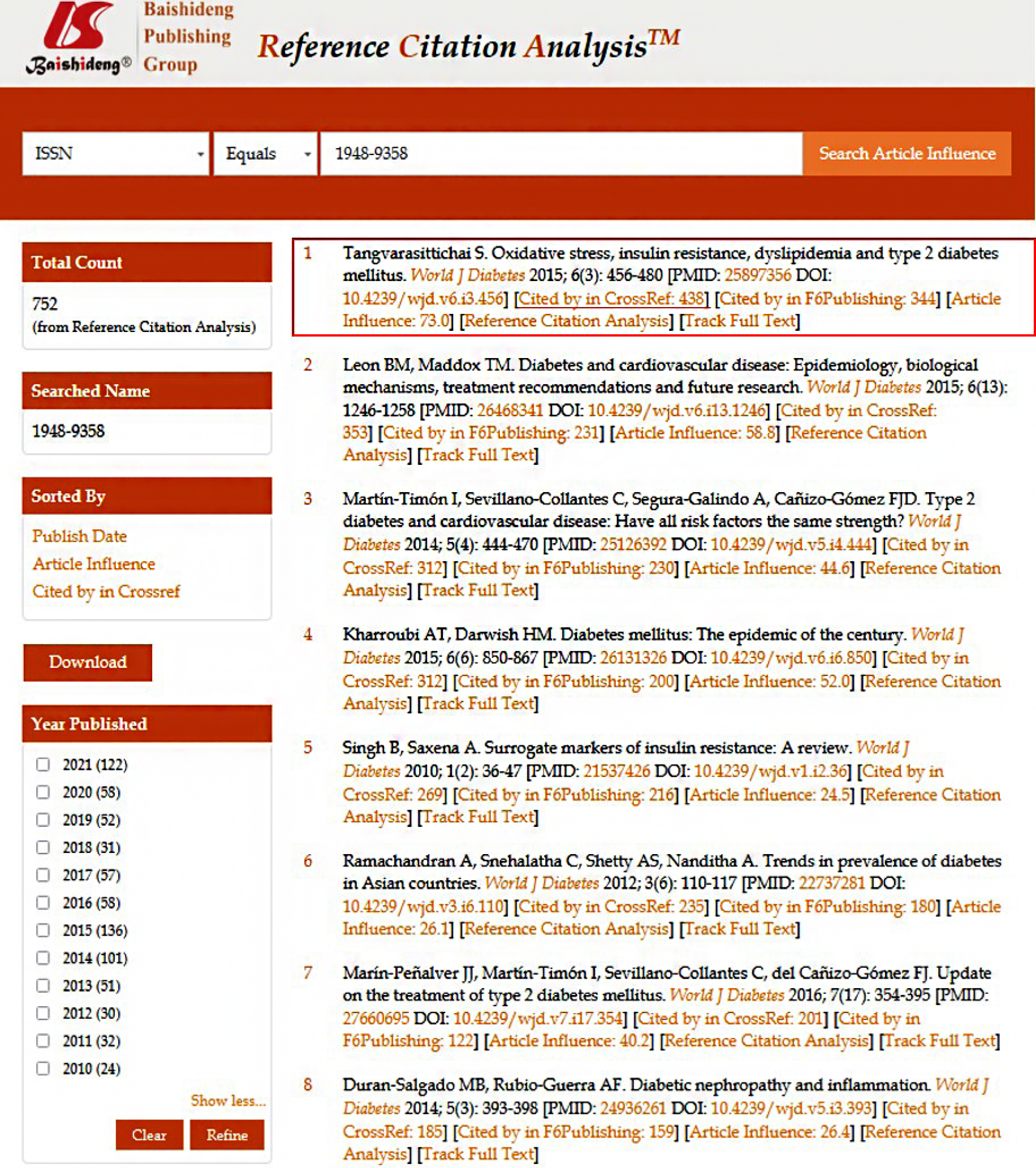
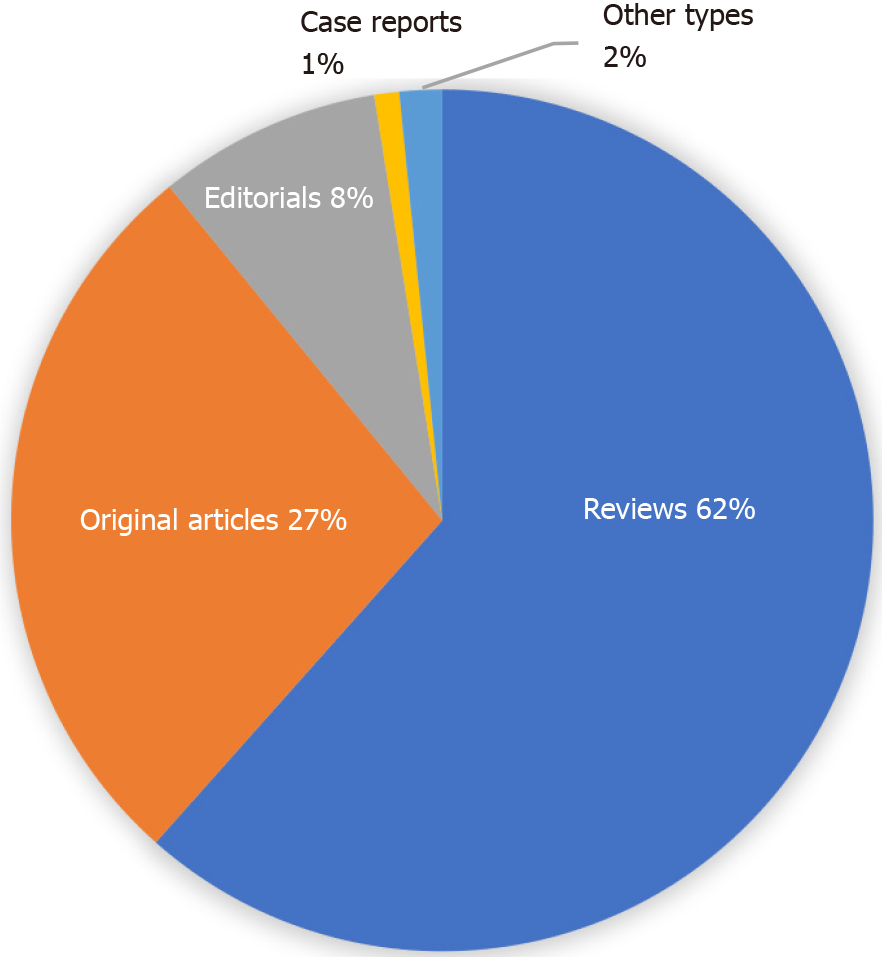
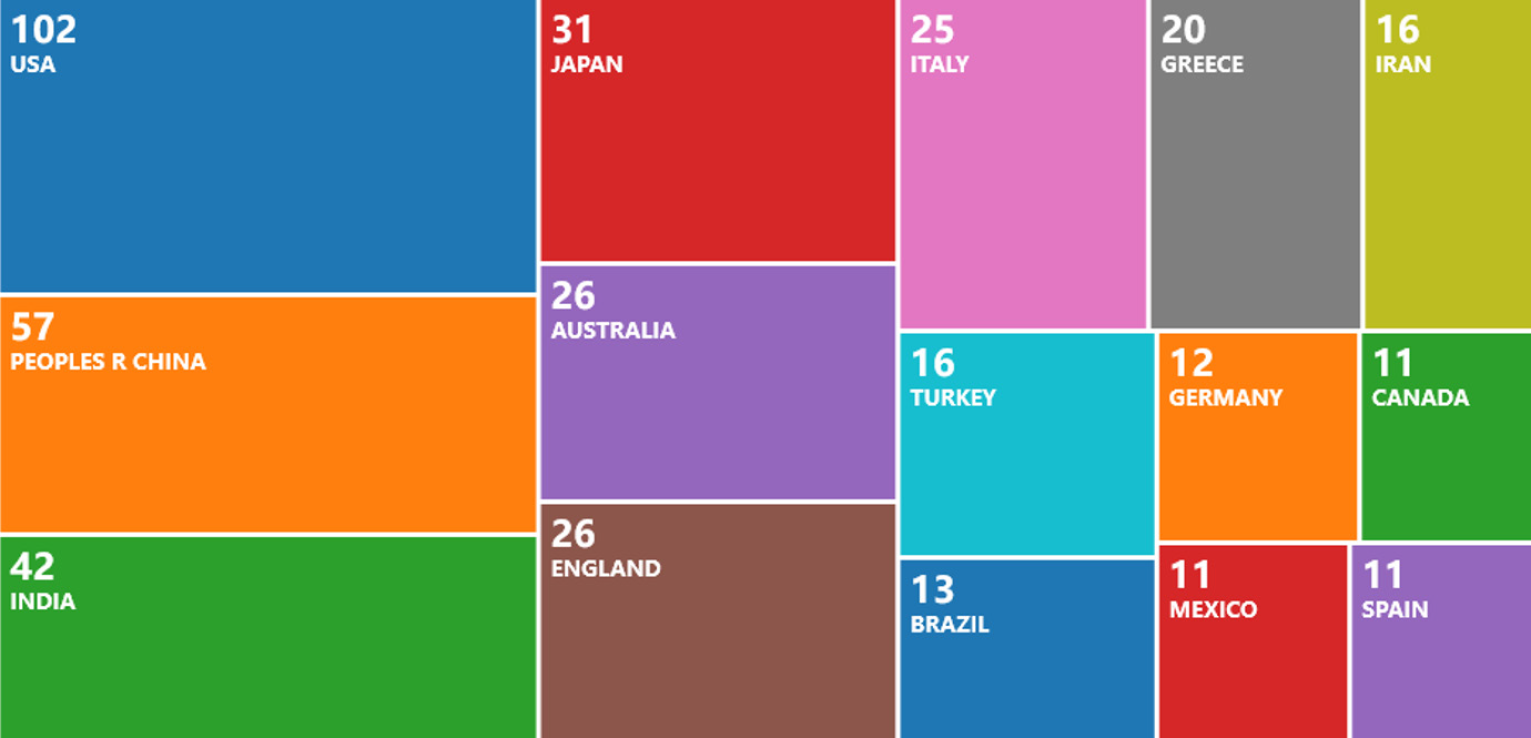
Number of published manuscripts during 2010-2021: Based on our recently developed “Reference Citation Analysis” system (https://www.referencecitationanalysis.com/), the WJD published 752 articles since its launch in 2010 to 2021. Of note, the five most cited articles include: one article published in 2015[1] has been cited 438 times, its article influence (Calculation for Article Influence: Times cited/Number of years = Article influenceTM) is 73.0 (Figure 4); another article published in 2015[2] has been cited 353 times, its article influence is 58.8; one article published in 2014[3] has been cited 312 times, its article influence is 44.6; one article published in 2015[4] has been cited 312 times, its article influence is 52.0; and one article published in 2010[5] has been cited 269 times, its article influence is 24.5. The total 752 articles published in WJD during 2010-2021 includes 463 reviews, 207 original articles, 63 editorials, 7 case reports, and 12 articles of other types (Figure 5). As of November 8, 2021, 500 of the articles are indexed in the Web of Science, the authors of which are located in 51 countries/territories, including United States (102 articles, 20.4%), China (57 articles, 11.4%), India (42 articles, 8.4%), Japan (31 articles, 6.2%), Australia (26 articles, 5.2%), and United Kingdom (26 articles, 5.2%), etc. (data from Web of Science; Figure 6).
Number of published articles in 2021:As of November 8, 2021, the WJD had published 122 articles in the calendar year. One article[6] published on February 15, 2021 was cited 8 times in the current year, and other five articles[7-11] were cited 3 times in the current year.
Number of submission and publications during 2013-2021: Compared with the numbers of submissions and publications in 2020, WJD submissions and publications increased by 117.4% and 110.3%, respectively, in 2021 (Figure 7).
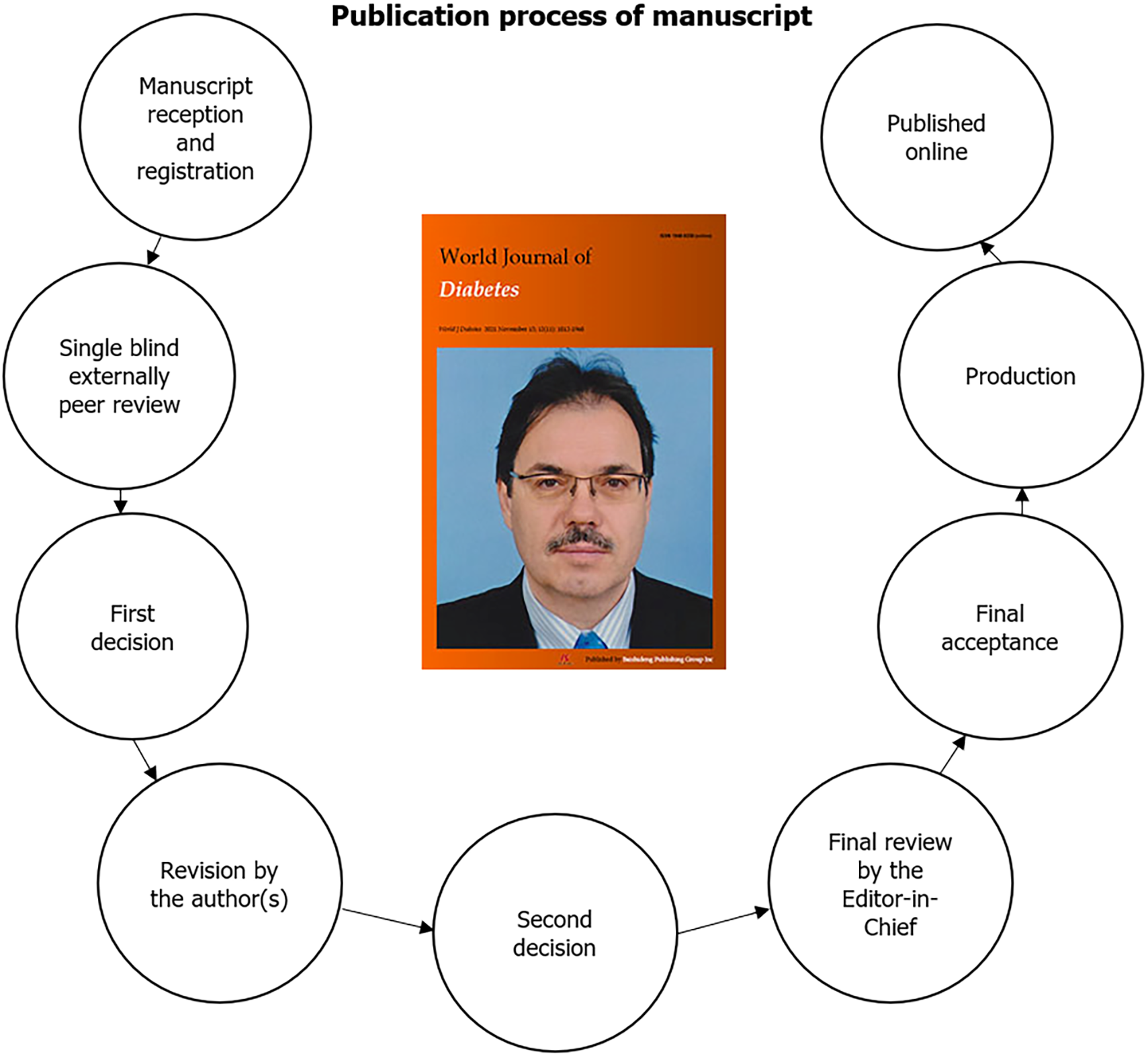
The publication process for any manuscript submitted to the WJD is as follows: Manuscript reception and registration; Single-blind external peer review; First decision; Revision by the author(s); Second decision; Final review by the EiC; Final acceptance; Production; and Published online (Figure 8).
Single-blind external peer review: The peer review model is single-blinded; however, the reviewer can choose to hide or not hide his/her name to the author. Both invited and unsolicited manuscripts will be externally peer reviewed. Our artificial intelligence system automatically selects 20 external peer reviewers for each manuscript from our database of high-impact experts and scholars. At the same time, our science editor manually selects 10 Editorial Board Members in a single-blind manner to review the manuscript. Usually, the peer review process takes 7-14 d to complete. Before the formal peer review is initiated, peer reviewers should consider and answer the following two questions: (1) Does the manuscript have a conflict with your interests? And (2) Does the research content of the manuscript meet the requirements of ethical norms?
First decision by Academic Editor/Editorial Board/Science Editor: After the manuscript’s peer review is completed by the peer reviewer(s) and/or editorial board member(s), we invite the Academic Editor/Editorial Board/Science Editor to make the first decision for the manuscript and write an evaluation report of this first decision. The main task of the first decision is to verify and evaluate the academic quality of manuscripts based on the peer-review report and key points for first decision of manuscripts. Academic editors will independently decide to accept or reject the manuscript or suggest to the authors a transfer of the manuscript to another of our journals. Currently, the WJD has 8 online Academic Editors.
Second decision: After the authors have revised the manuscript in accordance with the peer-review report and the criteria for manuscript revision, and responded to the issues raised in the peer-review report, the revised manuscript will be edited by the science editor according to the journal’s guidelines. Then, the EiCs will make the second decision to reject or accept the manuscript based on all relevant documents submitted by science editor. And the company EiC (internal) will re-verify whether the manuscript conforms to academic ethics, rules, and norms and makes the final decision to accept or reject the manuscript.
F6Publishing is an artificial intelligence-based system that integrates the functions of online manuscript submission, peer review, manuscript revision by authors, manuscript production, manuscript publishing and release, editing and publishing management, and statistics of publishing fees and costs (https://www.f6publishing.com).
Maximize article impact for authors: To enable more peers to read, share, and cite authors’ published research results, to help enhance authors’ global academic influence, and to promote the overall development of the field, Baishideng accurately sends published articles to 1000-10000 highly influential experts. After completing this, Baishideng will formally notify authors of the number of experts to whom their manuscript was sent via email.
The 2021 Editorial Board of WJD is composed of 101 Editorial Board Members. They are from 35 countries or regions, including 20 (19.8%) in China, 10 (9.9%) in United States, 8 (7.9%) in Italy, 6 (5.9%) in India, 5 (5.0%) in Greece, and 52 (51.5%) in other countries or regions.
Responsibilities of EiCs: In addition to the responsibilities of the Editorial Board members, the EiCs of the WJD will be involved in the second decision making (final reviewing) of manuscripts.
Responsibilities of Editorial Board Members: (1) Conducting peer review of at least six manuscripts each year. Reviewing the academic and language quality of manuscripts to ensure the academic level of journals. Conducting the manuscript peer-review task timely and carefully. Making a fair and objective evaluation of manuscripts, and giving detailed reasons for acceptance/rejection of a manuscript and detailed comments for its revision; (2) Willingness to track the post-publication evaluations on the manuscripts you have reviewed; (3) Willingness to organize a special topic, carried out by inviting 7-10 manuscripts from experts and scholars in the field to contribute manuscripts on a hot topic; (4) Recommending high-quality manuscripts for submission to the journal; (5) Promoting published articles, including thorough use of personal social media to forward the articles published in the journal and share them with more colleagues; and (6) Recommending distinguished experts and scholars in the field to join the Editorial Board as new members.
Privileges of Editorial Board Members: (1) Regular invitations to contribute editorials and review articles for the journal, for which the publication fee will be waived; (2) A 10% discount of the publishing fee for other articles submitted by the member; (3) A listing of personal professional information on the journal’s homepage; (4) Public acknowledgement of related contributions to the journal, by posting of the member’s name and number of manuscripts he/she reviewed on the journal’s website. For details, please visit: https://www.f6publishing.com/HighlyInfluentialPeerReviewers; and (5) Selection of outstanding members of the Editorial Board to appear as the cover figures published on the cover page of each issue.
As of November 8, 2021, the WJD has received a total of 109 titles of invited manuscripts, including 43 (39.4%) for review articles, 56 (51.4%) for original articles, and 10 (9.2%) for other types of articles.
In December 2021, we plan to continue to invite global experts and scholars in the field of diabetes to write high-quality reviews, original articles, and special issue articles for the WJD in 2022.
Professor Islam cited concern about the publication process for manuscripts. He provided alternative opinions about the processes for manuscript peer-review, manuscript first decision, manuscript acceptance, etc. He suggested that the Associate Editors and the EiCs should be responsible for the academic quality of the manuscript, and the following editorial work flow was suggested: (1) The manuscripts should initially checked by the journal office and sent back to authors or sent to an Associate Editor in that area of research; (2) The Associate Editor will carry out scientific scrutinization and may reject or send the manuscript to multiple peer-reviewers for review; (3) That same Associate Editor will judge the peer-review report and send the manuscript back to the authors for revision or reject the manuscript; (4) If the manuscript is acceptable after revision, then a preliminary decision will be made by that same Associate Editor, who will send it to one of the EiCs to make a final decision; and (5) If the manuscript is accepted, the manuscript will go the production editor for production purposes and the journal office will assume handling from that point onwards.
Professor Cai also suggested that an Associate Editor should carry out the scientific scrutinization and thereafter decide to send the manuscript to peer-review or reject the manuscript immediately.
Professor Islam pointed out that the EiCs’ responsibilities should be more focused. The EiCs do not necessarily need to participate in the production of manuscripts and other editing processes of the manuscript. Professor Xiao pointed out that the EiCs can recommend Editorial Board Members and organize special issues on hot topics.
Professor Islam pointed out that the publisher should be more focused on the production of the manuscript, and not interfere with the academic quality control of the manuscript. The EiCs and/or the Associate Editor should control the academic quality of the manuscripts.
First, the editorial office clarified that (1) the academic quality of the manuscripts will be controlled by the EiCs through their conducting of the first decision for peer-reviewed manuscripts and final review of the revised manuscript, (2) to avoid conflicts of interest, the technical quality of the publications will remain controlled by the publisher, and (3) the copyrights of the published articles will continue to belong to the authors.
Second, the editorial office updated the responsibilities of EiCs and Associate Editors, as follows in detail: (1) Conduct of the first-decision of peer-reviewed manuscripts. The main task of this work is to verify and evaluate the academic quality of manuscripts submitted for consideration of publication, based on the peer-review report and key points for first decision. The purpose of this work is to ensure the academic quality of articles published in our journals, thereby leading academic innovation in general alongside the healthy development of Baishideng journals. Relying on the key points for first decision of manuscripts (including manuscript theme, peer-review report, manuscript content, figures and tables, language quality, manuscript format, medical ethics, and statistical analysis), EiCs will independently decide to accept or reject the manuscript or suggest to the authors a transfer of the manuscript to another, more appropriate Baishideng journal. They will also provide a summary of this decision, in order to help the authors and the journal to further improve the academic quality of the manuscript under consideration; (2) Inviting manuscripts for the journal. This task involves organizing a special topic by inviting 7-10 manuscripts on a hot topic from experts and scholars in the field. These invited manuscripts will be published free-of-charge after successful completion of peer review; (3) Conduct of peer review of manuscripts. This task involves conducting peer review of at least six manuscripts each year. The focus of this review activity is the academic and language quality of the manuscripts, to ensure the academic level of the journals. The manuscript peer-review task should be conducted in both a timely and careful manner. The ultimate aim is to make a fair and objective evaluation of manuscripts, giving detailed reasons for acceptance/rejection of a manuscript and detailed comments for revision; (4) Final review of the authors’ revised manuscript; and (5) Other responsibilities. This task relies on a willingness to track the post-publication evaluations of the manuscripts you have reviewed. The EiCs will also recommend high-quality manuscripts for submission to the journal, promote its published articles, including through use of personal social media to forward the articles published in the journal and share them with more colleagues, and recommend distinguished experts and scholars in the field to join the Editorial Board as new members.
Third, after discussion with our colleagues, the editorial office carefully updated the editorial workflow according to Professor Islam’s suggestions, and more detailed clarifications were added to the editorial workflow (Figure 9).
All EiCs expressed commitment and enthusiasm to help the journal grow. Both the EiCs and the editorial office are on the same team and moving toward the same goal on an agreed upon path; therefore, we will work together to make the WJD better and promote it to be a top journal in the field. Future online editorial board meetings are expected to be set every 3 months. All editorial members are welcome to attend any and all future meetings. Stay tuned for more details please!
The WJD editorial office thanks all the EiCs for their enthusiasm, guidance and contributions to the journal’s growth.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Endocrinology and Metabolism
Country/Territory of origin: United States
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): B
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: El-Yazbi AF, Rydosz A S-Editor: Liu JH L-Editor: A P-Editor: Liu JH
| 1. | Tangvarasittichai S. Oxidative stress, insulin resistance, dyslipidemia and type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes. 2015;6:456-480. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 649] [Cited by in RCA: 769] [Article Influence: 76.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (10)] |
| 2. | Leon BM, Maddox TM. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Epidemiology, biological mechanisms, treatment recommendations and future research. World J Diabetes. 2015;6:1246-1258. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 587] [Cited by in RCA: 722] [Article Influence: 72.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (13)] |
| 3. | Martín-Timón I, Sevillano-Collantes C, Segura-Galindo A, Del Cañizo-Gómez FJ. Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease: Have all risk factors the same strength? World J Diabetes. 2014;5:444-470. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 472] [Cited by in RCA: 558] [Article Influence: 50.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (6)] |
| 4. | Kharroubi AT, Darwish HM. Diabetes mellitus: The epidemic of the century. World J Diabetes. 2015;6:850-867. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 584] [Cited by in RCA: 575] [Article Influence: 57.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (42)] |
| 5. | Singh B, Saxena A. Surrogate markers of insulin resistance: A review. World J Diabetes. 2010;1:36-47. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 390] [Cited by in RCA: 428] [Article Influence: 28.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 6. | Luo EF, Li HX, Qin YH, Qiao Y, Yan GL, Yao YY, Li LQ, Hou JT, Tang CC, Wang D. Role of ferroptosis in the process of diabetes-induced endothelial dysfunction. World J Diabetes. 2021;12:124-137. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 48] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 25.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Kumric M, Ticinovic Kurir T, Borovac JA, Bozic J. Role of novel biomarkers in diabetic cardiomyopathy. World J Diabetes. 2021;12:685-705. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 30] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 8. | Rajbhandari J, Fernandez CJ, Agarwal M, Yeap BXY, Pappachan JM. Diabetic heart disease: A clinical update. World J Diabetes. 2021;12:383-406. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 11.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 9. | Serbis A, Giapros V, Kotanidou EP, Galli-Tsinopoulou A, Siomou E. Diagnosis, treatment and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. World J Diabetes. 2021;12:344-365. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 35] [Article Influence: 8.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (12)] |
| 10. | Zhou Y, Ma XY, Han JY, Yang M, Lv C, Shao Y, Wang YL, Kang JY, Wang QY. Metformin regulates inflammation and fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease through TNC/TLR4/NF-κB/miR-155-5p inflammatory loop. World J Diabetes. 2021;12:19-46. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 39] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Mitrofanova A, Burke G, Merscher S, Fornoni A. New insights into renal lipid dysmetabolism in diabetic kidney disease. World J Diabetes. 2021;12:524-540. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 25] [Cited by in RCA: 56] [Article Influence: 14.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |