Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Diabetes. Apr 15, 2022; 13(4): 319-337
Published online Apr 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i4.319
Published online Apr 15, 2022. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i4.319
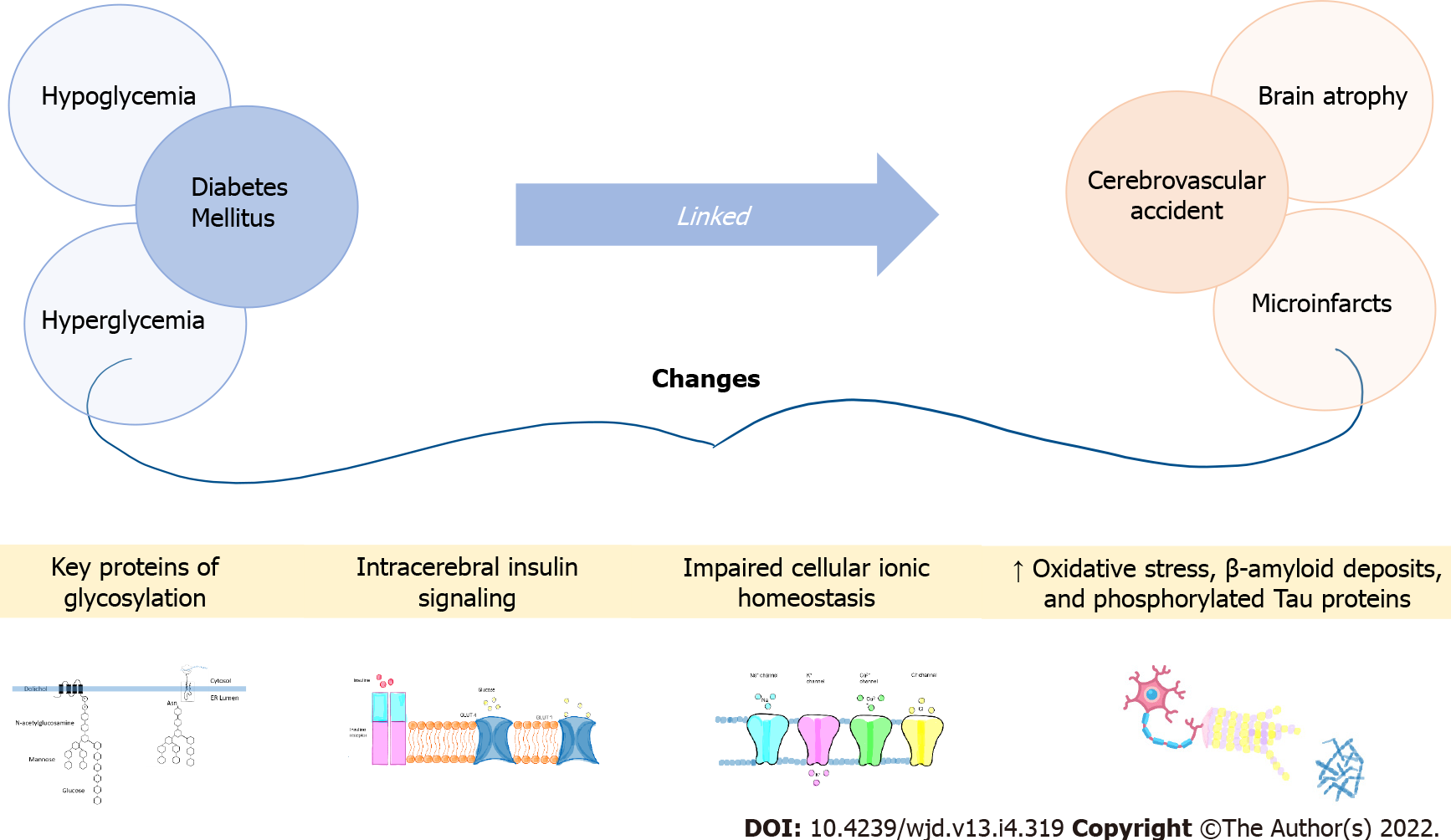
Figure 1 Diabetes Mellitus and its association with Dementia.
The alteration in the peripheric and central glucose levels increases the risk of cerebrovascular accidents due to different causes associated with vascular or mixed dementia. The figure has been designed using some resources from Falticon.com.
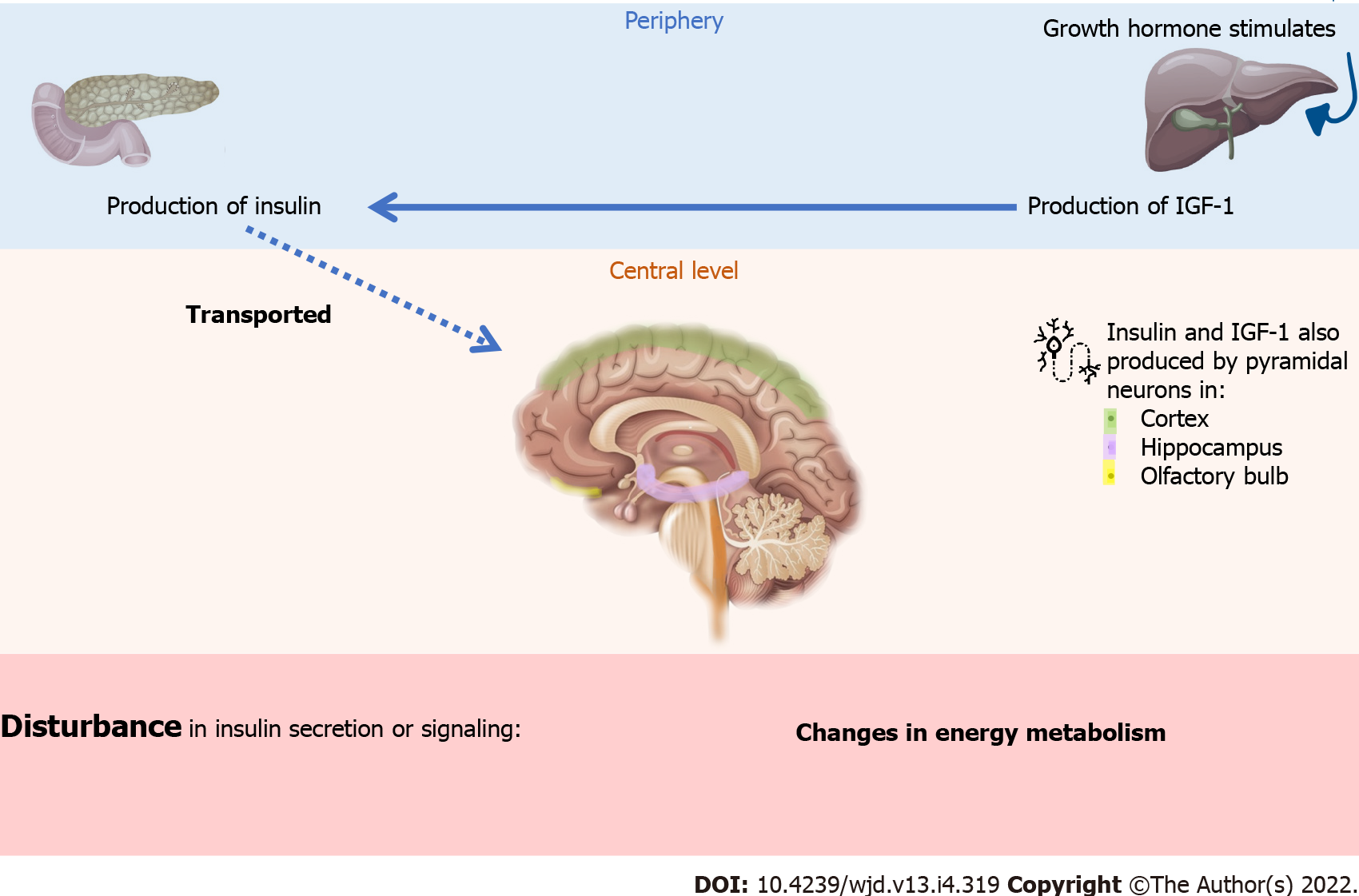
Figure 2 Insulin and insulin-like growth factor 1 production.
Both can be produced at the periphery and transported to the brain through the blood-brain barrier, but pyramidal neurons can also produce them. The figure has been designed using some resources from Freepik.com and Flaticon.com. IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1.
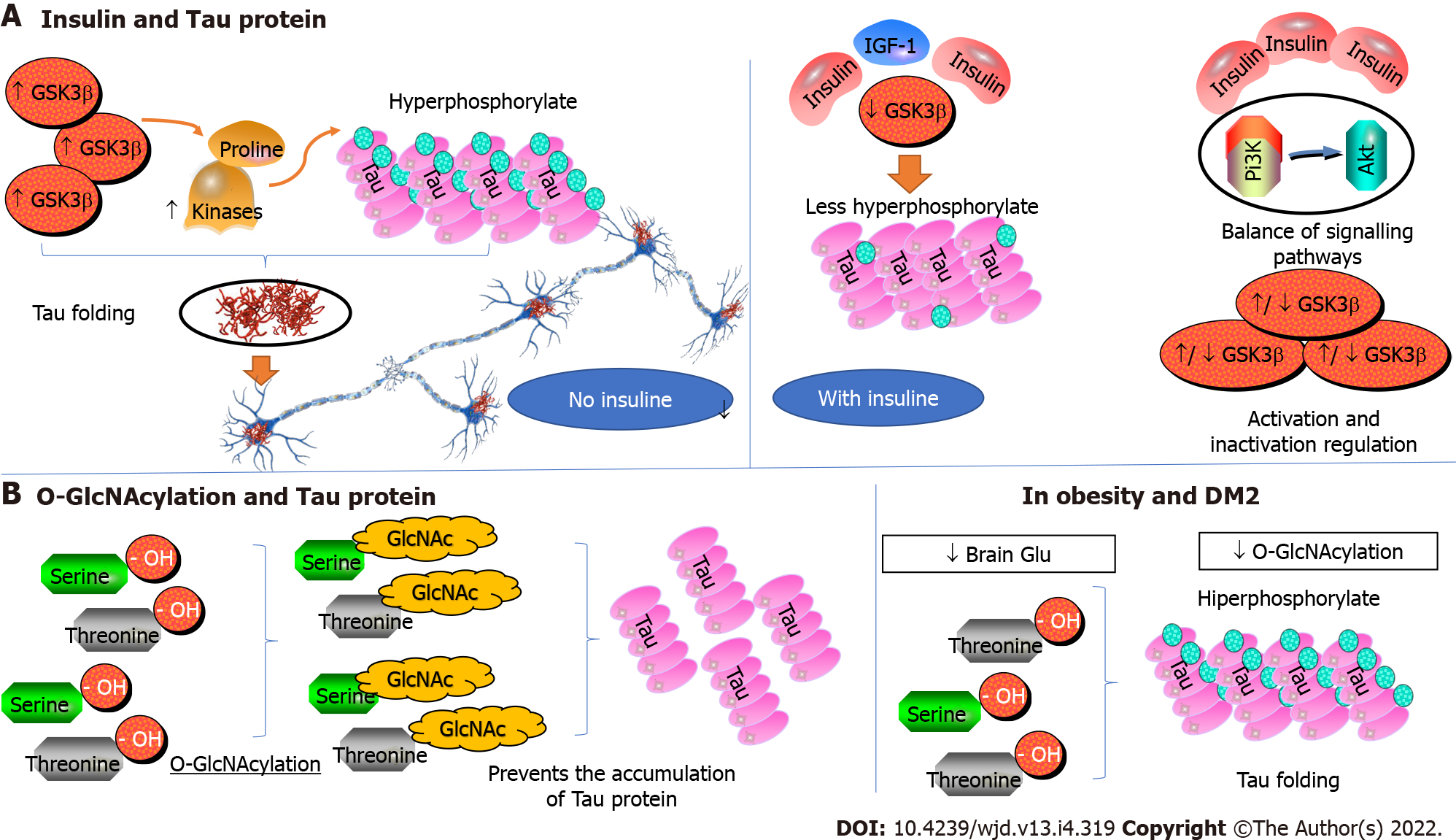
Figure 3 Tau protein regulation.
A: Insulin and Tau protein with no insulin increase hyperphosphorylate of Tau folding the protein; B: O-GlcNAcylation and Tau protein can regulate glucose amination to serine and threonine decrease the formation of Tau folding. Some pictures were taken from Qiagen Pathways. GSK3: Glycogen synthase kinase-3; IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; Pi3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; Akt: Serine/threonine specific protein kinase; GlcNAc: O-GlcNAcylation.
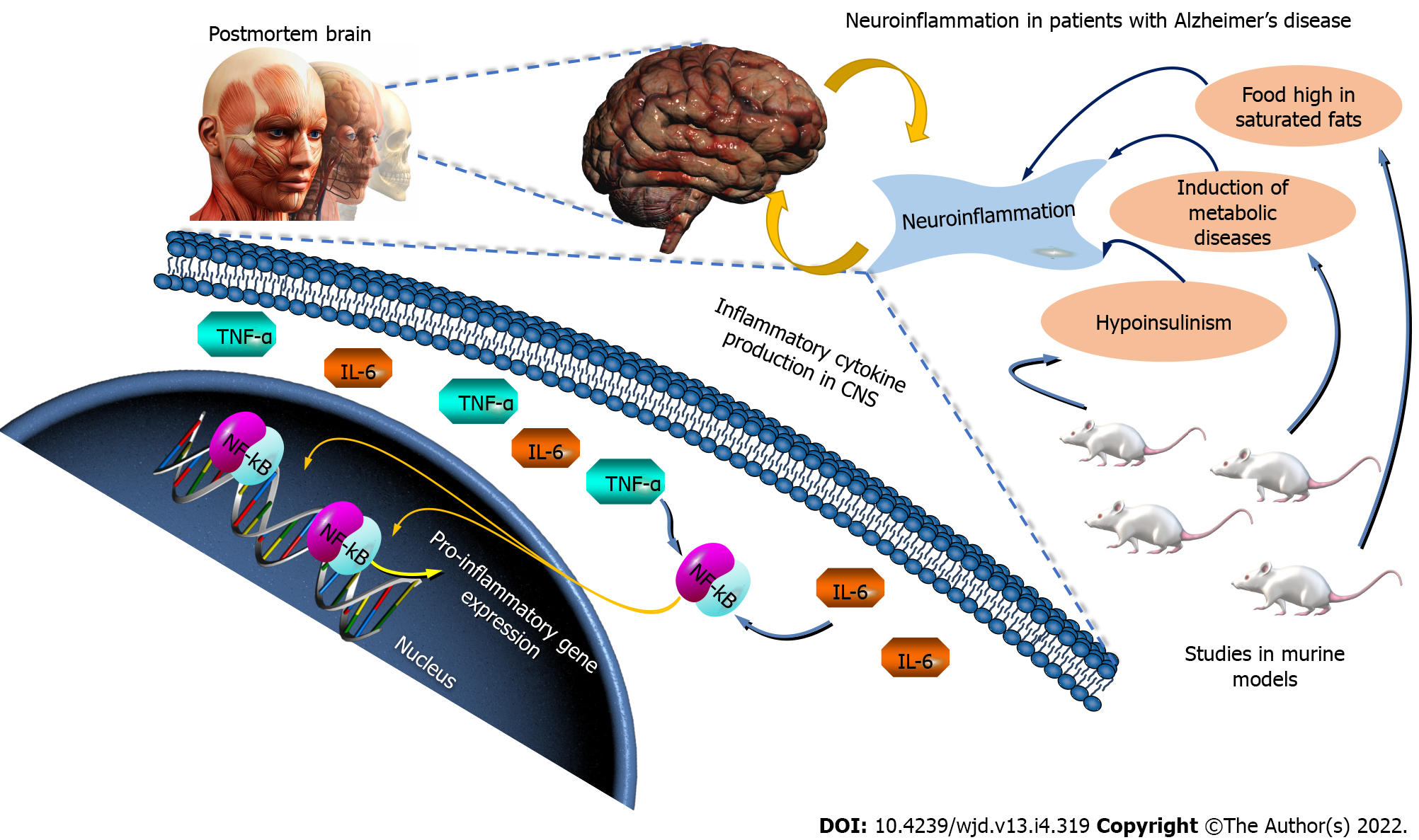
Figure 4 Neuroinflammation in patients with Alzheimer’s disease.
Inflammation leads to the production of inflammation cytokines in central nervous system, activating x that impacts the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes. Some pictures were taken from Qiagen Pathways. TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; IL-6: Interleukin 6; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa beta; CNS: Central nervous system.
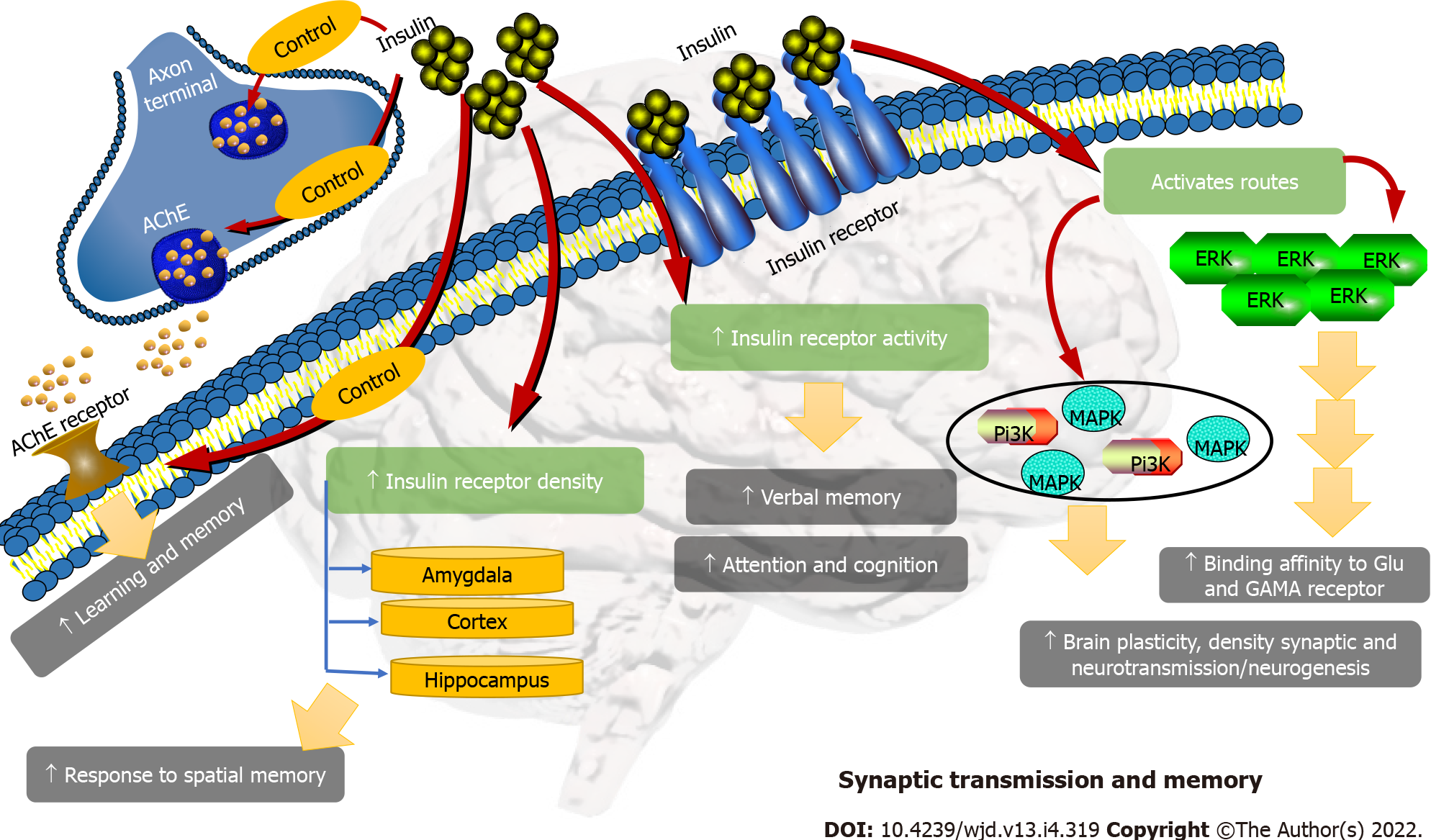
Figure 5 Synaptic transmission and memory.
Insulin increases the density of insulin receptors, its activity, the activation of routes such as phosphoinositide-3 kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase and regulates the binding of acetylcholine with its receptors, modulating cognition, memory, neurotransmission, and neurogenesis. Some pictures were taken from Qiagen Pathways. AChE: Acetylcholine; Pi3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; ERK: Extracellular signal-regulated kinase.
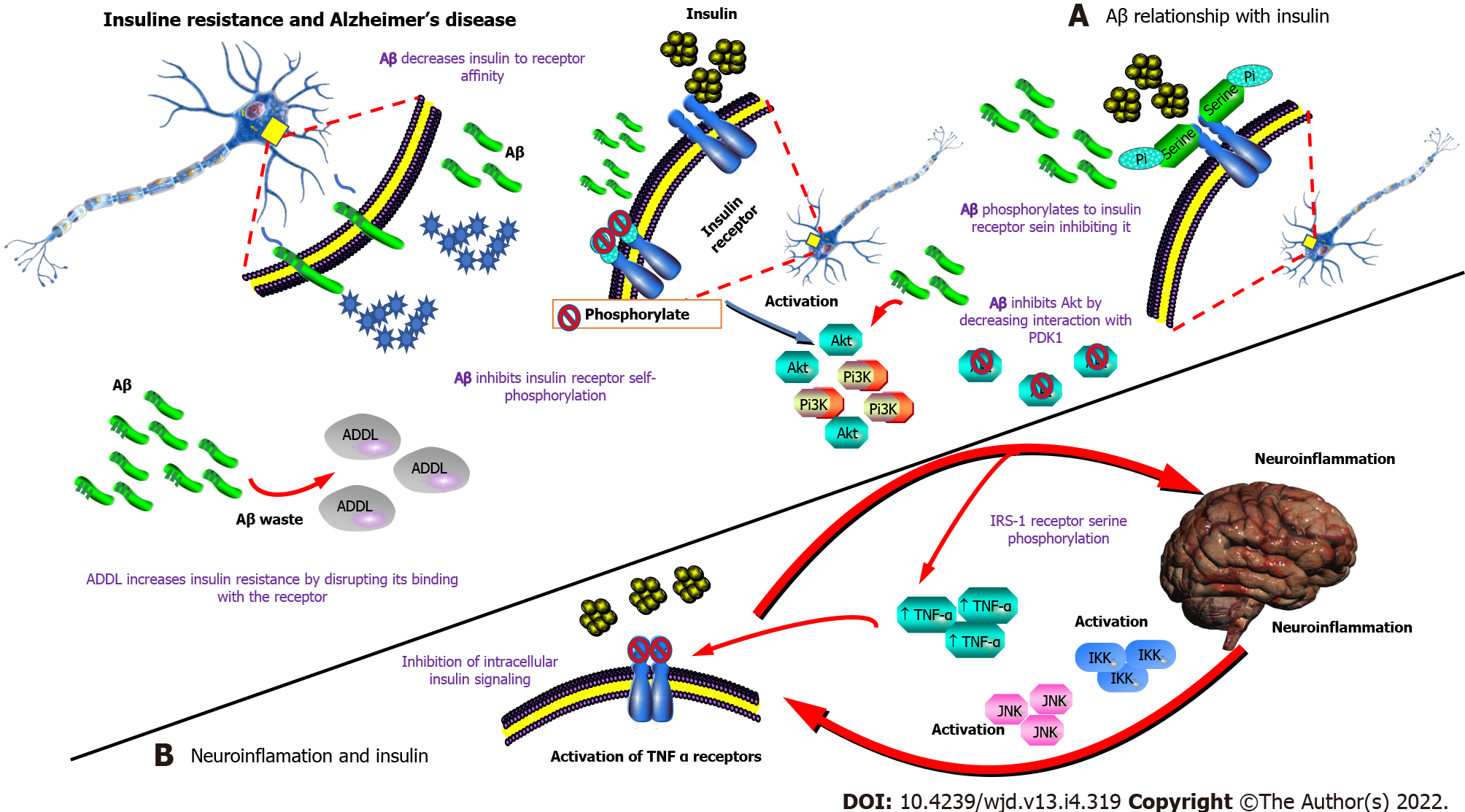
Figure 6 Insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease.
A: Amyloid beta (Aβ) relationship with insulin, the effect of Aβ plaques on insulin signaling, Aβ increases insulin resistance; B: Neuroinflammation and insulin inflammation disrupts insulin signaling pathways by impacting metabolic transducers. Some pictures were taken from Qiagen Pathways. Aβ: Amyloid beta; Pi3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase; Akt: Serine/threonine specific protein kinase; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha.
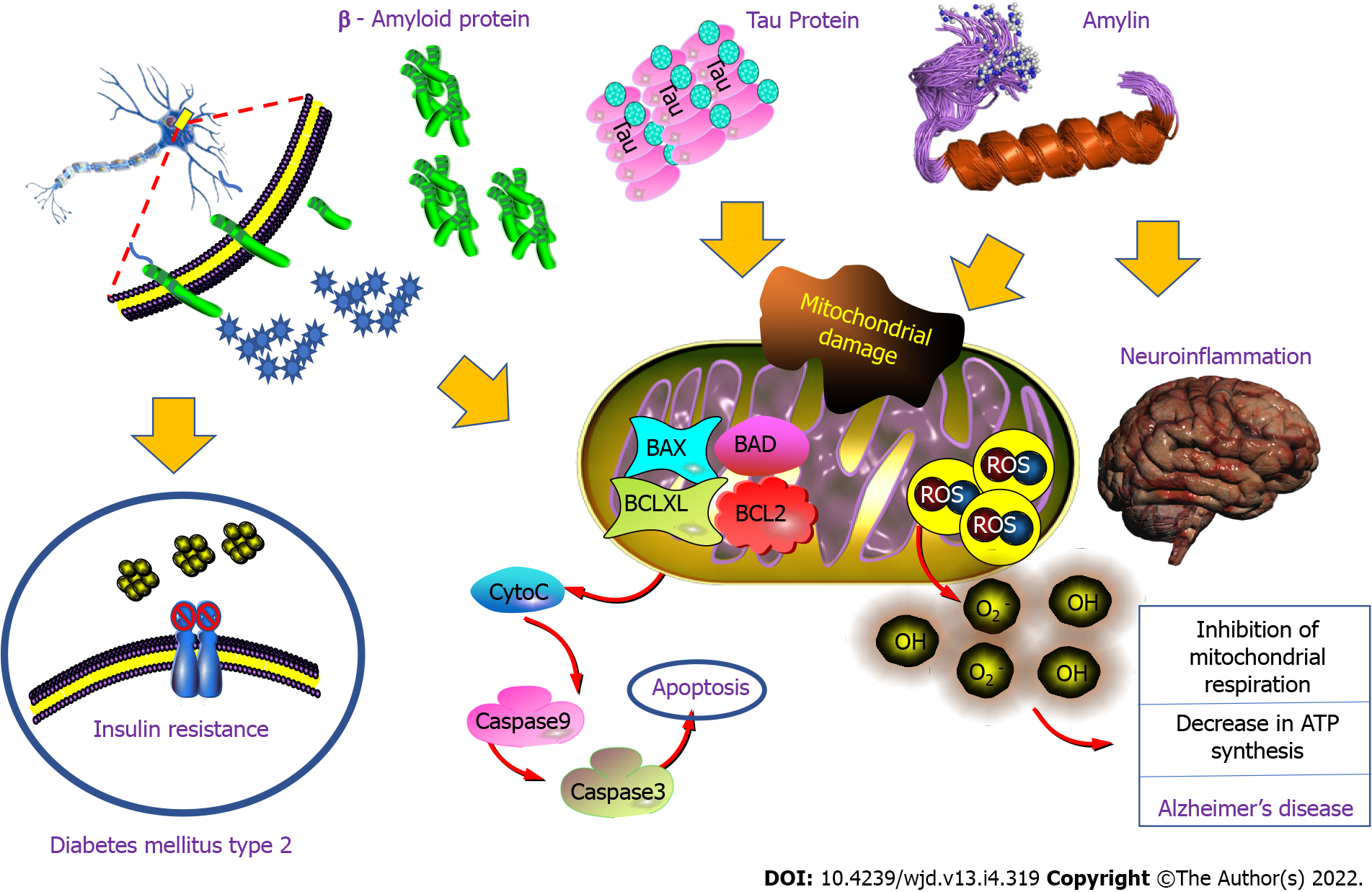
Figure 7 Relation type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease.
The interconnection between β-amyloid protein, Tau protein and amylin increases the accumulation of amyloid deposit, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation, insulin resistance and cell death; factors that explain the evolution to type 2 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease. Some pictures were taken from Qiagen Pathways.
- Citation: Ortiz GG, Huerta M, González-Usigli HA, Torres-Sánchez ED, Delgado-Lara DL, Pacheco-Moisés FP, Mireles-Ramírez MA, Torres-Mendoza BM, Moreno-Cih RI, Velázquez-Brizuela IE. Cognitive disorder and dementia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Diabetes 2022; 13(4): 319-337
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v13/i4/319.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v13.i4.319