Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Diabetes. Aug 15, 2021; 12(8): 1325-1362
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i8.1325
Published online Aug 15, 2021. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i8.1325
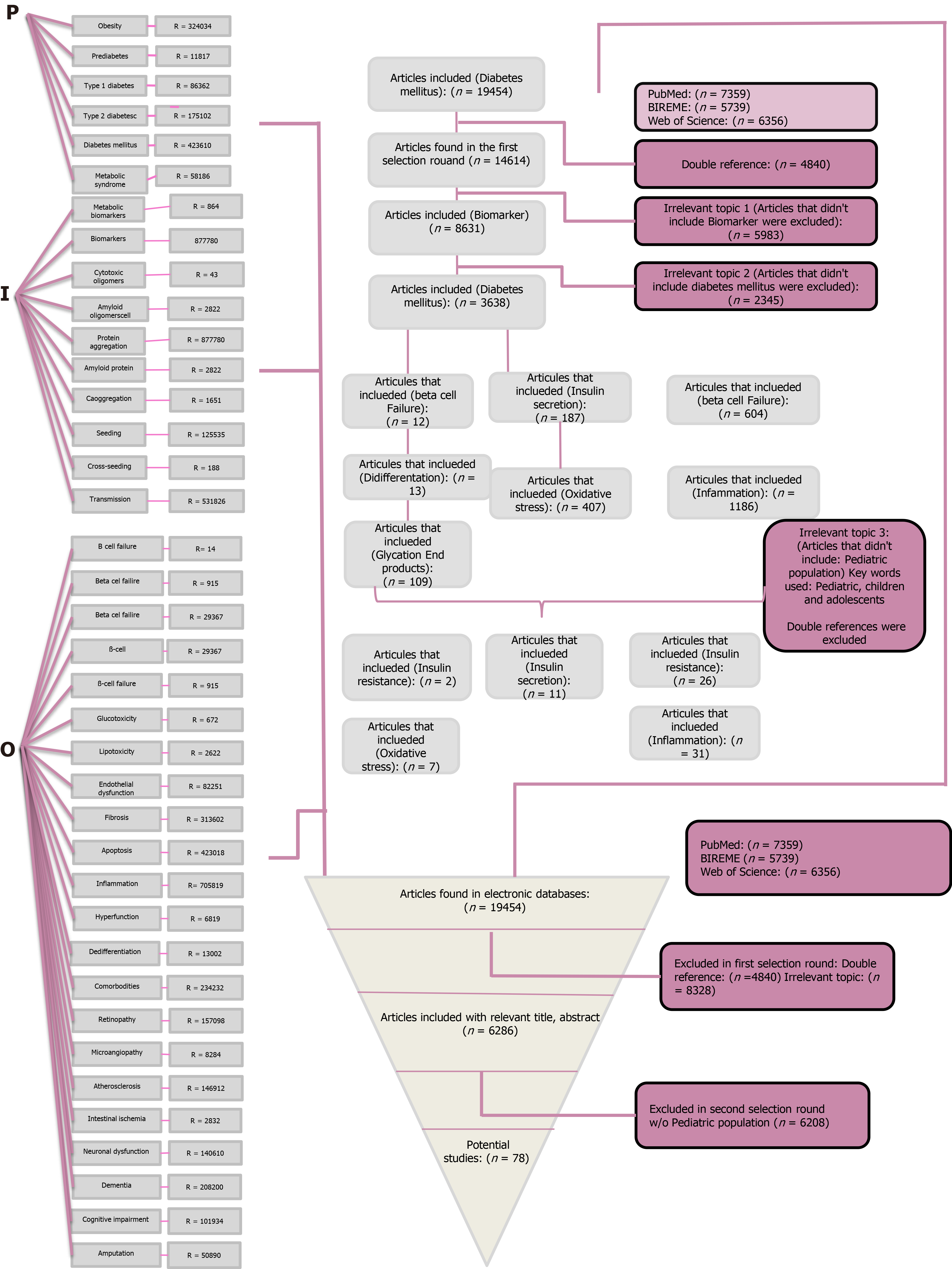
Figure 1 Modified PICO (PIO) approach for the systematic review.
P (Participants) I (Intervention) and O (Outcome). Flowchart review process for the analyzed articles.
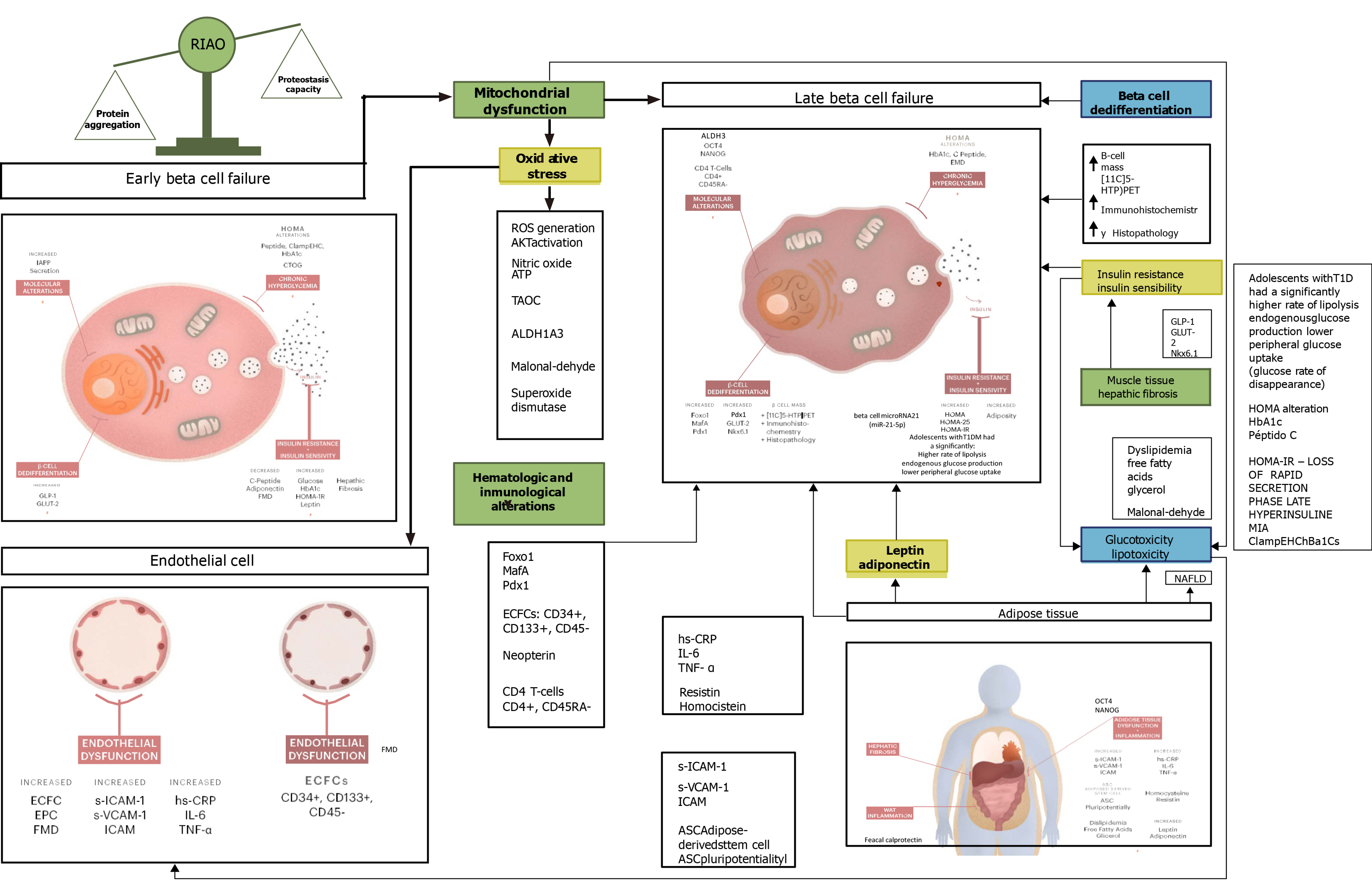
Figure 2 Global view of the main biomarkers analyzed on the articles included for this review.
The biomarkers are divided into the ones that substantially appear on early beta cell damage (characterized by increased insulin and lipid and islet amyloid polypeptide secretion) and increased insulin resistance and of late beta cell damage (characterized by increased oxidative stress and insulin resistance, a markedly insulin secretion and an impaired mitochondrial function, which translates into islet amyloid polypeptide fibrillation). RIAO: Real human islet amyloid polypeptide amyloid oligomers; FMD: Flow-mediated dilatation; CAM: Cytoadhesive molecule; hs-CRP: High-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
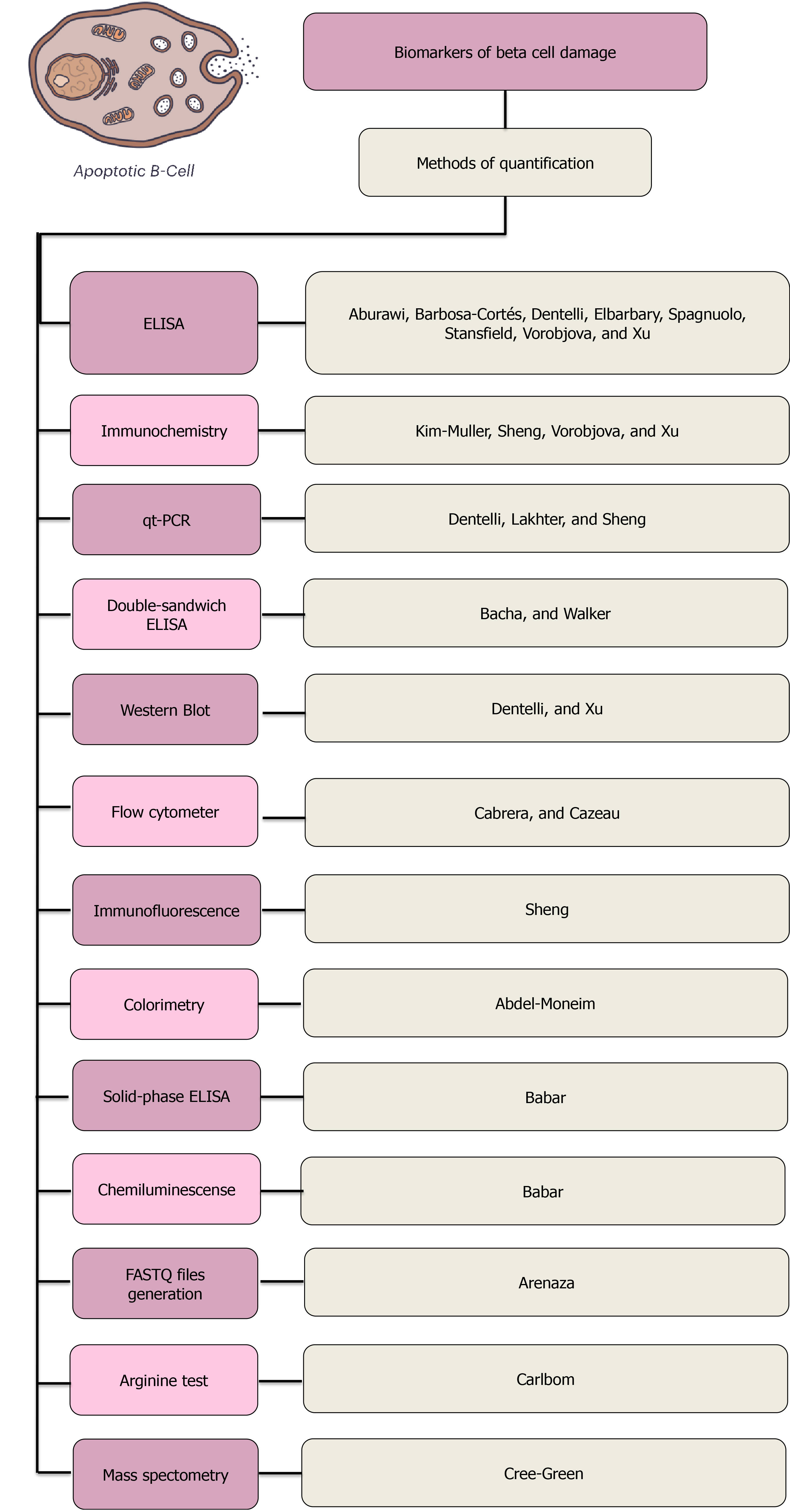
Figure 3 Diagnostic methods found in the articles included for this review.
The methods are ordered from the most used to the least used. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was the most commonly used method; a total of 8 articles used it as a diagnostic method. ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; qt-PCR: Quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
- Citation: Calderón-Hernández MF, Altamirano-Bustamante NF, Revilla-Monsalve C, Mosquera-Andrade MB, Altamirano-Bustamante MM. What can we learn from β-cell failure biomarker application in diabetes in childhood? A systematic review. World J Diabetes 2021; 12(8): 1325-1362
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-9358/full/v12/i8/1325.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v12.i8.1325