Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Jun 15, 2025; 17(6): 105140
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.105140
Published online Jun 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.105140
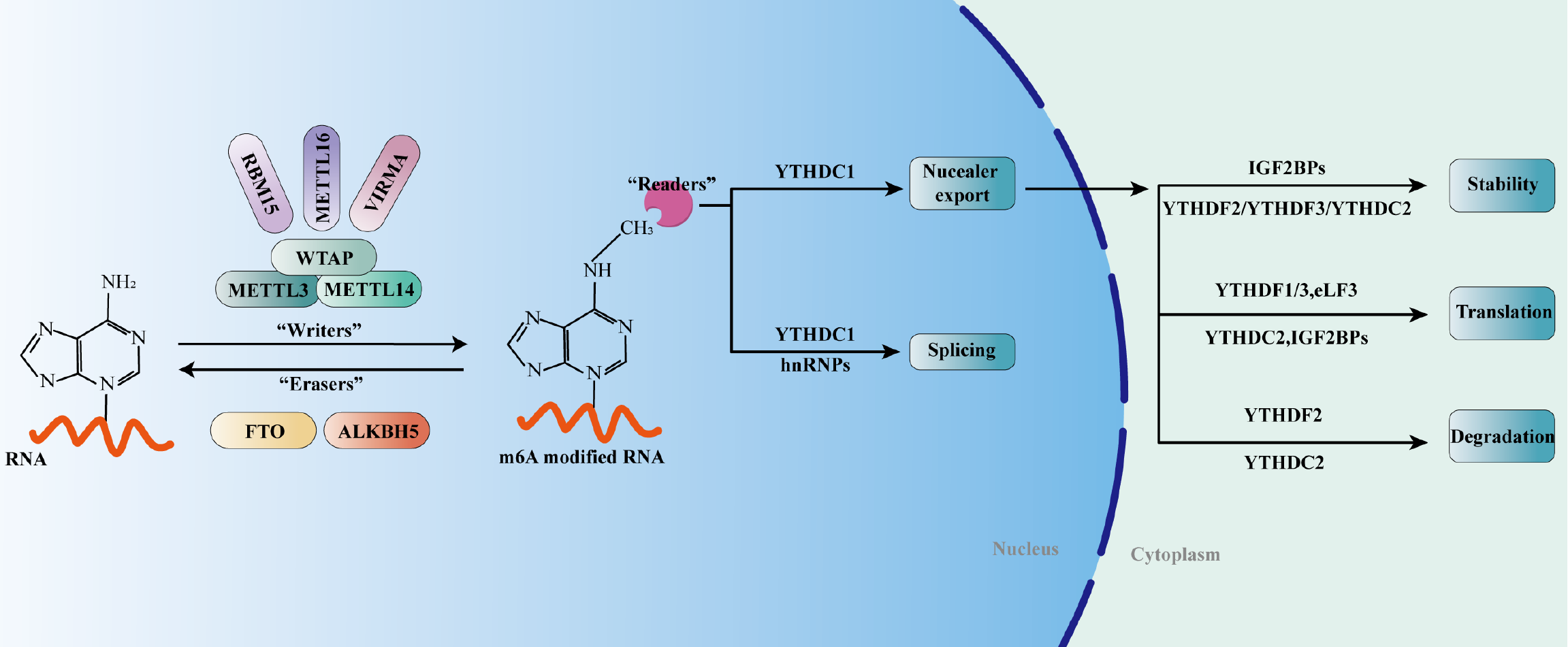
Figure 1 Schematic depiction of N6-methyladenosine modification in RNA metabolism.
The installation of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) is facilitated by writers such as METTL3, METTL14, WTAP, RBM15, VIRMA, and METTL16. Conversely, erasers like FTO and ALKBH5 are responsible for removing these m6A modifications. Essential to this process are readers, which recognize m6A and implement post-transcriptional regulation. Collectively, writers, erasers, and readers intricately orchestrate RNA’s splicing, export, translation, decay, and overall stability.
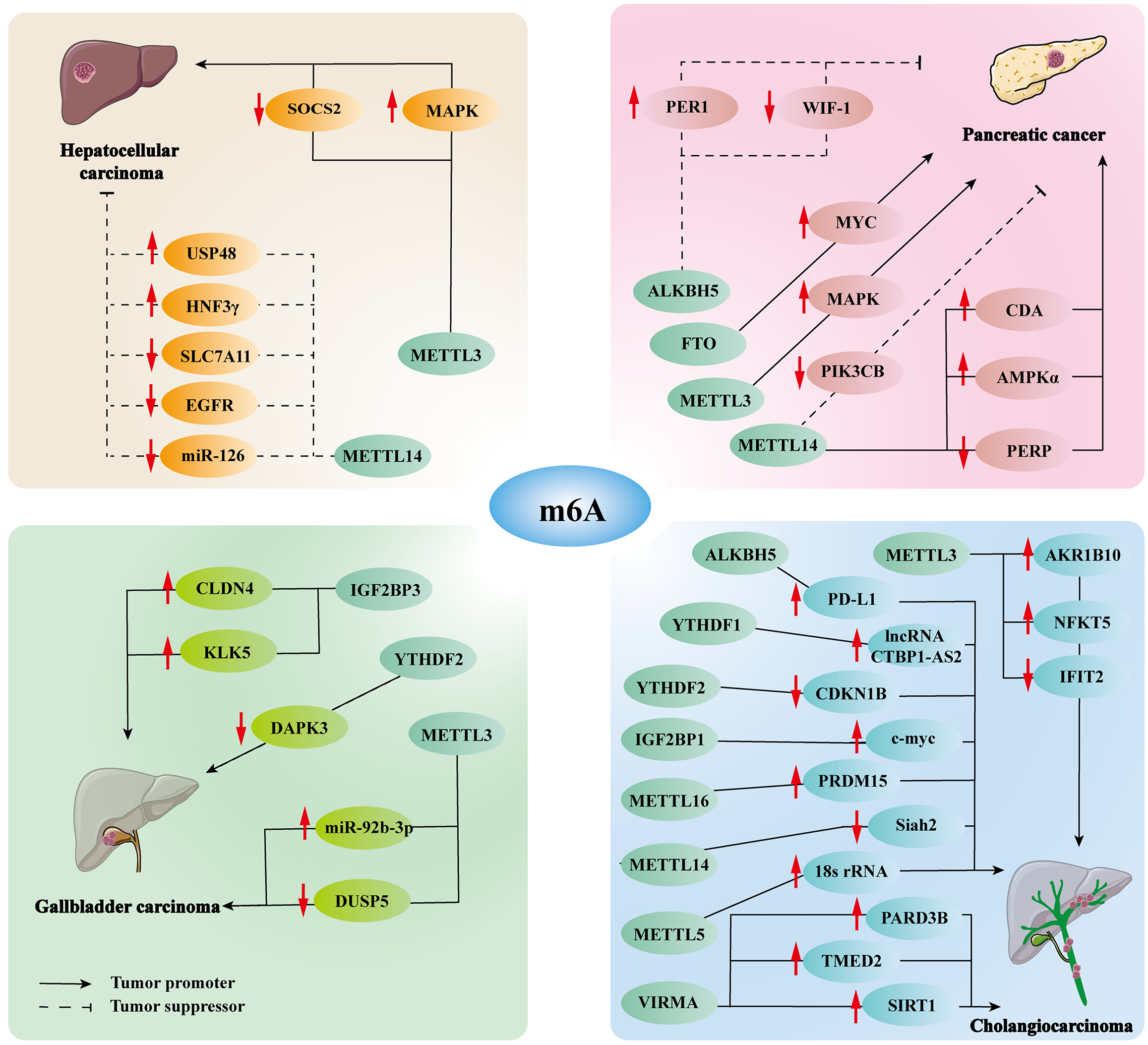
Figure 2 Concise overview of N6-methyladenosine modifiers’ functions in hepatobiliary carcinoma.
Diverse N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-related regulators, through aberrant m6A modifications, specifically target various genes or pathways, influencing the onset and progression of the tumor.
- Citation: Jia C, Lang QF, Yin ZJ, Sun J, Meng QH, Pei TM. Role, mechanism, and application of N6-methyladenosine in hepatobiliary carcinoma. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(6): 105140
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i6/105140.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i6.105140