Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. May 15, 2025; 17(5): 105417
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105417
Published online May 15, 2025. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105417
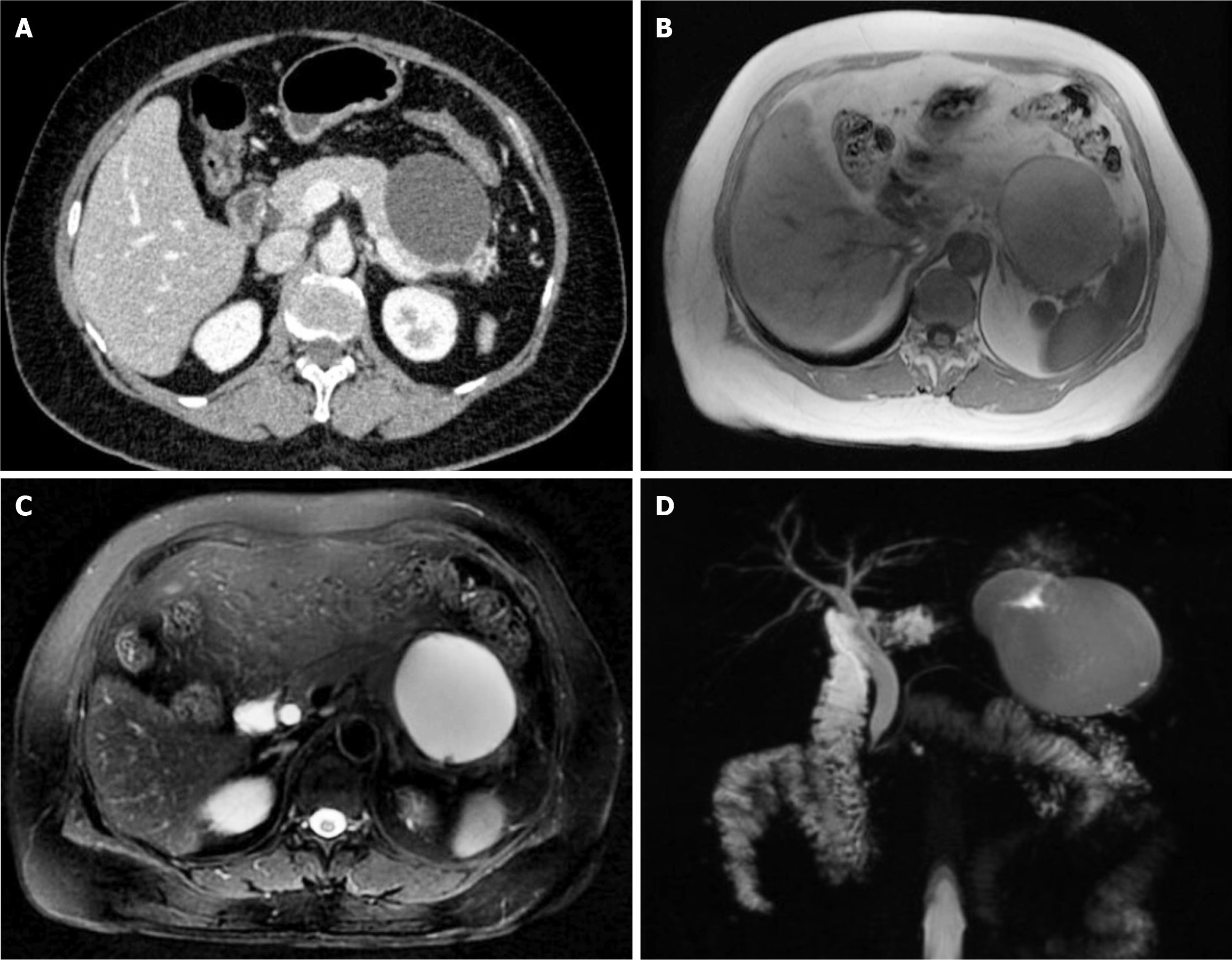
Figure 1 Initial imaging showing the cystic mass located in the tail of the pancreas and pushing against the stomach wall.
A: Abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan; B and C: Magnetic resonance imaging; D: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
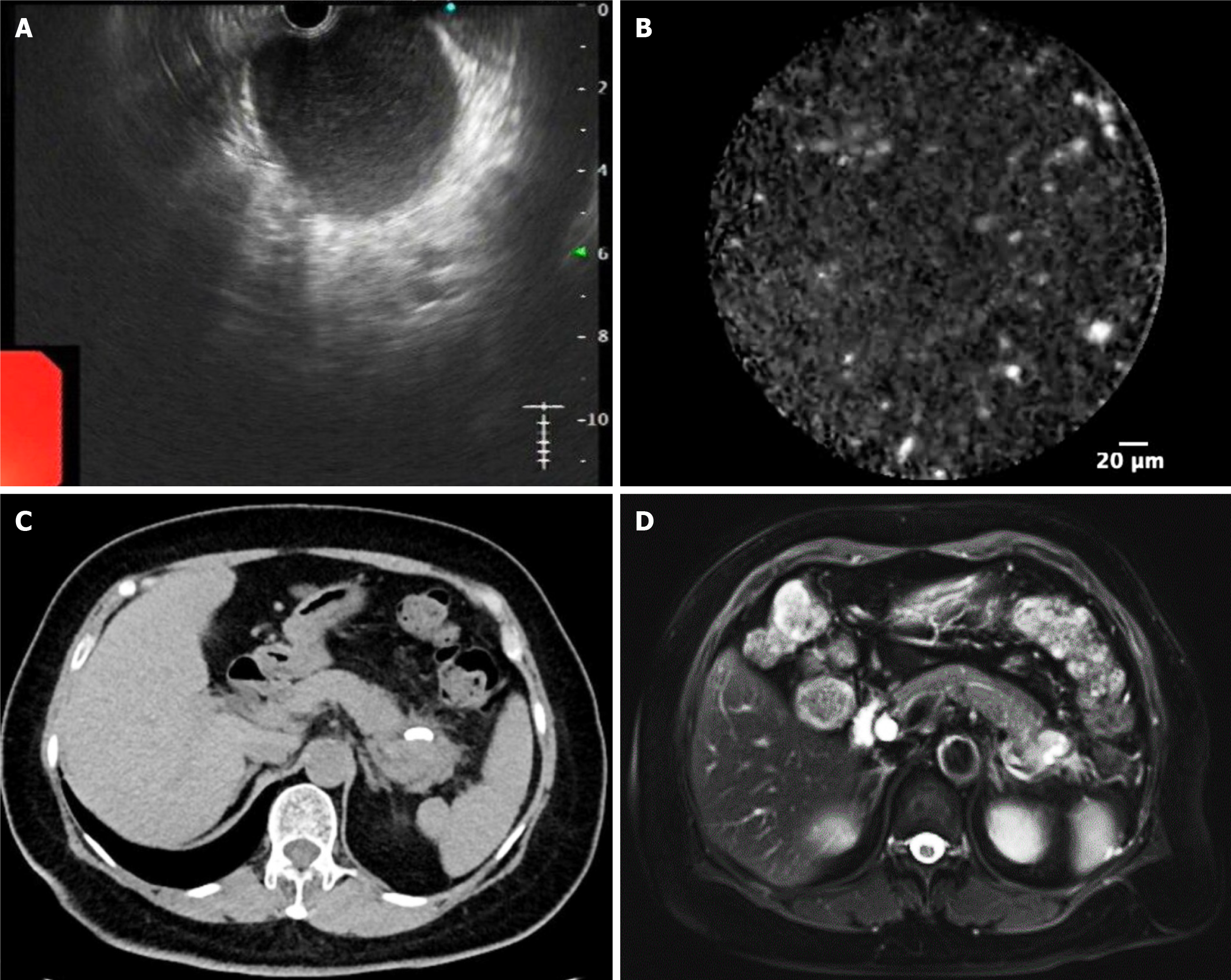
Figure 2 Further evaluation and subsequent follow-up.
A and B: Further evaluation by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration and needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy; C and D: Follow-up computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging.
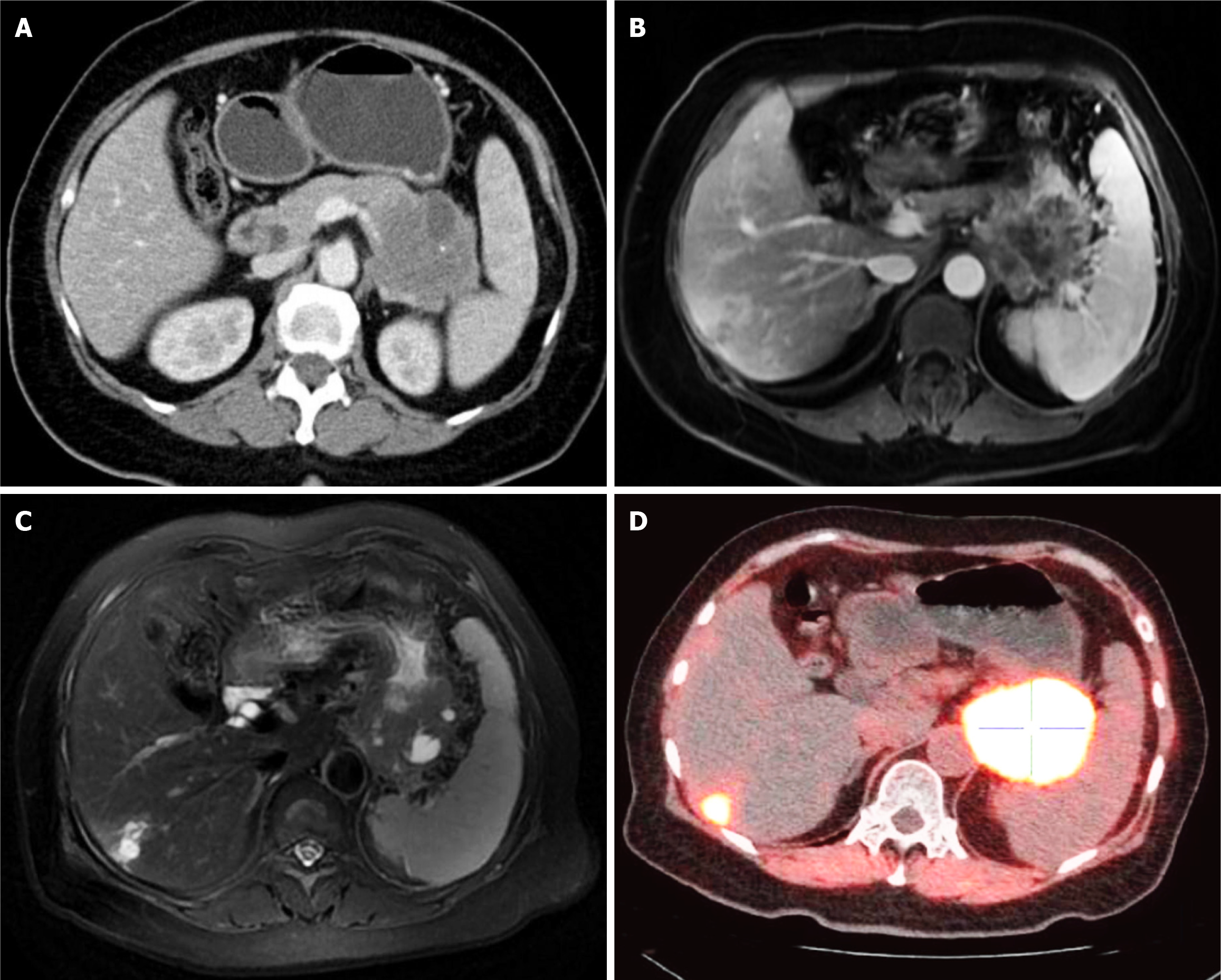
Figure 3 Imaging and nuclear medicine scans showed the advanced cystic mass on second admission to our hospital.
A: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography scan; B and C: Magnetic resonance imaging; D: Fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose- and fluorine 18-labeled fibroblast-activation protein inhibitor-positron emission tomography/computed tomography.
- Citation: Yan ZY, Shi W, Guo T, Yang AM. Mucinous cystic neoplasm mimicking pancreatic pseudocyst and progressing to adenocarcinoma: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2025; 17(5): 105417
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v17/i5/105417.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v17.i5.105417