Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2024; 16(4): 1660-1667
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1660
Published online Apr 15, 2024. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1660
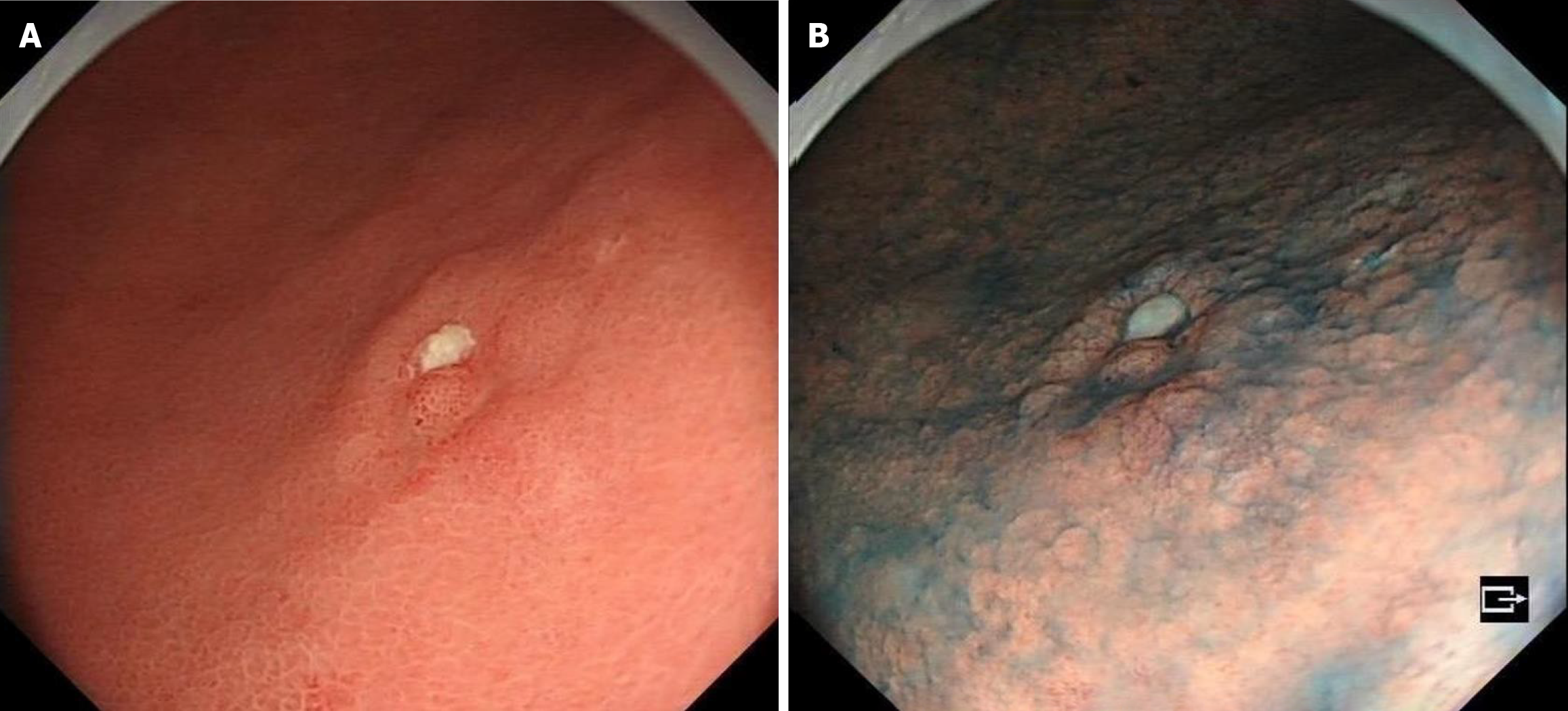
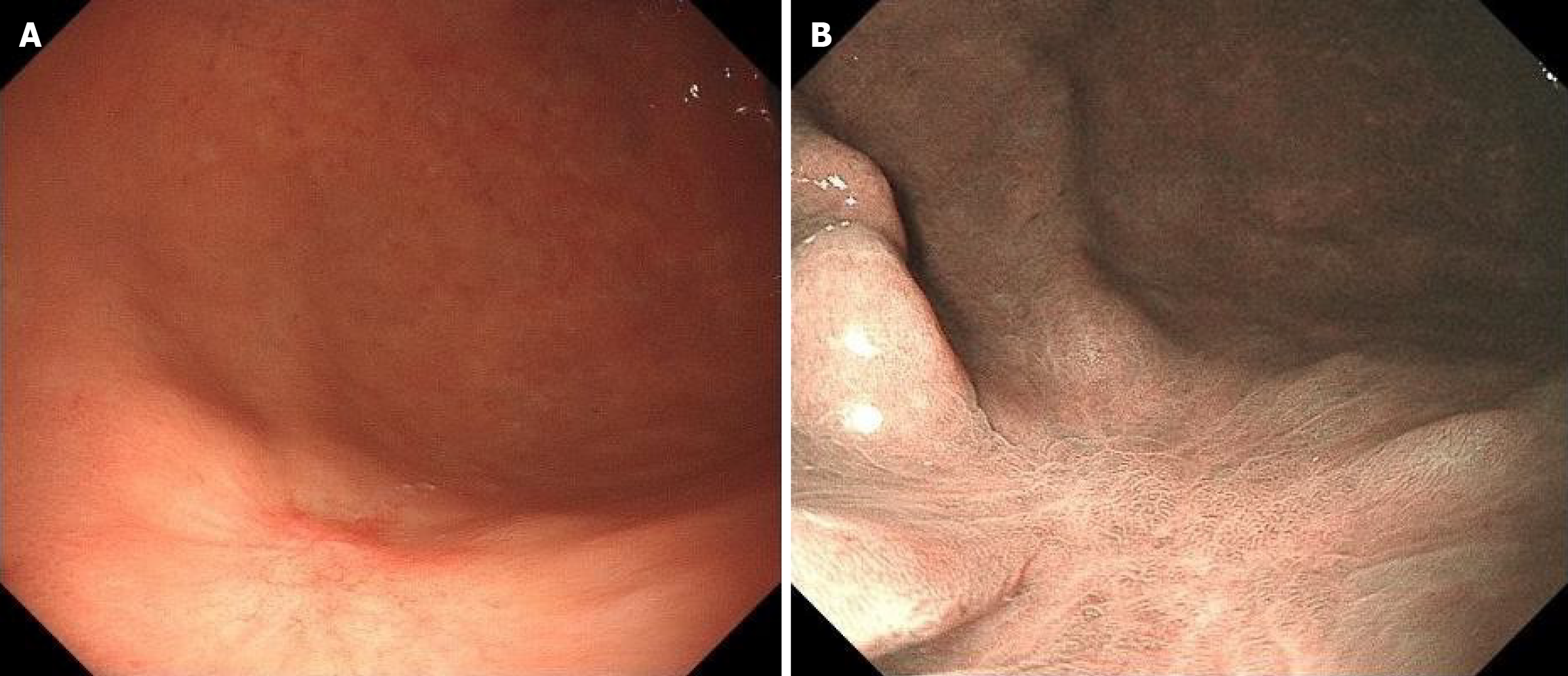
Figure 1 History of present illness.
A: Gastroscopy shows that the mucosa of the gastric sinus is thickened, red and white, and the sheet is congested; B: Indigo carmine staining is shallow depression and the surrounding boundary is clear.
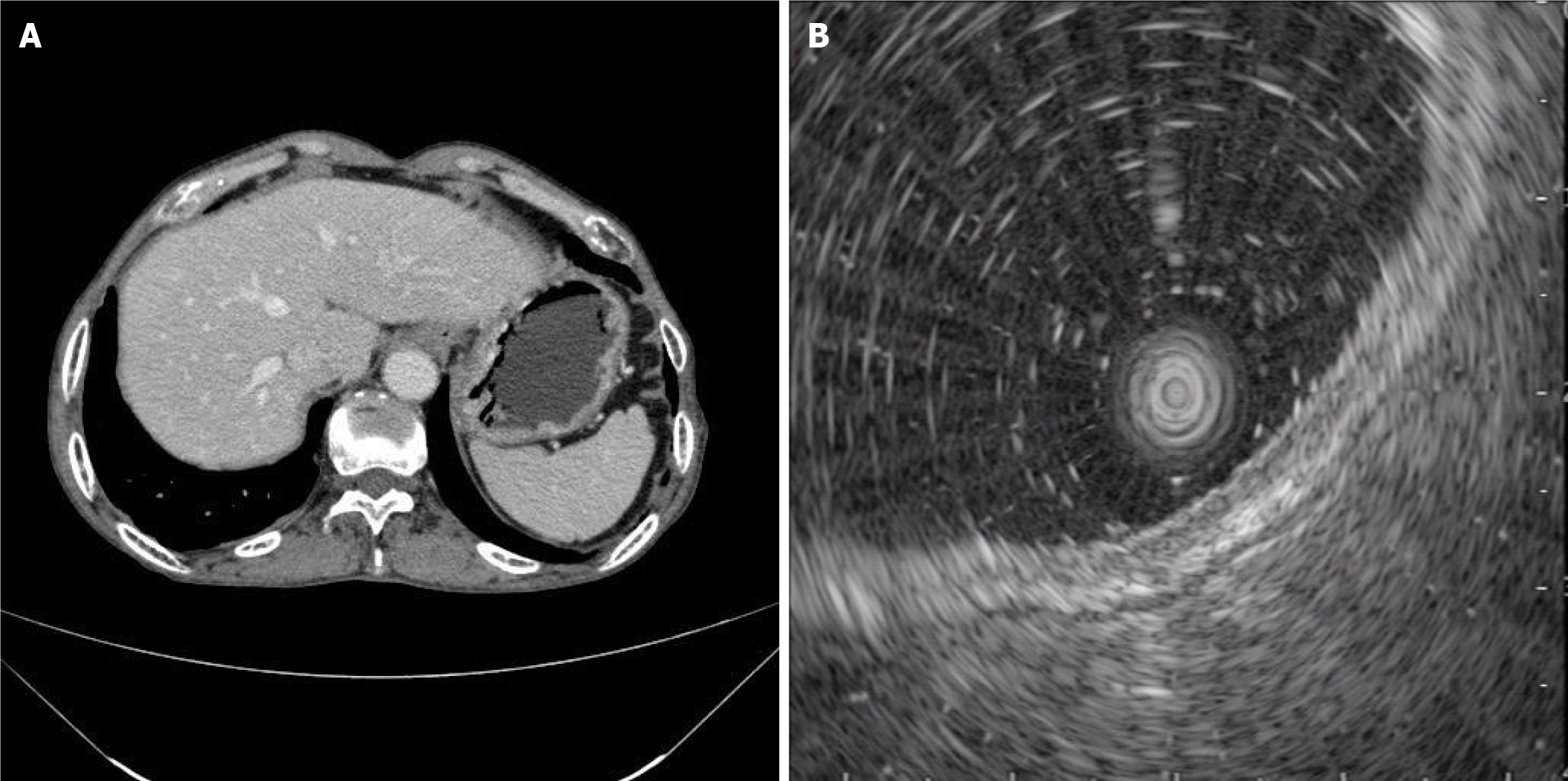
Figure 2 Imaging examinations.
A: Results of upper abdominal enhanced computed tomography examination after admission; B: Ultrasound gastroscopy suggests that the lesion is located within the mucosa.
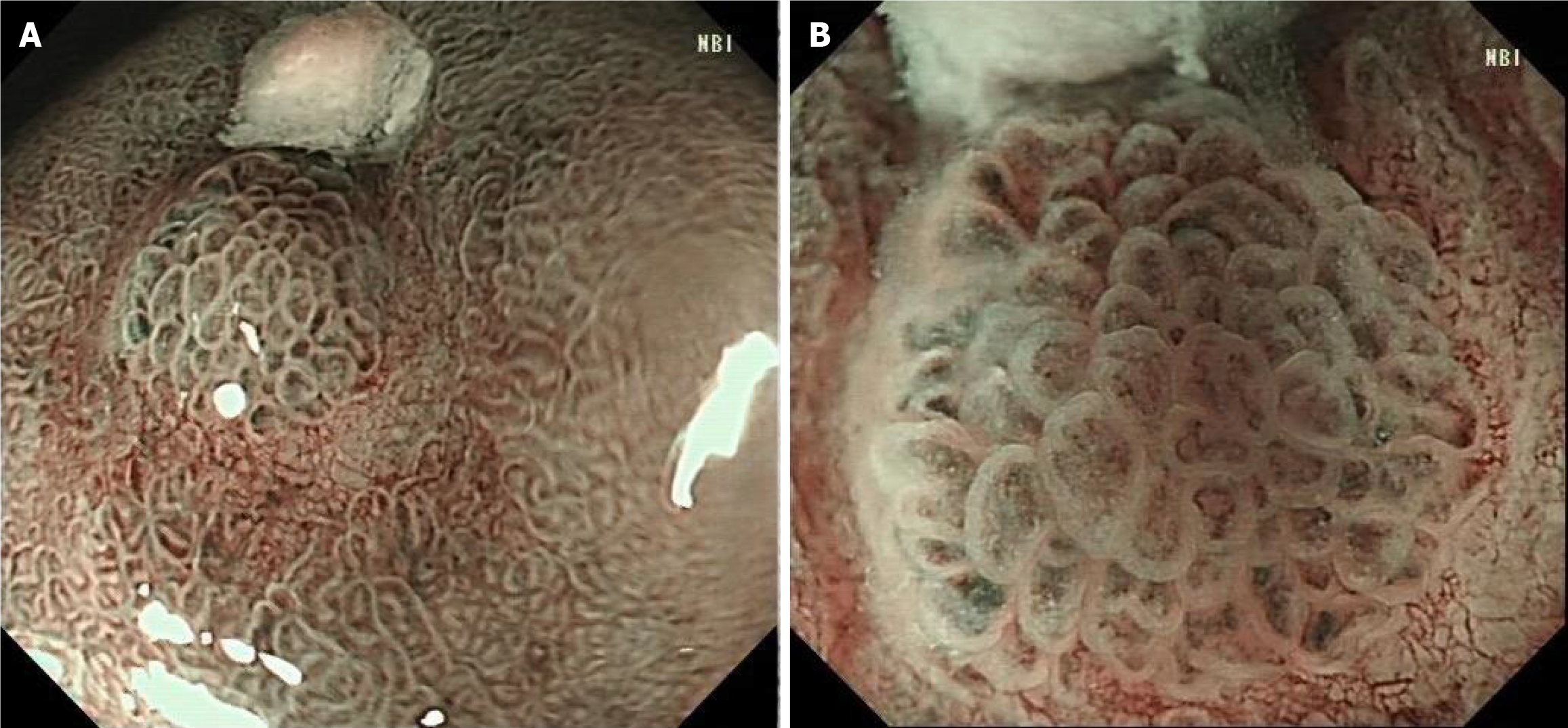
Figure 3 Narrow-band imaging endoscopy.
A: Under narrow-band imaging endoscopy, the lesions were dark tea-coloured and the boundary was clear; B: Under magnifying endoscopy, the micro glandular structure on the surface of the lesions was, of different sizes, and the microvessels were slightly tortuous and expanded, forming a bright boundary with the periphery.
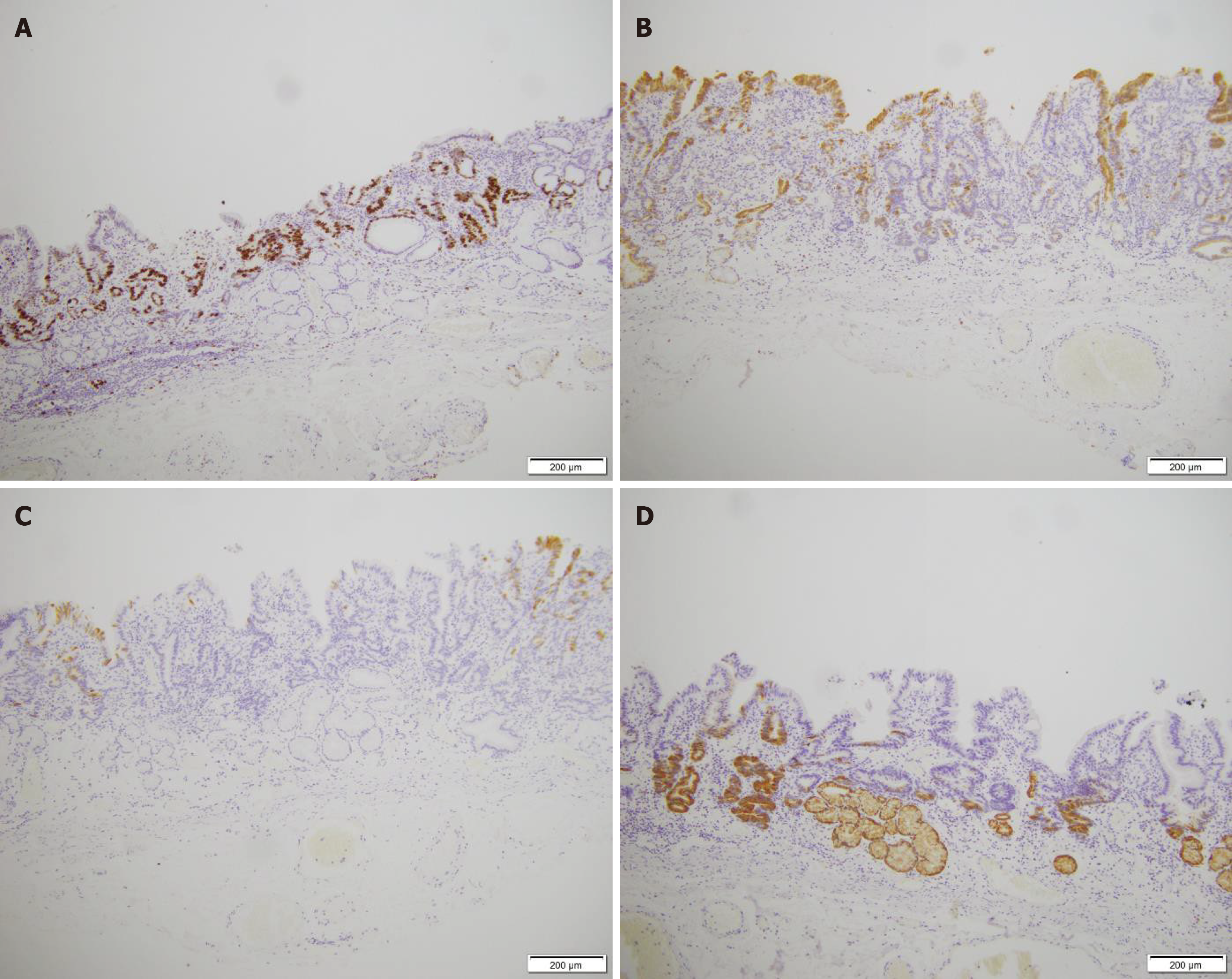
Figure 4 Immunohistochemical examination results.
A: Ki-67 positivity in tissue; B: MUC2 partially positive; C: MUC5AC negative; D: MUC6 partially positive (× 10).
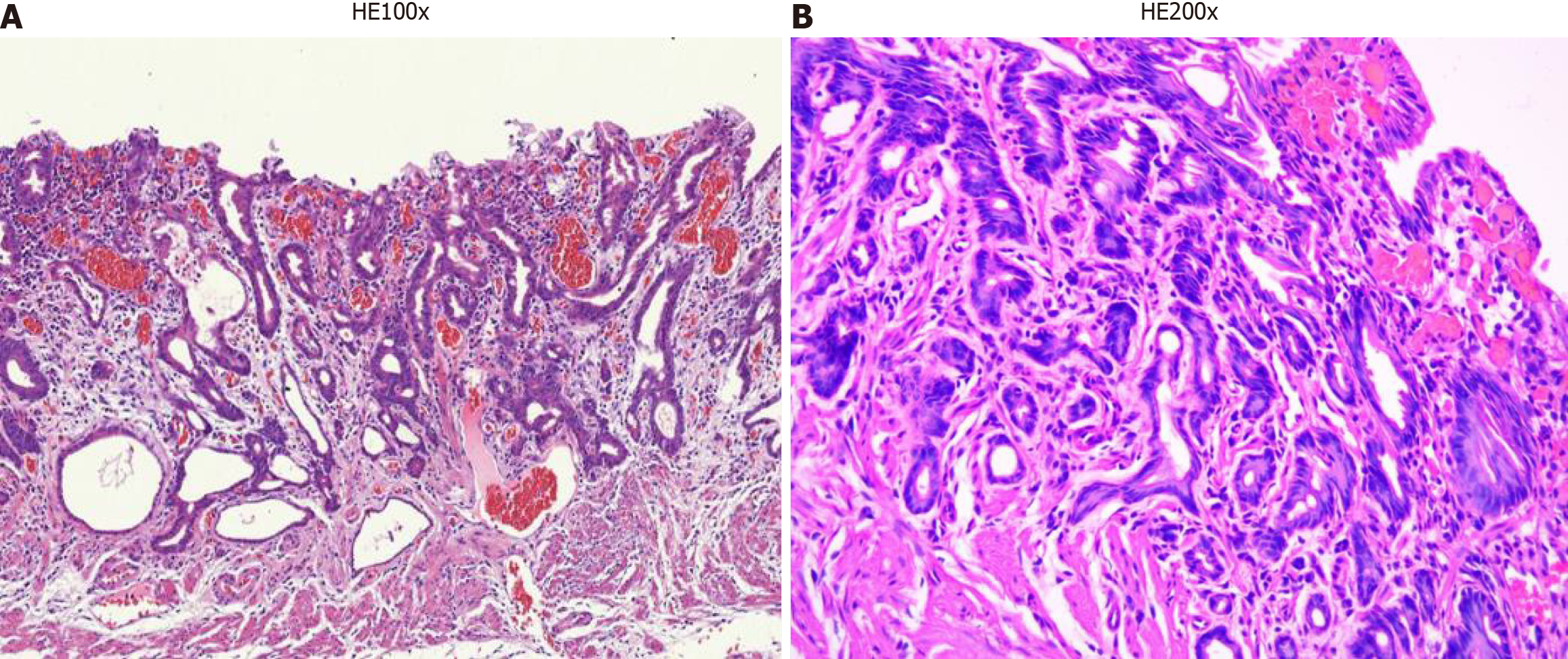
Figure 5 Hematoxylin and eosin stain of pathological tissue.
A: Poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma cells were detected only in the submucosa and were restricted at the low elevated lesion; B: The density of the gastric submucosal gland is low, and the basement membrane of the gland is discontinuous.
Figure 6 After endoscopic submucosal dissection treatment, the patient reviewed their endoscopic findings.
A: Common endoscopic findings after Endoscopic submucosal dissection treatment; B: The endoscopic findings after Indigo carmine staining.
- Citation: Xu YW, Song Y, Tian J, Zhang BC, Yang YS, Wang J. Clinical pathological characteristics of “crawling-type” gastric adenocarcinoma cancer: A case report. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2024; 16(4): 1660-1667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v16/i4/1660.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v16.i4.1660