Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Oncol. Apr 15, 2021; 13(4): 265-278
Published online Apr 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i4.265
Published online Apr 15, 2021. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v13.i4.265
Figure 1 Results for Epstein-Barr virus infection by in situ hybridization and for microsatellite instability, E-cadherin, and p53 expression by immunohistochemistry in remnant gastric cancer and primary gastric cancer patients.
A: Remnant gastric cancer; B: Primary gastric cancer. EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; MSI: Microsatellite instability; NA: No alteration.
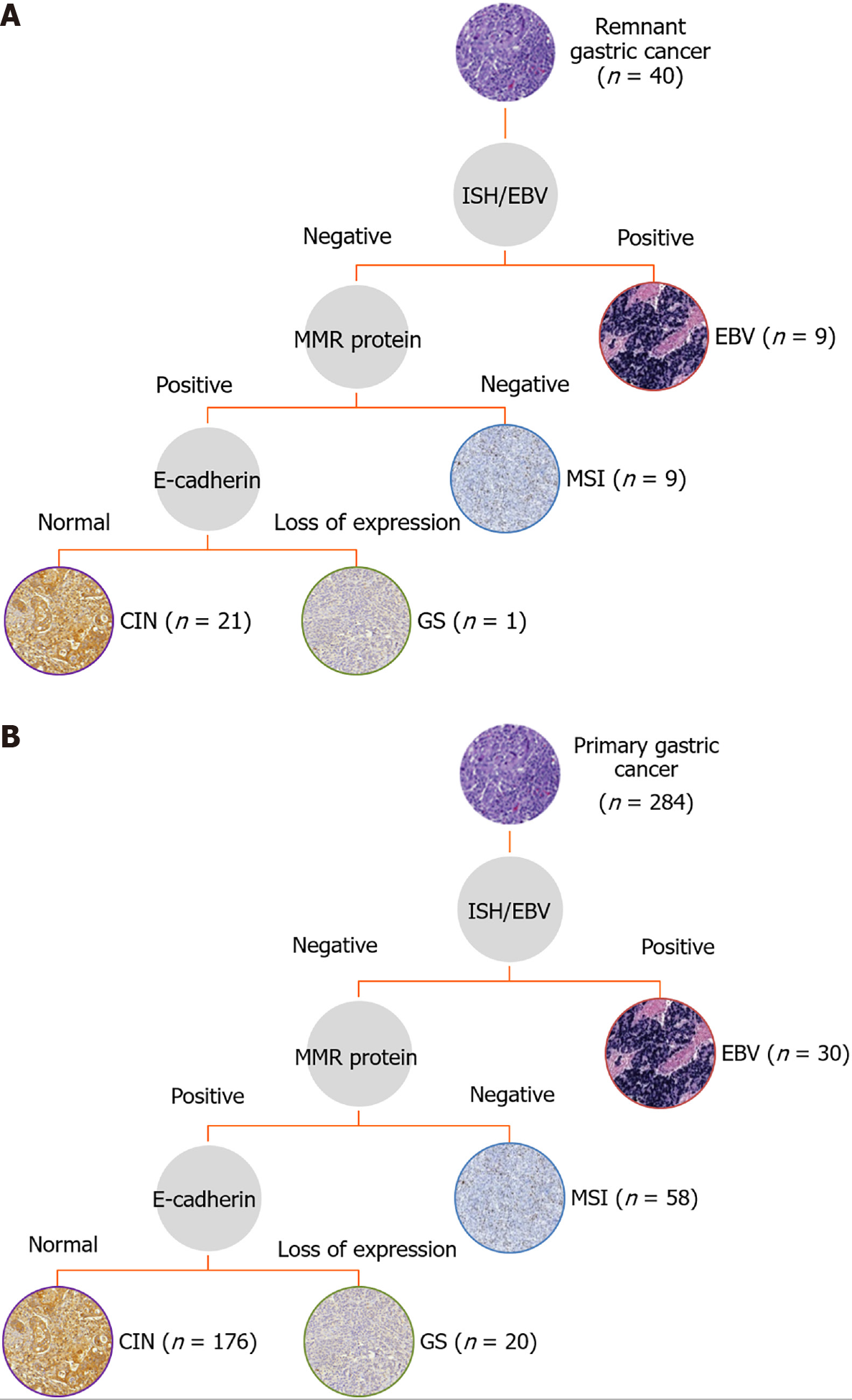
Figure 2 Flowchart showing the classification of molecular subtypes and final distribution.
A: Remnant gastric cancer; B: Primary gastric cancer. CIN: Chromosomal instability; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; GS: Genomically stable; ISH: In situ hybridization; MMR: Mismatch repair; MSI: Microsatellite instability.
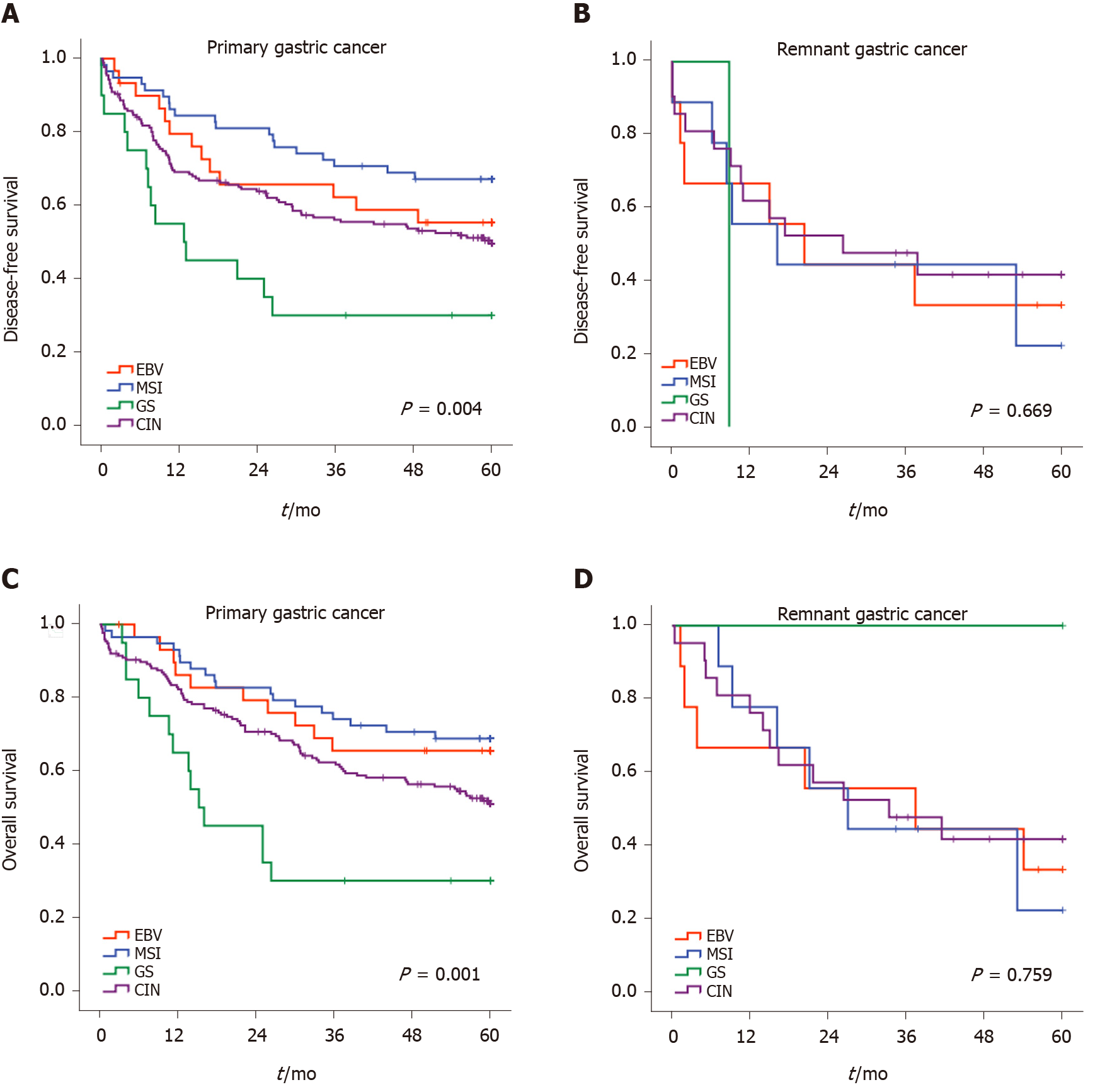
Figure 3 Disease-free survival and overall survival according to the subtypes of molecular classification for remnant gastric cancer and primary gastric cancer.
A: Disease-free survival of primary gastric cancer; B: Disease-free survival of remnant gastric cancer; C: Overall survival of primary gastric cancer; D: Overall survival of remnant gastric cancer. CIN: Chromosomal instability; EBV: Epstein-Barr virus; GS: Genomically stable; MSI: Microsatellite instability.
- Citation: Ramos MFKP, Pereira MA, Cardili L, de Mello ES, Ribeiro Jr U, Zilberstein B, Cecconello I. Expression profiles of gastric cancer molecular subtypes in remnant tumors. World J Gastrointest Oncol 2021; 13(4): 265-278
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5204/full/v13/i4/265.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4251/wjgo.v13.i4.265