Copyright
©2010 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2010; 2(12): 434-441
Published online Dec 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.434
Published online Dec 27, 2010. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.434
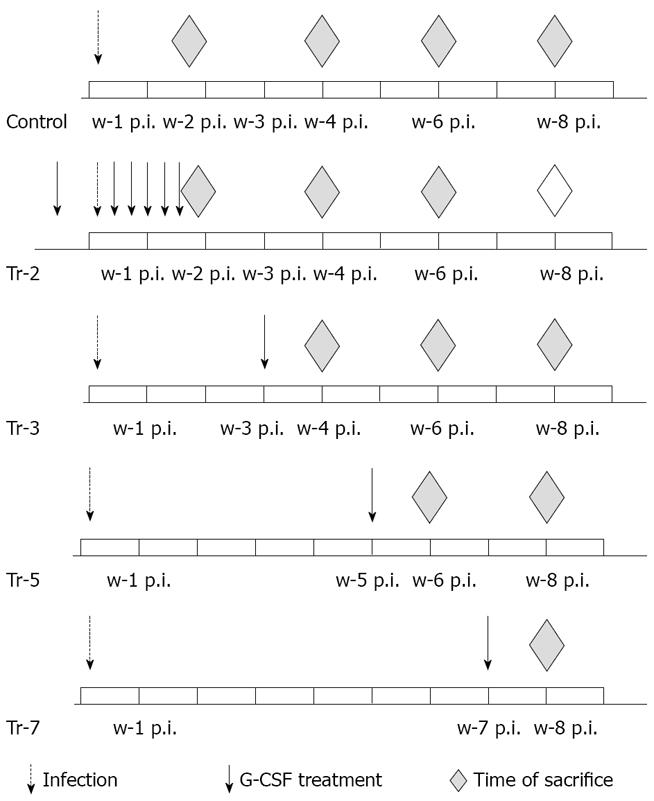
Figure 1 Experimental design.
w: week; p.i.: post infection.
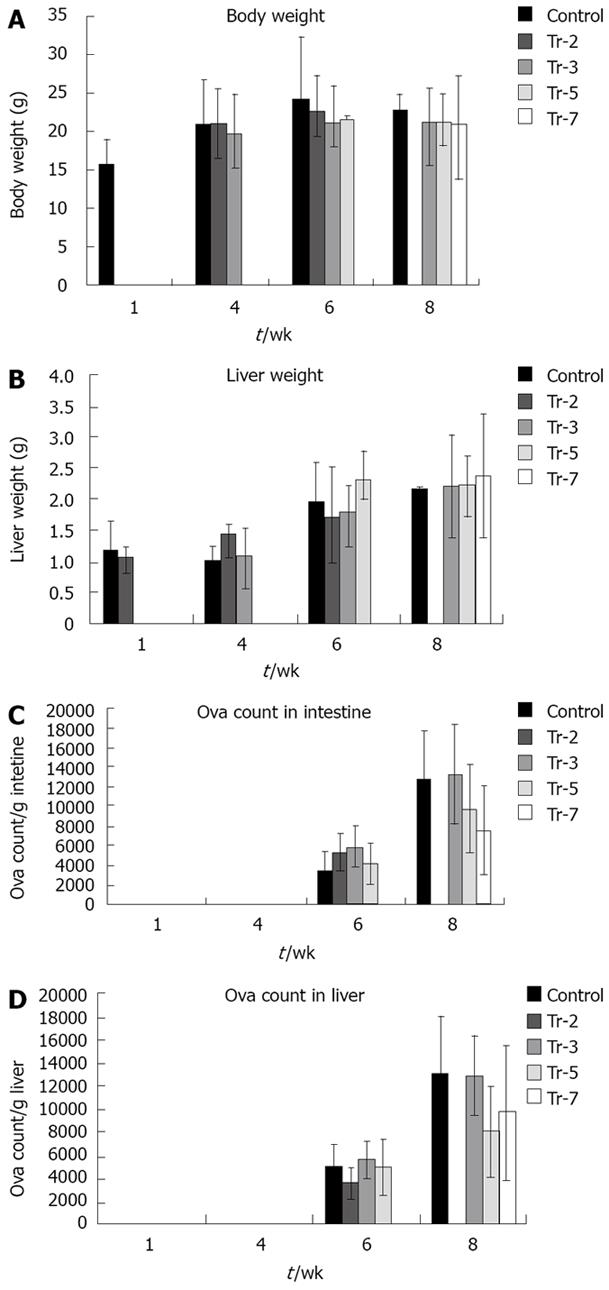
Figure 2 Effect of treatment on.
A: body weight; B: liver weight; C: egg load in intestine; and D: egg load in liver.
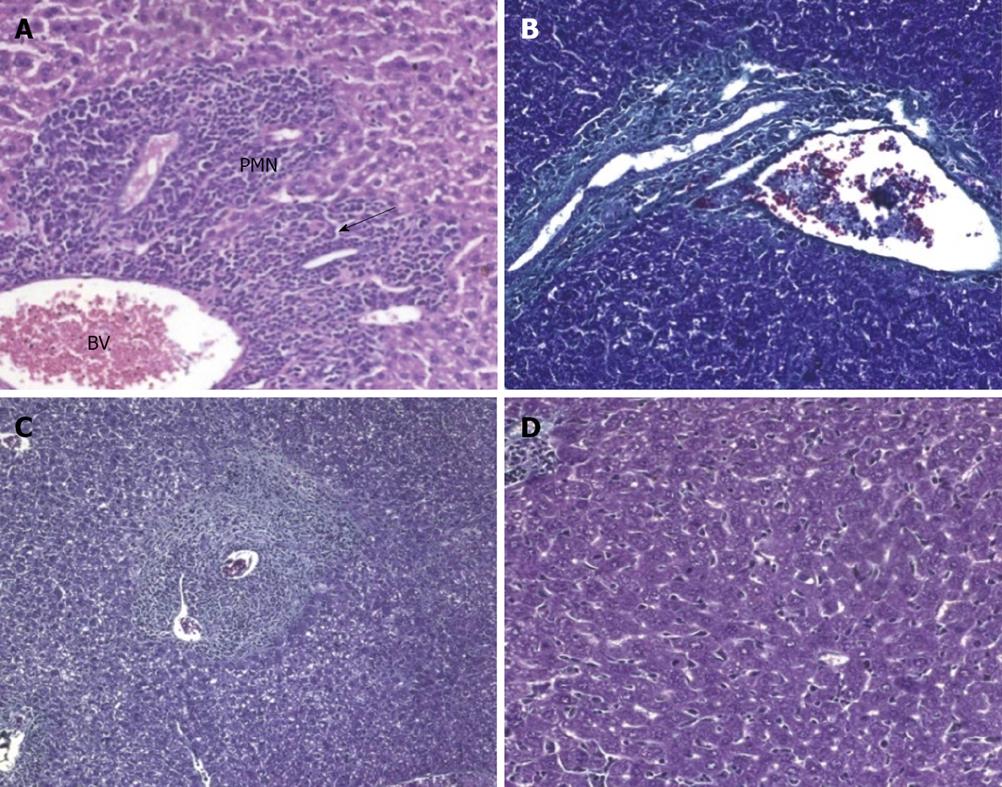
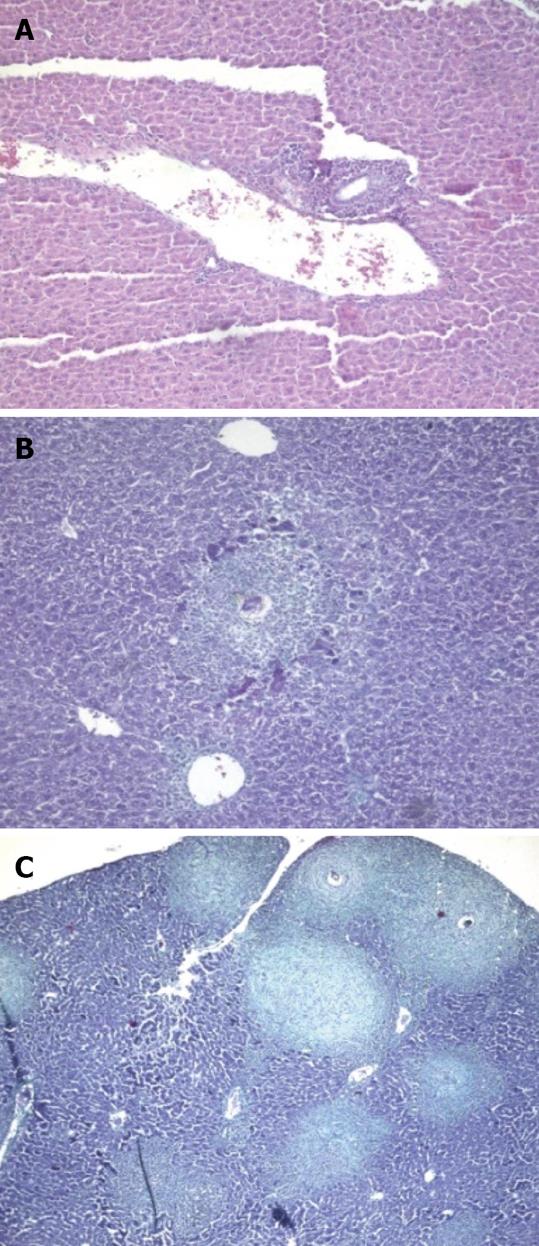
Figure 3 Preinfection treated animals sacrificed.
A: 10 d post infection (H&E × 200); B: 4 wk post infection (wpi) (Masson trichrome × 200); C,D: 6 wpi (Masson trichrome and H&E × 200). PMN: polymorphonuclear.
Figure 4 Liver sections in Schistosoma mansoni-infected untreated mice.
A,B: 10 d post infection (H&E × 200); C: 4 wk post infection (wpi) (H&E × 200); D: 6 wpi (Masson trichrome × 100); E: 8 wpi (Masson trichrome × 100).
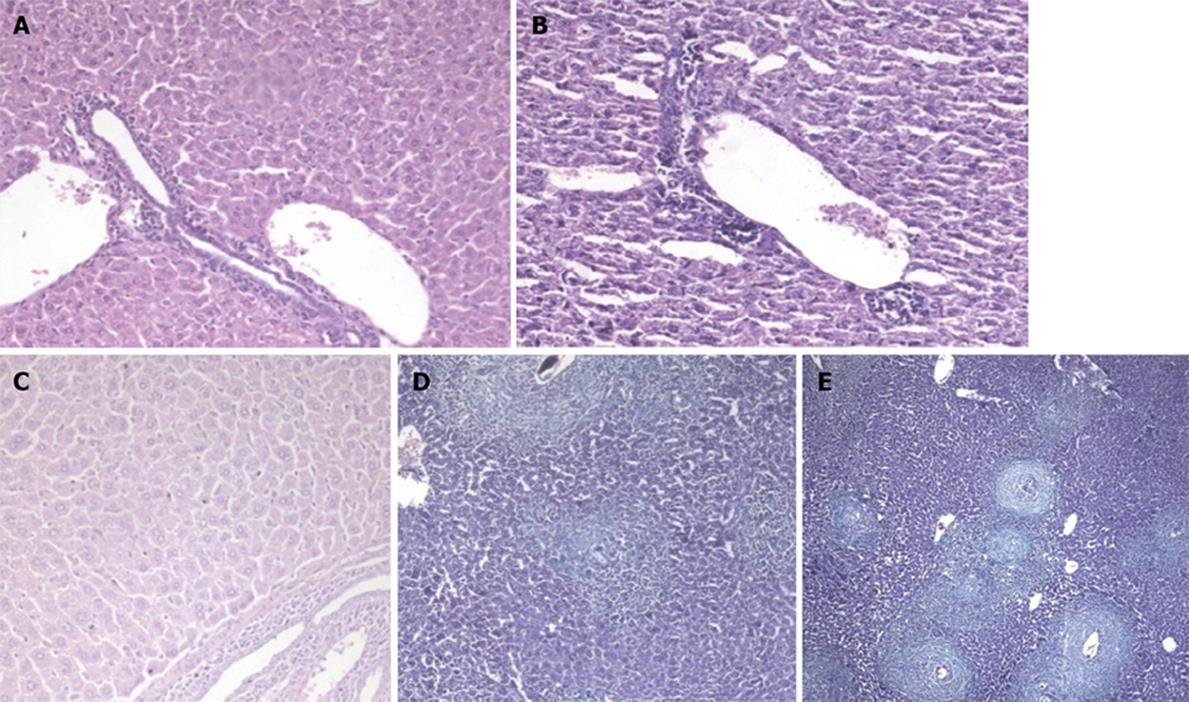
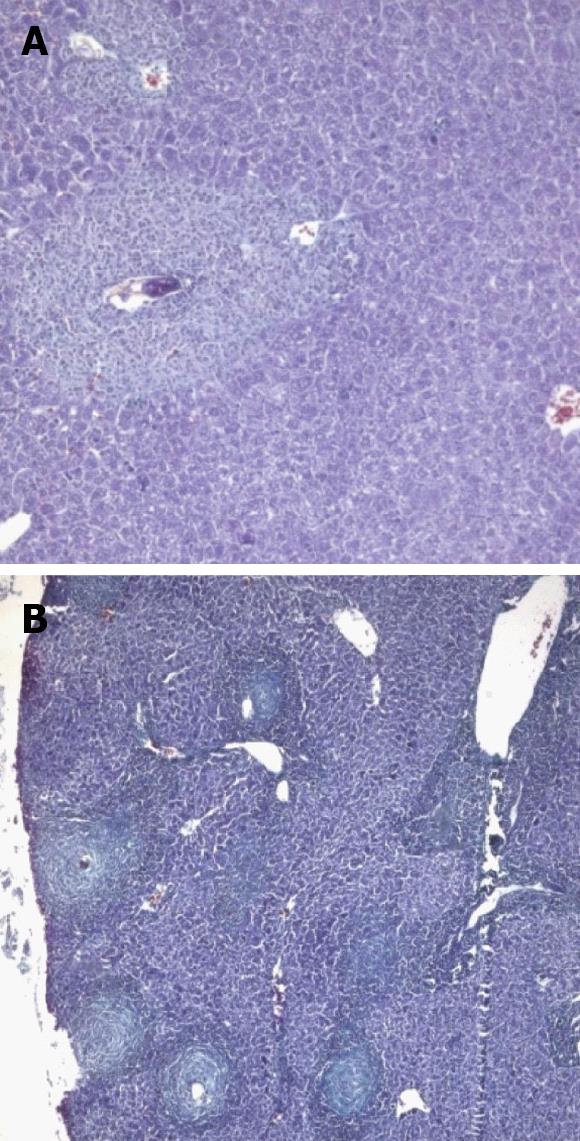
Figure 5 Animals treated 3 wk post infection and sacrificed.
A: 4 wk post infection (wpi) (H&E × 100); B: 6 wpi (Masson trichrome × 100); C: 8 wpi (Masson trichrome × 100).
Figure 6 Mice treated 5 wk post infection and sacrificed.
A: 6 wk post infection (wpi) (Masson trichrome × 200); B: 8 wpi (Masson trichrome × 100).
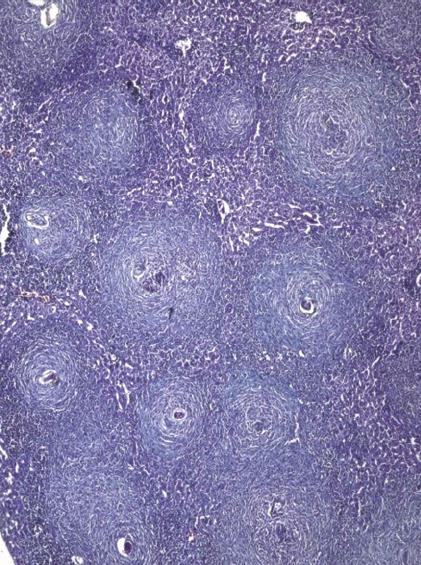
Figure 7 Mice treated at 7 wk post infection and sacrificed at 8 wk post infection showing multiple variablesized fibrocellular and fibrous lobular granulomas distorting the hepatic lobular architecture (Masson trichrome × 200).
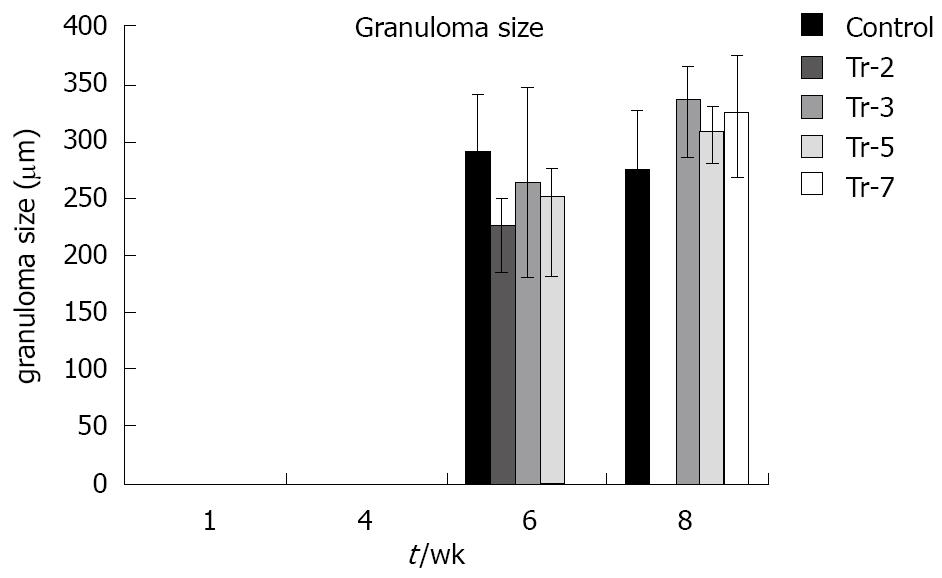
Figure 8 The effect of therapy on granuloma diameter.
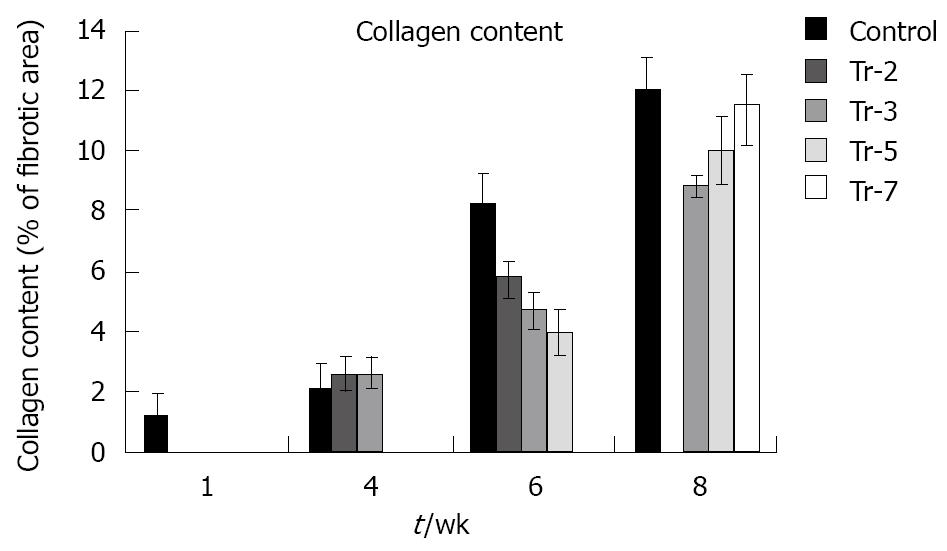
Figure 9 Effect of treatment on collagen content.
- Citation: Ghanem LY, Dahmen U, Dirsch O, Nosseir MM, Mahmoud SS, Mansour WA. Does granulocyte-colony stimulating factor administration induce damage or repair response in schistosomiasis? World J Hepatol 2010; 2(12): 434-441
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v2/i12/434.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v2.i12.434