Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2025; 17(6): 106849
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.106849
Published online Jun 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.106849
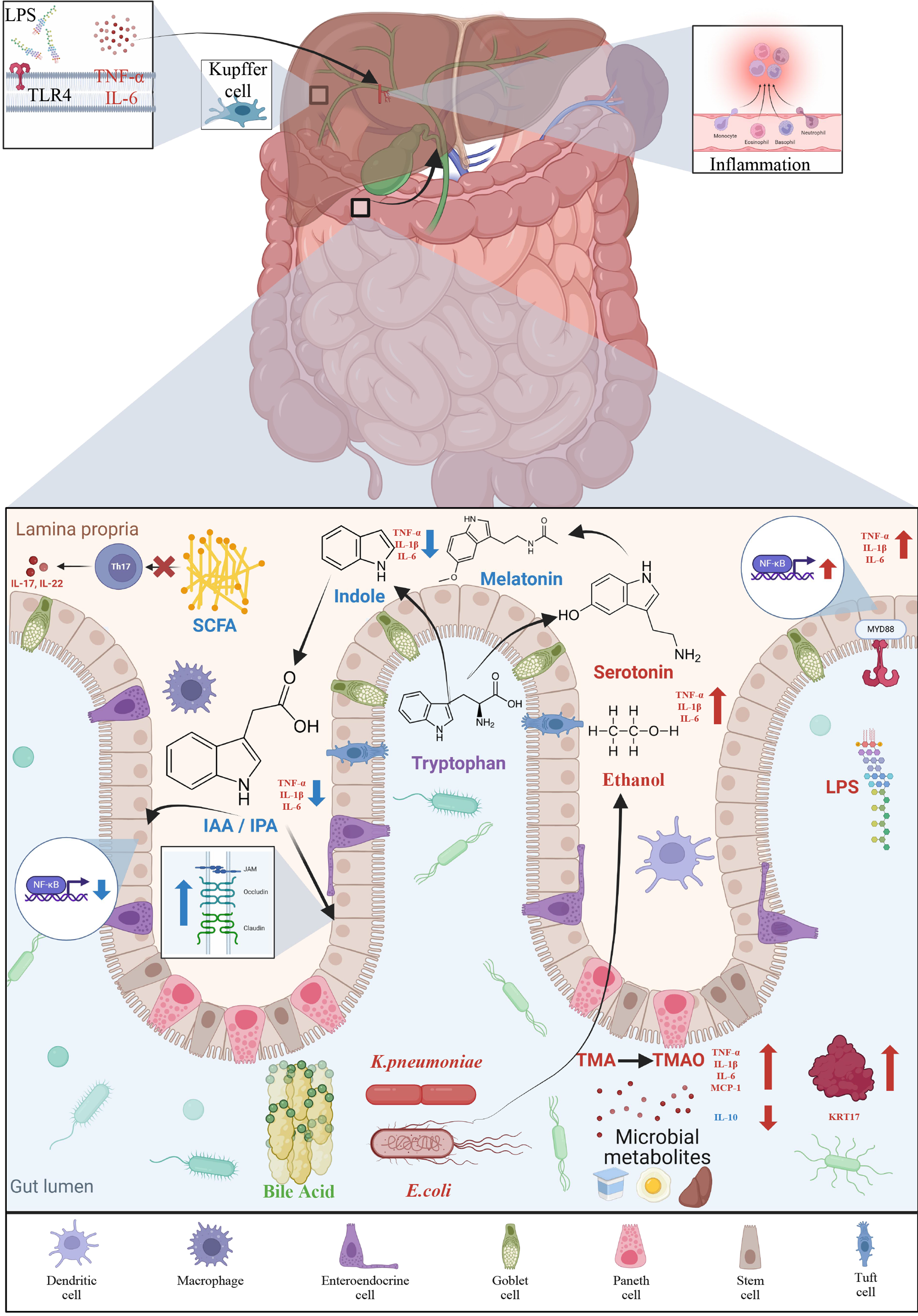
Figure 1 Gut microbiota metabolites in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease progression.
Figure created with BioRender.com. LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; TLR: Toll-like receptor; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; Th17: T helper type 17 cell; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acids; NF-κB: Nuclear factor kappa B; IAA: Indole-3-acetic acid; IPA: Indole-3-propionic acid; K. pneumoniae: Klebsiella pneumoniae; E. coli: Escherichia coli; TMA: Trimethylamine; TMAO: Trimethylamine N-oxide; MCP-1: Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.
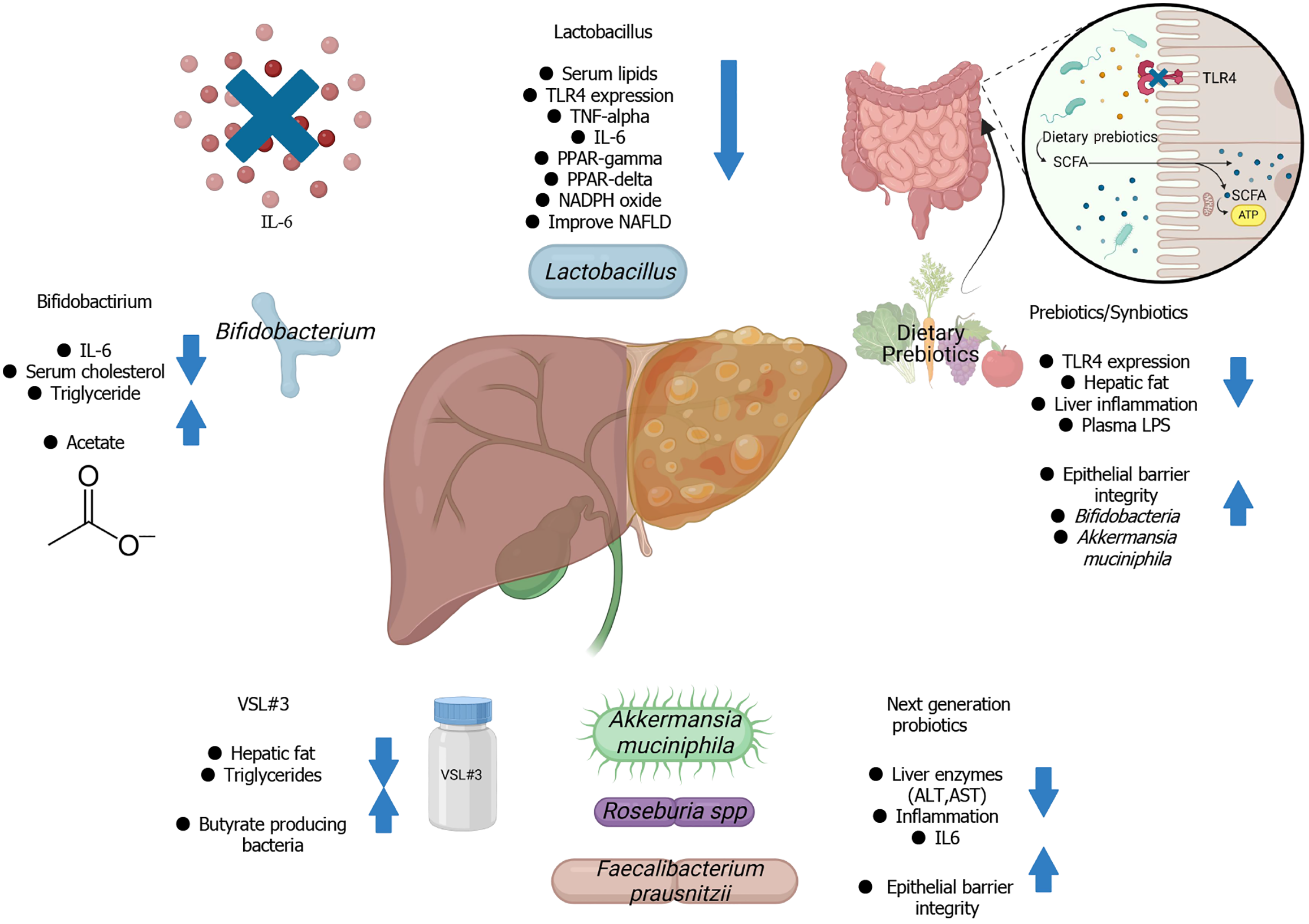
Figure 2 Microbiota-targeted therapies for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease treatment.
Figure created with BioRender.com. IL-6: Interleukin-6; TLR: Toll-like receptor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; PPAR: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor; NAFLD: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acids.
- Citation: Pandey H, Goel P, Srinivasan VM, Tang DWT, Wong SH, Lal D. Gut microbiota in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapeutics. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(6): 106849
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i6/106849.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i6.106849