Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106488
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
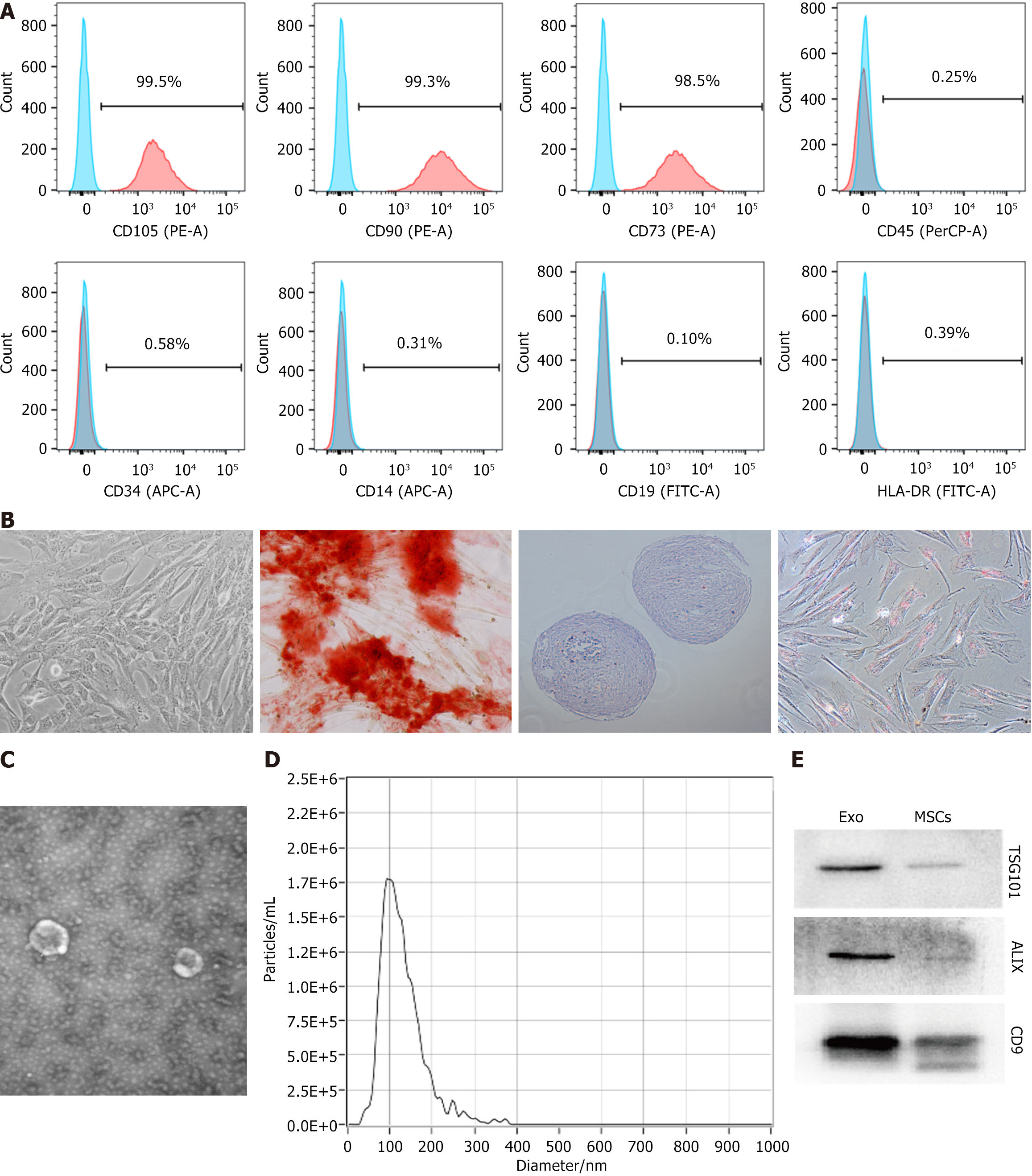
Figure 1 Identification of mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes.
A: Identification of mesenchymal stem cells surface marker proteins (CD105, CD90, CD73, D45, CD34, CD14, CD19 and HLA-DR) by flow cytometry; B: The morphology (× 100) of mesenchymal stem cells, and identification of osteogenic (× 100), chondrogenic (× 100) and adipogenic (× 100) differentiation abilities of mesenchymal stem cells; C: Electron microscopic image of exosomes; D: Particle diameter of exosomes detected by nanoparticle tracking analysis; E: Western blot assay utilized for the detection of the surface marker proteins (ALIX, tumor susceptibility gene 101 and CD9) of exosomes (n = 1). EXO: Exosomes; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; TSG101: Tumor susceptibility gene 101.
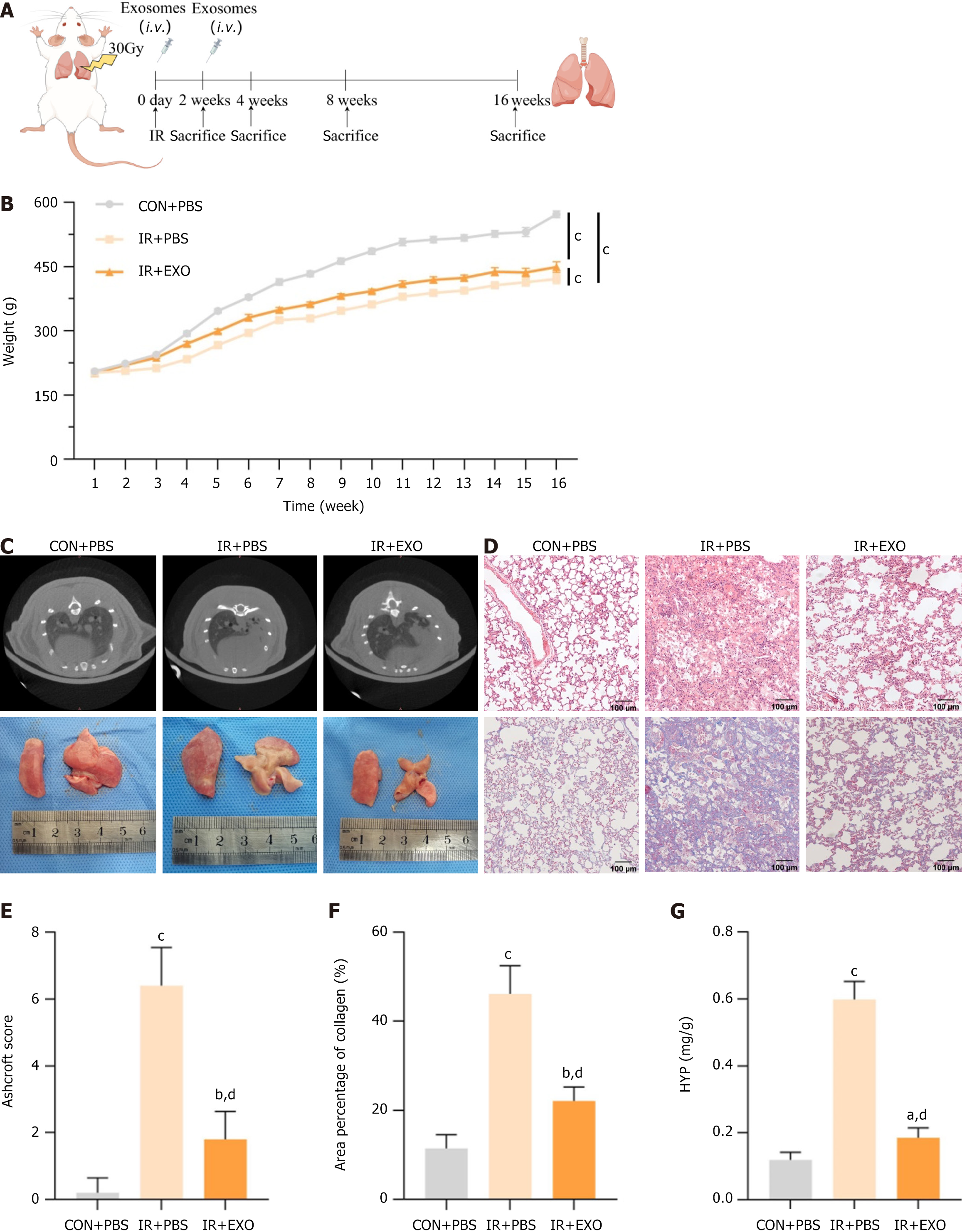
Figure 2 Therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis rats.
A: Schematic diagram of the strategy for radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats; B: Changes of body weight of rats in each group (n = 6); C: Computed tomography images of rat lungs and morphological changes in lung tissue; D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Masson staining of lung tissue among different groups; E: Quantification of fibrosis by Ashcroft score (n = 6); F: Quantification of area percentage of collagen (n = 6); G: Hydroxyproline content in lung tissues (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, bP < 0.01 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, cP < 0.0001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, dP < 0.0001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline. CON: Control; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; IR: Irradiation; EXO: Exosomes; HYP: Hydroxyproline.
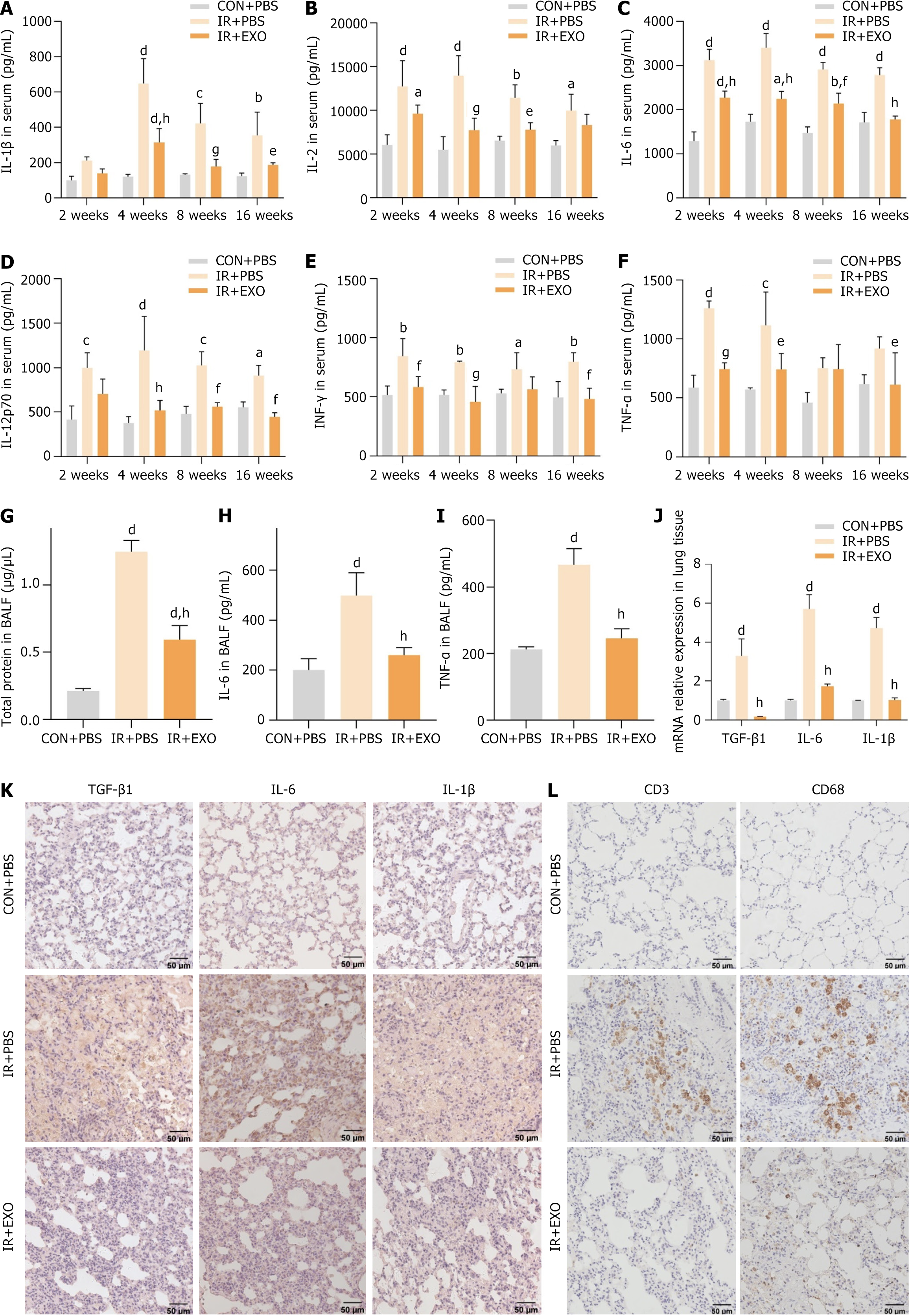
Figure 3 Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes ameliorated radiation induced inflammation in radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis rats.
A-F: Changes in the level of inflammatory cytokines [interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-12p70, interferon-γ and tumor necrosis factor-α] of serum samples collected at different time points in three groups (n = 6); G: The total protein concentration in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of rats at 16 weeks (n = 6); H and I: Changes in inflammatory factors (IL-6 and tumor necrosis factor-α) in rat bronchoalveolar lavage fluid at 16 weeks (n = 6); J: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction detection of transforming growth factor-β1, IL-6 and IL-1β mRNA levels in rat lung tissue (n = 6); K and L: Immunohistochemical staining to observe the staining intensity of transforming growth factor-β1, IL-6, IL-1β, CD3 and CD68 in rat lung tissue. aP < 0.05 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, bP < 0.01 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, cP < 0.001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, dP < 0.0001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, eP < 0.05 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, fP < 0.01 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, gP < 0.001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, hP < 0.0001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline. CON: Control; IR: Irradiation; EXO: Exosomes; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; IL: Interleukin; IFN: Interferon; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; TGF: Transforming growth factor; BALF: Bronchoalveolar lavage fluid.
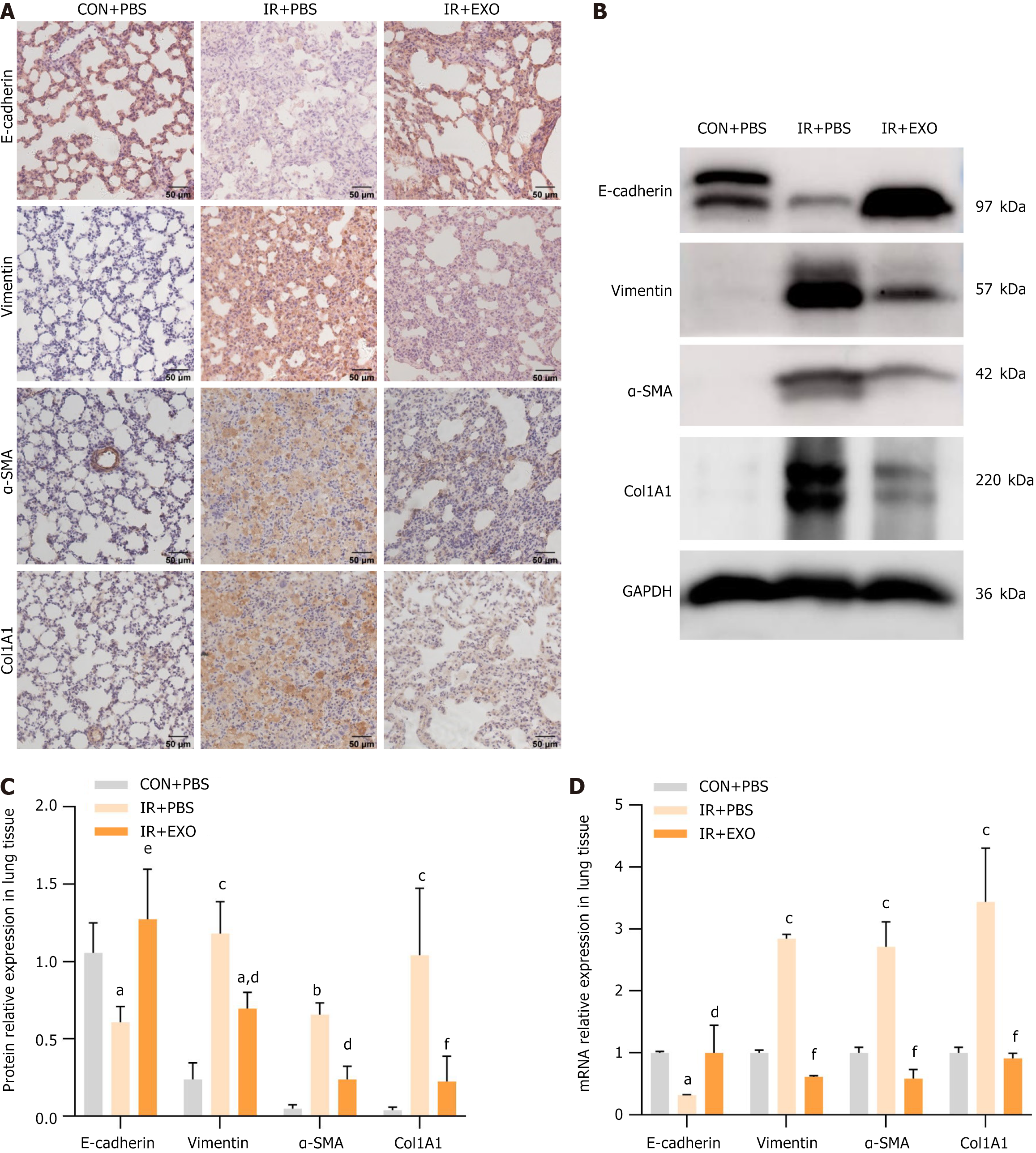
Figure 4 Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes suppressed radiation induced extracellular matrix and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis rats.
A: Immunohistochemical staining to observe the staining intensity of E-cadherin, vimentin, alpha-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) and collagen type 1 alpha 1 (COL1A1) in rat lung tissue; B and C: Western blotting detection of E-cadherin, vimentin, α-SMA and COL1A1 protein expression levels in rat lung tissue (n = 3); D: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction detection of E-cadherin, vimentin, α-SMA and COL1A1 mRNA levels in rat lung tissue (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, bP < 0.01 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, cP < 0.0001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, dP < 0.05 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, eP < 0.001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, fP < 0.0001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline. CON: Control; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; IR: Irradiation; EXO: Exosomes; α-SMA: Alpha-smooth muscle actin; COL1A1: Collagen type 1 alpha 1.
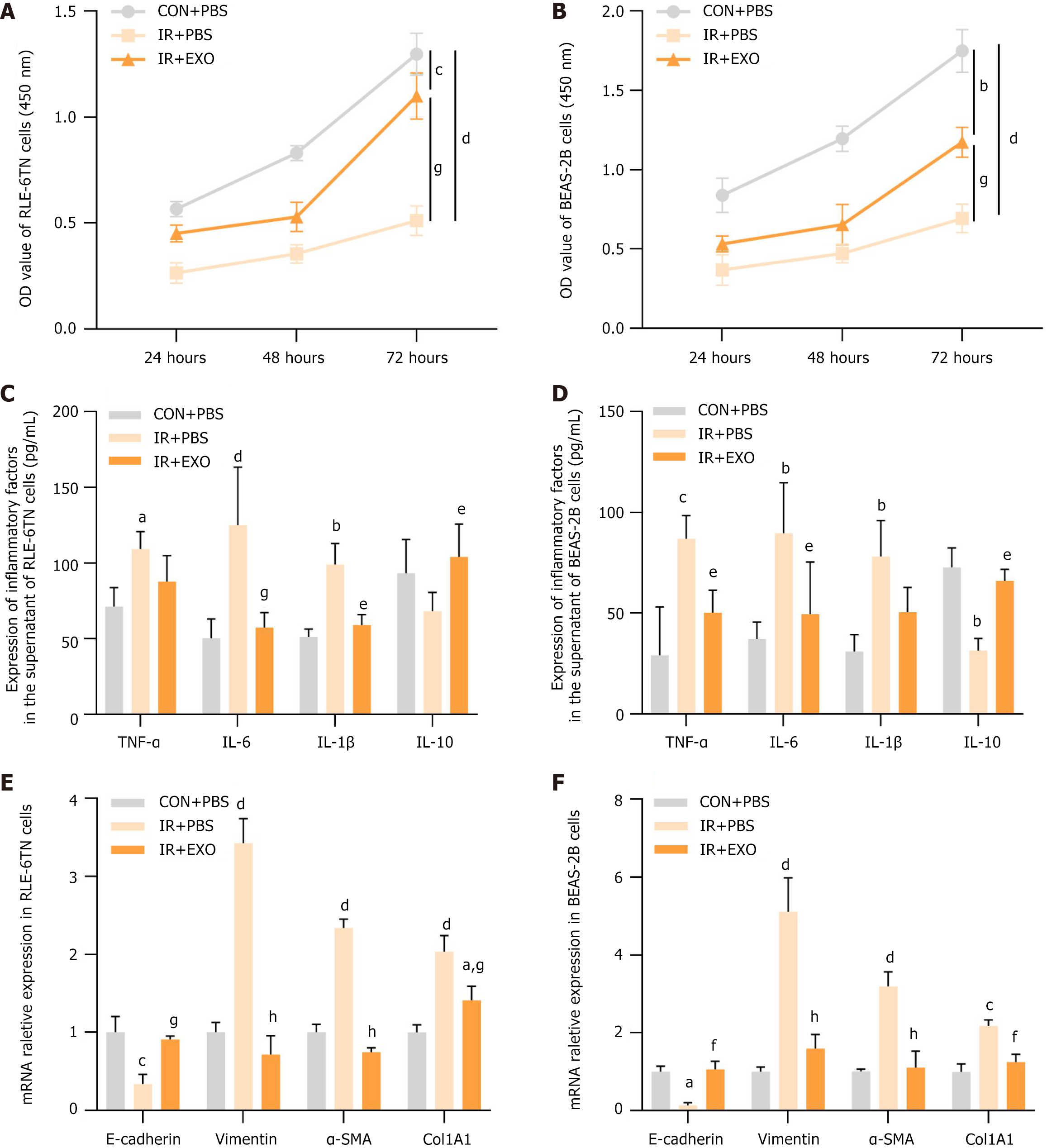
Figure 5 Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes promoted proliferation and suppressed inflammation, extracellular matrix, epithelial-mesenchymal transition in radiation induced alveolar epithelial cells.
A and B: The cell proliferations of RLE-6TN and BEAS-2B cells were detected by CCK8 assay. OD value (450 nm) was measured at 24 hours, 48 hours and 72 hours (n = 3); C and D: The secretion levels of inflammatory chemokines [tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-1β, IL-10] in the culture supernatants were measured by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (n = 3); E and F: The mRNA expressions of E-cadherin, vimentin, alpha-smooth muscle actin and collagen type 1 alpha 1 were detected by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction in RLE-6TN and BEAS-2B cells (n = 3). aP < 0.05 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, bP < 0.01 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, cP < 0.001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, dP < 0.0001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, eP < 0.05 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, fP < 0.01 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, gP < 0.001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline, hP < 0.0001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline. CON: Control; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; IR: Irradiation; EXO: Exosomes; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor; α-SMA: Alpha-smooth muscle actin; COL1A1: Collagen type 1 alpha 1.
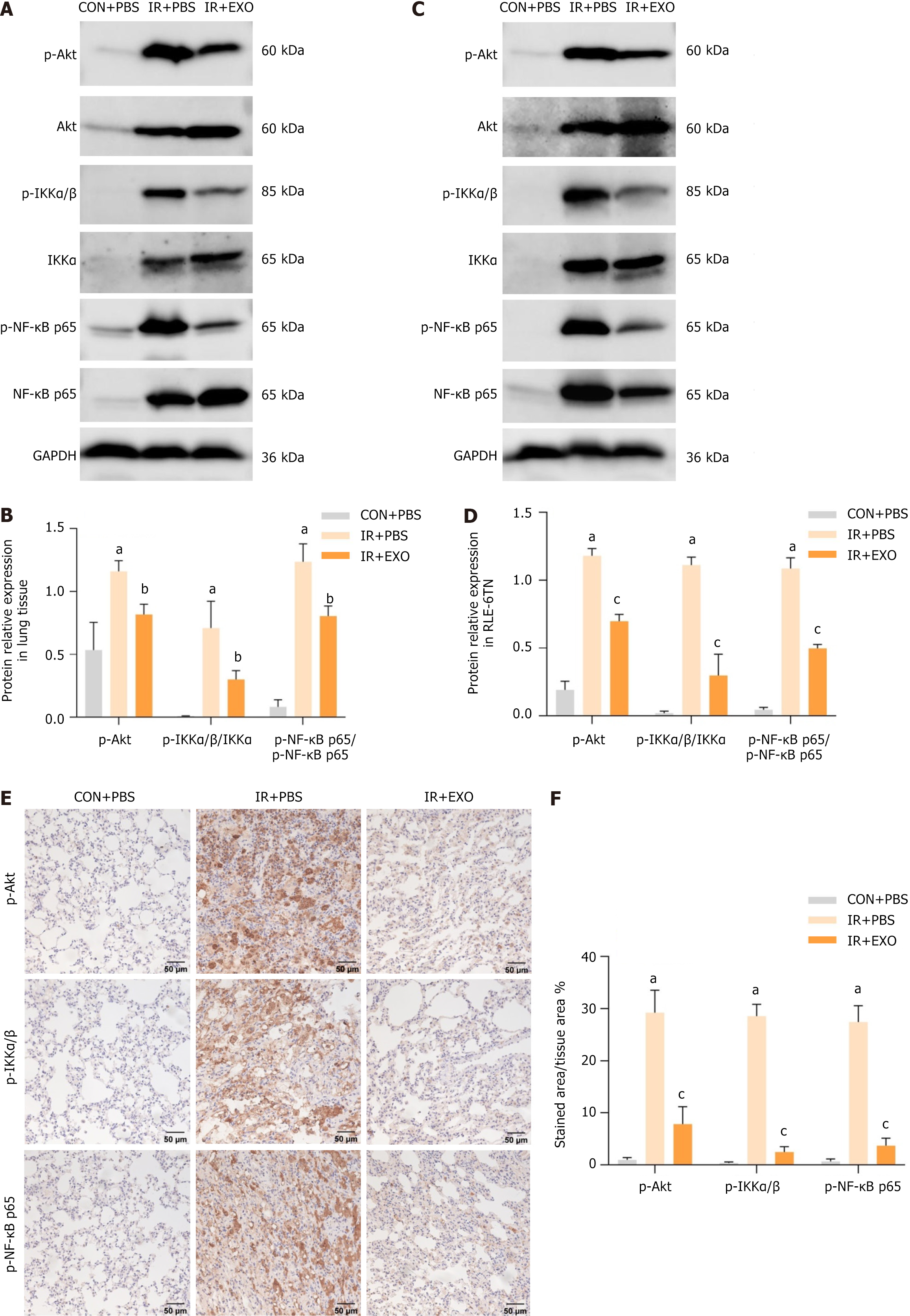
Figure 6 Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes inhibited protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B signaling in radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis.
A-D: Western blot analysis of protein kinase B (Akt)/nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway expression levels in rat lung tissue at 16 weeks (n = 3) (A and B); western blot analysis of Akt/NF-κB signaling pathway expression levels in RLE-6TN cells (n = 3) (C and D); E and F: Immunohistochemistry was used to determine the staining intensity of p-Akt, p-IkappaB kinase α/β and p-NF-κB p65 in rat lung tissue at 16 weeks (n = 6). aP < 0.0001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, bP < 0.01 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, cP < 0.0001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline. CON: Control; IR: Irradiation; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; EXO: Exosomes; Akt: Protein kinase B; IKK: IkappaB kinase; NF-κB: Kinase nuclear factor kappa B.
- Citation: Wang LL, Ouyang MY, Yang ZE, Xing SN, Zhao S, Yu HY. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B pathway. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(6): 106488
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i6/106488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488