Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106488
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
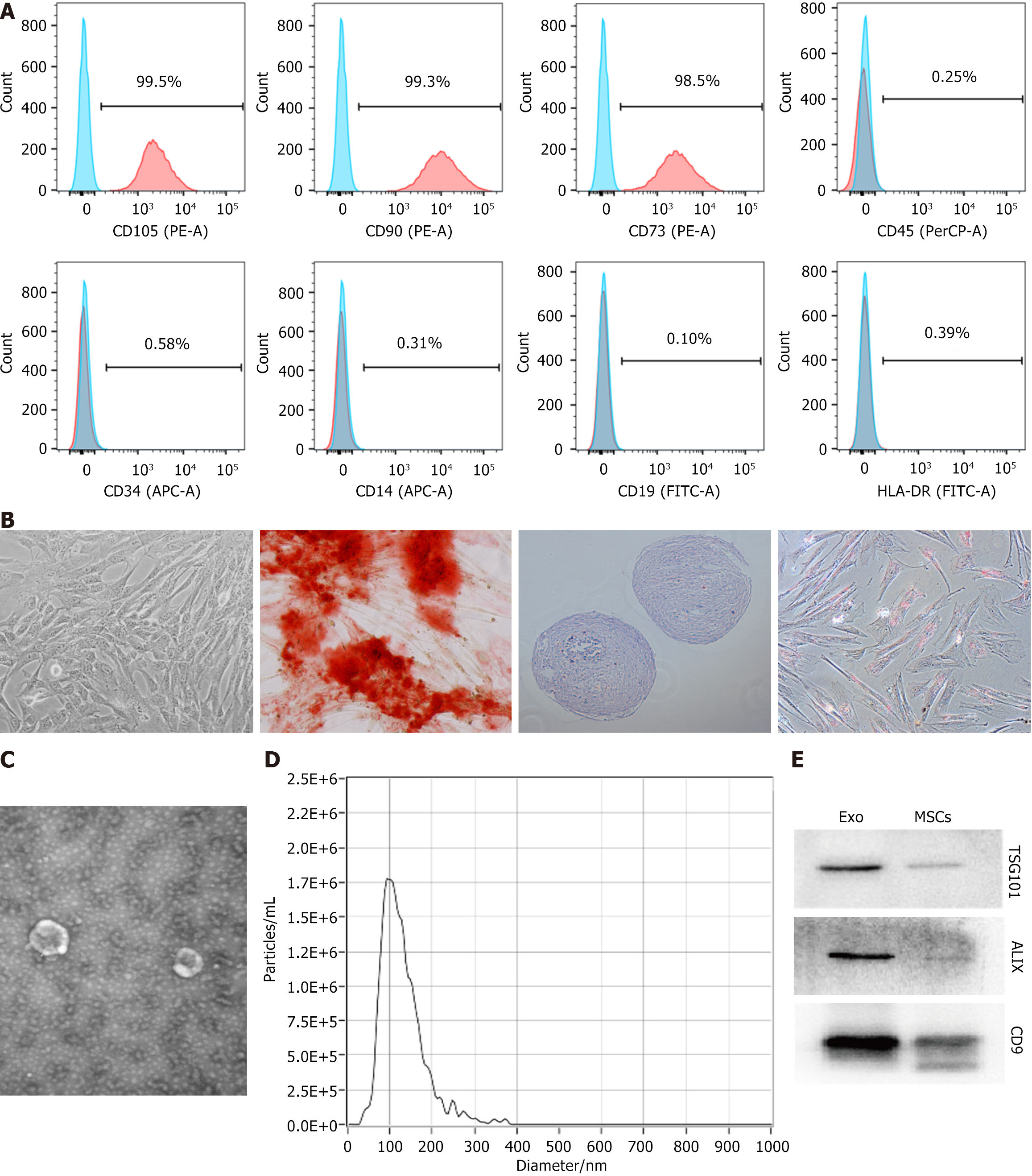
Figure 1 Identification of mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes.
A: Identification of mesenchymal stem cells surface marker proteins (CD105, CD90, CD73, D45, CD34, CD14, CD19 and HLA-DR) by flow cytometry; B: The morphology (× 100) of mesenchymal stem cells, and identification of osteogenic (× 100), chondrogenic (× 100) and adipogenic (× 100) differentiation abilities of mesenchymal stem cells; C: Electron microscopic image of exosomes; D: Particle diameter of exosomes detected by nanoparticle tracking analysis; E: Western blot assay utilized for the detection of the surface marker proteins (ALIX, tumor susceptibility gene 101 and CD9) of exosomes (n = 1). EXO: Exosomes; MSCs: Mesenchymal stem cells; TSG101: Tumor susceptibility gene 101.
- Citation: Wang LL, Ouyang MY, Yang ZE, Xing SN, Zhao S, Yu HY. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B pathway. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(6): 106488
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i6/106488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488