Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Stem Cells. Jun 26, 2025; 17(6): 106488
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
Published online Jun 26, 2025. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488
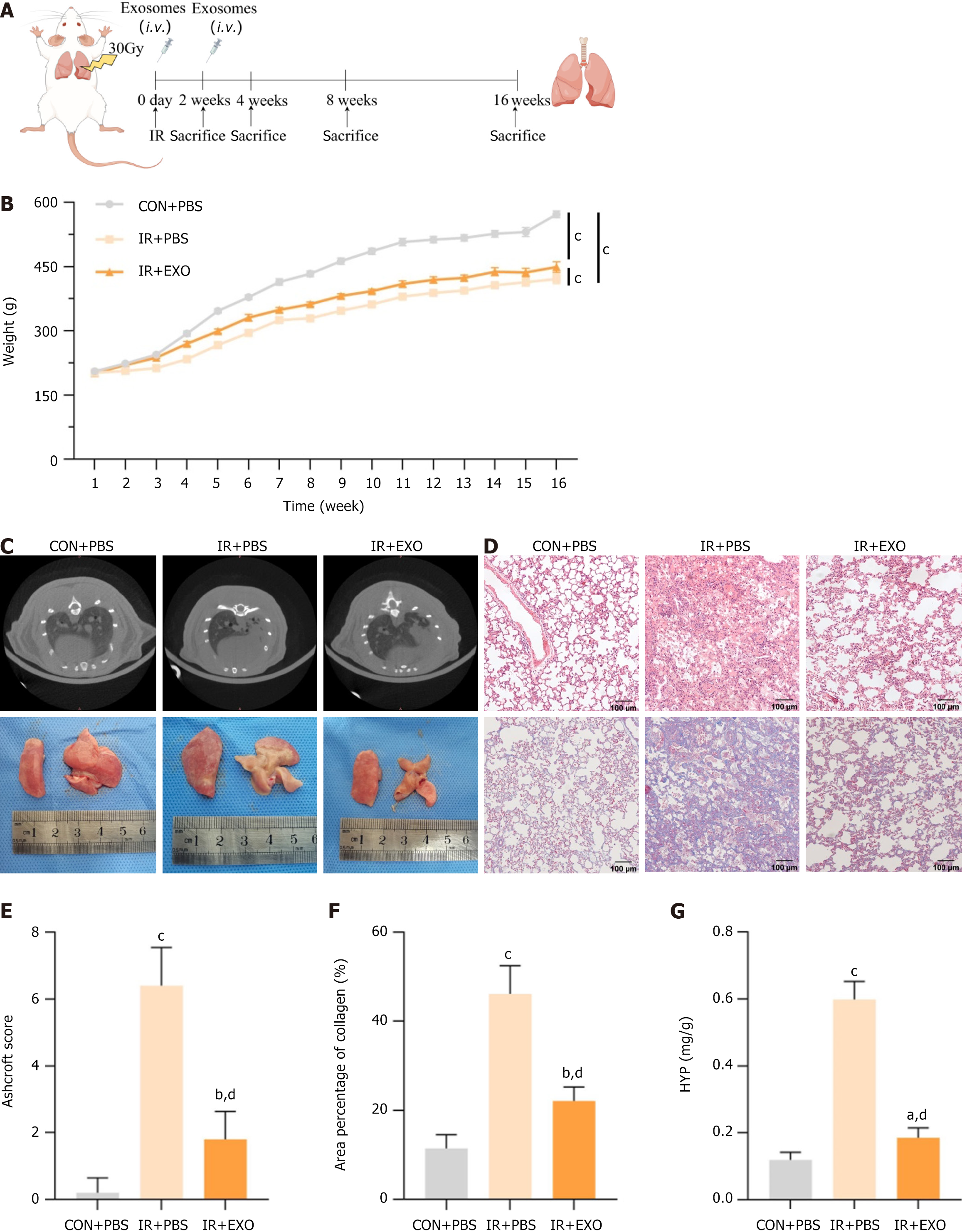
Figure 2 Therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes in radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis rats.
A: Schematic diagram of the strategy for radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats; B: Changes of body weight of rats in each group (n = 6); C: Computed tomography images of rat lungs and morphological changes in lung tissue; D: Hematoxylin and eosin staining and Masson staining of lung tissue among different groups; E: Quantification of fibrosis by Ashcroft score (n = 6); F: Quantification of area percentage of collagen (n = 6); G: Hydroxyproline content in lung tissues (n = 6). aP < 0.05 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, bP < 0.01 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, cP < 0.0001 vs control + phosphate buffered saline, dP < 0.0001 vs irradiation + phosphate buffered saline. CON: Control; PBS: Phosphate buffered saline; IR: Irradiation; EXO: Exosomes; HYP: Hydroxyproline.
- Citation: Wang LL, Ouyang MY, Yang ZE, Xing SN, Zhao S, Yu HY. Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes alleviate radiation induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the protein kinase B/nuclear factor kappa B pathway. World J Stem Cells 2025; 17(6): 106488
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-0210/full/v17/i6/106488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4252/wjsc.v17.i6.106488