Copyright
©The Author(s) 2001.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2001; 7(4): 496-499
Published online Aug 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i4.496
Published online Aug 15, 2001. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v7.i4.496
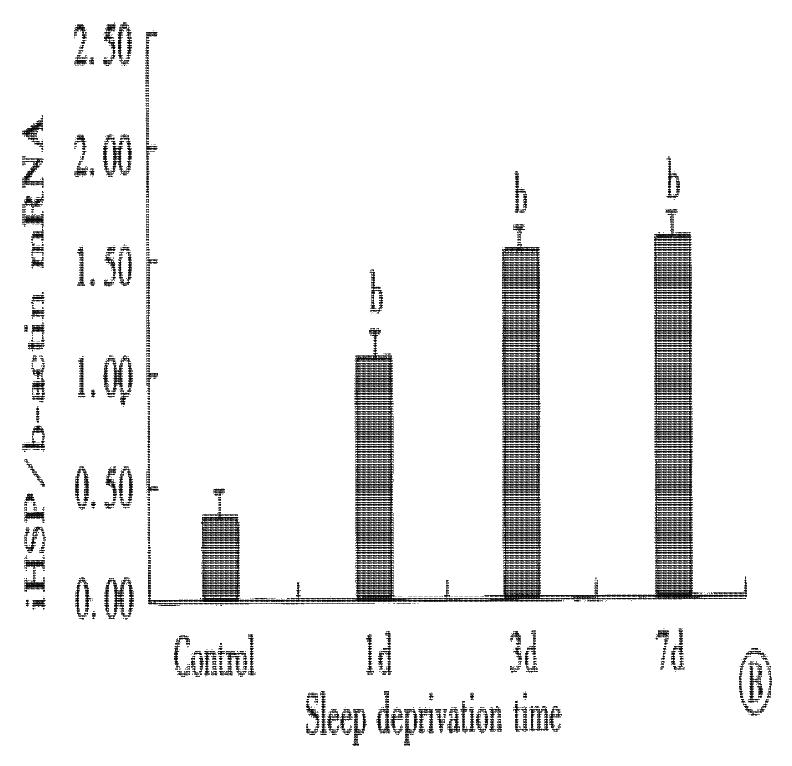
Figure 1 Effect of sleep deprivation in inducible heat shock protein 70 mRNA expression in gastric mucosa of rats.
Inducible heat shock protein 70 mRNA was determined by RT-PCR. (A). Gel photograph of PCR-amplified inducible heat shock protein 70 and β-actin cDNA derived from inducible heat shock protein 70 and β-actin mRNA. Lane 1: normal control; Lane 2: 1 d sleep deprivation; Lane 3: 3 d sleep deprivation; Lane 4: 7 d sleep deprivation. (B). Bar graph showing the relative amount of inducible heat shock protein 70 mRNA quantified by densitometry and expressed as mean of inducible heat shock protein 70 mRNA: β-actin mRNA ratios. Error bars represent SE, n = 8 for each group. bP < 0.01 vs control group.
Figure 2 Western blotting analysis of inducible heat shock protein 70 from gastric mucosa of sleep deprivation rats.
Lane 1 and 2: control; Lane 3 and 4: 1 d sleep deprivation; Lane 5 and 6: 3 d sleep deprivation; Lane 7 and 8: 7 d sleep deprivation.
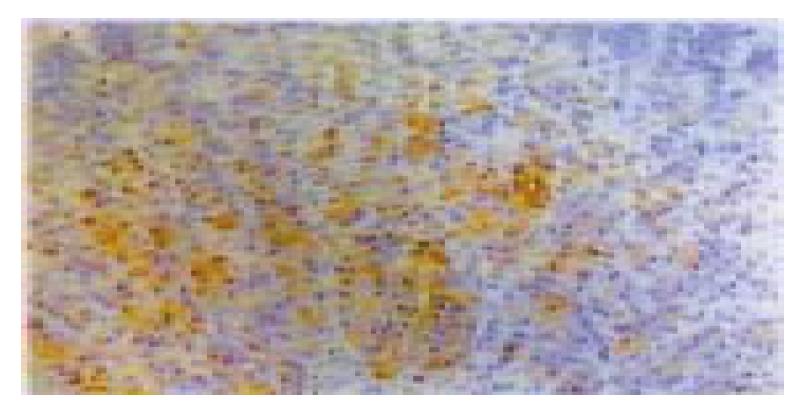
Figure 3 Inducible heat shock protein 70 immunohistochemistry in gastric mucosa of rats with 7 d sleep deprivation.
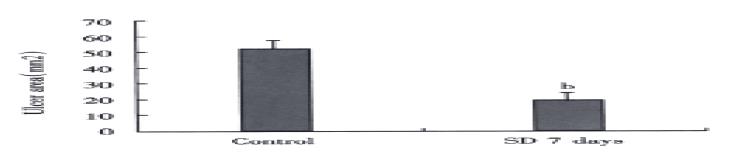
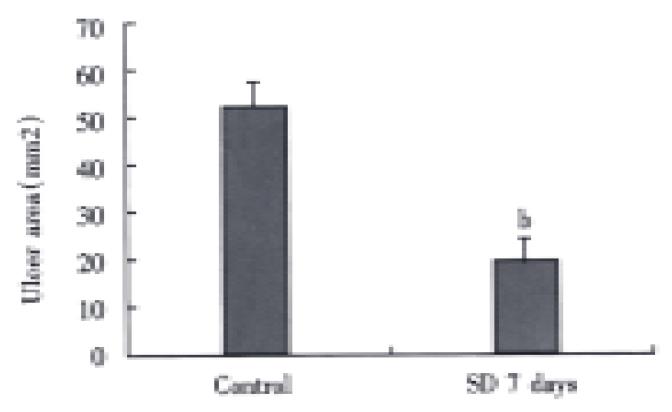
Figure 4 Effect of sleep deprivation in ethanol induced (50% ethanol 1 mL p.
o. for 2 h) gastric ulceration in rats. Error bars represent SE, n = 10 for each group. bP < 0.01 vs control group.
- Citation: Shen XZ, Koo MW, Cho CH. Sleep deprivation increase the expression of inducible heat shock protein 70 in rat gastric mucosa. World J Gastroenterol 2001; 7(4): 496-499
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v7/i4/496.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v7.i4.496