Copyright
©The Author(s) 2000.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 15, 2000; 6(4): 465-469
Published online Aug 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i4.465
Published online Aug 15, 2000. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v6.i4.465
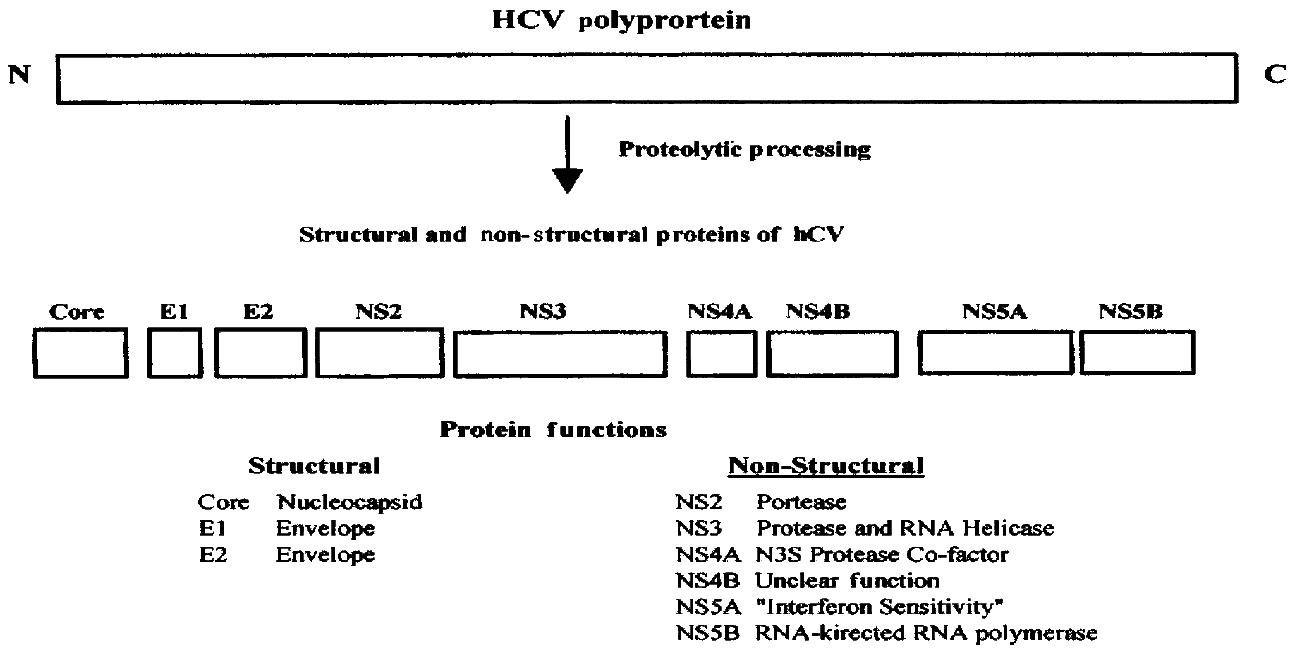
Figure 1 HCV proteins and their functions.
The positive-stranded RNA of about 10000 nuc leotides is translated into a polyprotein of approximately 3000 amino acids. The polyprotein is proteolytically cleaved into several smaller proteins. Core, E1, and E2 are structural polypeptides. Core protein is the virus nucleocapsid and E 1 and E2 are viral envelope proteins. A small polypeptide known as P7 (not shown ) is also produced by additional cleavage between E2 and NS2. The major non-str uctural proteins are NS2, NS3, NS4, and NS5. NS4 is further processed into NS4A a nd NS4B and NS5 into NS5A and NS5B. NS2 and part of NS3 are proteases that proce ss the viral polyprotein. NS3 also has RNA-helicase activity. NS4A is a cofacto r for the NS3 protease and NS5B is an RNA-dependent, RNA polymerase. The functi ons of NS4B and NS5A are less well understood but NS5A is thought to play a role in determining sensitivity to interferon.
- Citation: Worman HJ, Lin F. Molecular biology of liver disorders: the hepatitis C virus and molecular targets for drug development. World J Gastroenterol 2000; 6(4): 465-469
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v6/i4/465.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v6.i4.465