Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2025; 31(30): 109187
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109187
Published online Aug 14, 2025. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109187
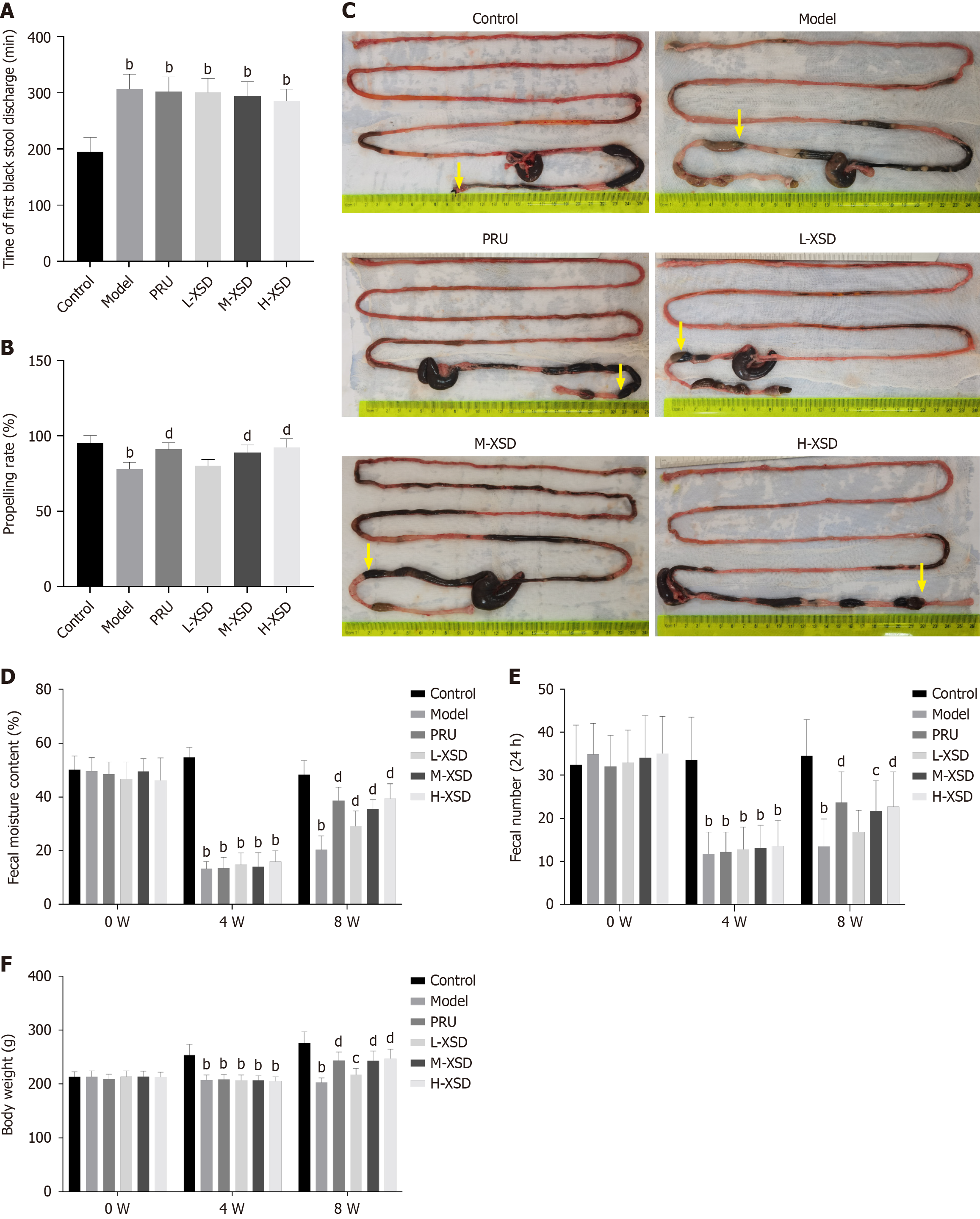
Figure 1 Improvement in slow transit constipation symptoms with Xuanshen decoction treatment.
A: Time of first black stool discharge (week 4, n = 15); B: Intestinal propelling rate (week 8, n = 15); C: Intestinal propelling length of carbon: The yellow arrow marks the distance to the end of the carbon; D: Fecal moisture content (n = 15); E: Fecal number (n = 15); F: Body weight (n = 15). Data were presented as mean ± SD. bP < 0.01 vs control, cP < 0.05 vs model, and dP < 0.01 vs model. PRU: Prucalopride; L-XSD: Low-dose Xuanshen decoction; M-XSD: Medium-dose Xuanshen decoction; H-XSD: High-dose Xuanshen decoction.
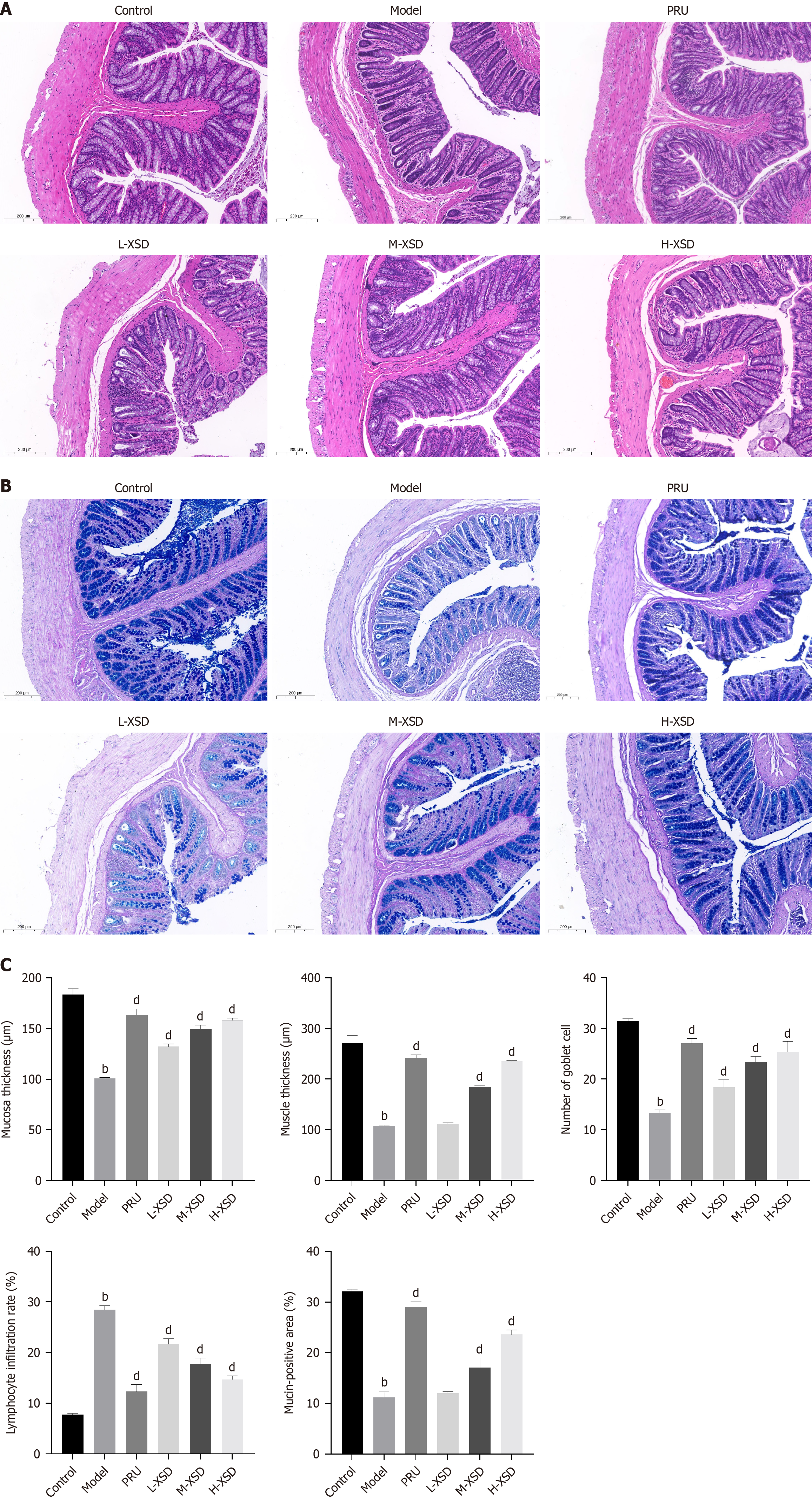
Figure 2 Hematoxylin and eosin and Alcian blue/periodic acid-Schiff staining results.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining; B: AB-PAS staining; C: Detection parameters (n = 3). bP < 0.01 vs control, and dP < 0.01 vs model. PRU: Prucalopride; L-XSD: Low-dose Xuanshen decoction; M-XSD: Medium-dose Xuanshen decoction; H-XSD: High-dose Xuanshen decoction.
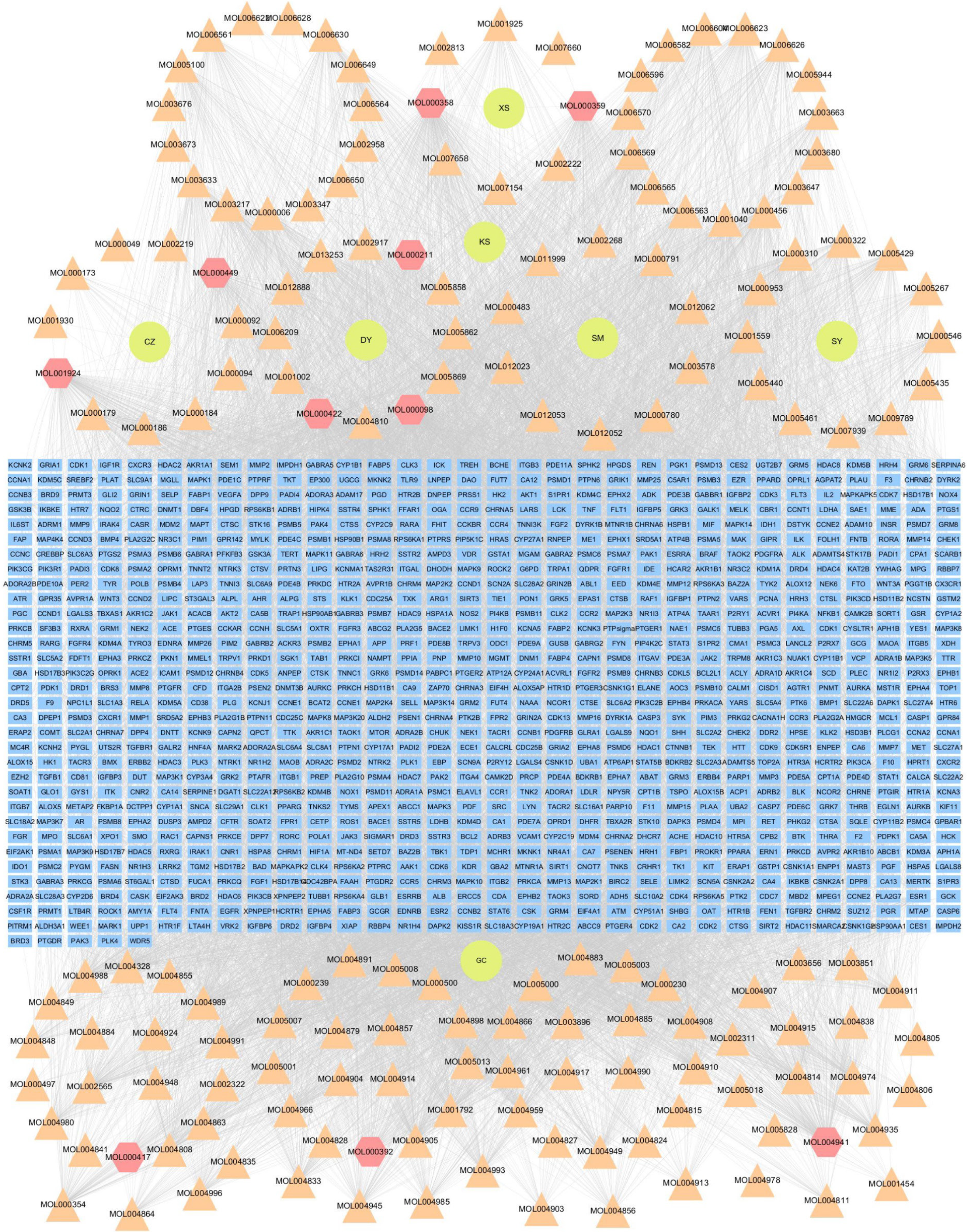
Figure 3 Herb-compound-target interaction network.
The yellow-green circle nodes symbolized the seven herbs of Xuanshen decoction; the triangular and hexagonal nodes symbolized the components; the hexagonal nodes symbolized the shared components of the herbs; the blue quadrilateral nodes denoted the target. MOL000422 and MOL000211 were the common compounds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis and Sanguisorba officinalis; MOL000392, MOL000417, and MOL004941 were the common compounds of Glycyrrhiza uralensis and Sophora flavescens; MOL001924 was the component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis and Cimicifuga heracleifolia; MOL000098 was the common component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Sanguisorba officinalis, Sophora flavescens; MOL000359 was the common component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Cimicifuga heracleifolia, and Scrophularia ningpoensis; MOL000449 was the common compound of Cimicifuga heracleifolia, Dioscorea polystachya, and Atractylodes lancea; MOL000358 was the common component of Glycyrrhiza uralensis, Sanguisorba officinalis, Dioscorea polystachya, and Scrophularia ningpoensis. XS: Scrophularia ningpoensis, KS: Sophora flavescens; CZ: Atractylodes lancea; DY: Sanguisorba officinalis; SM: Cimicifuga heracleifolia; SY: Dioscorea polystachya; GC: Glycyrrhiza uralensis; XSD: Xuanshen decoction.
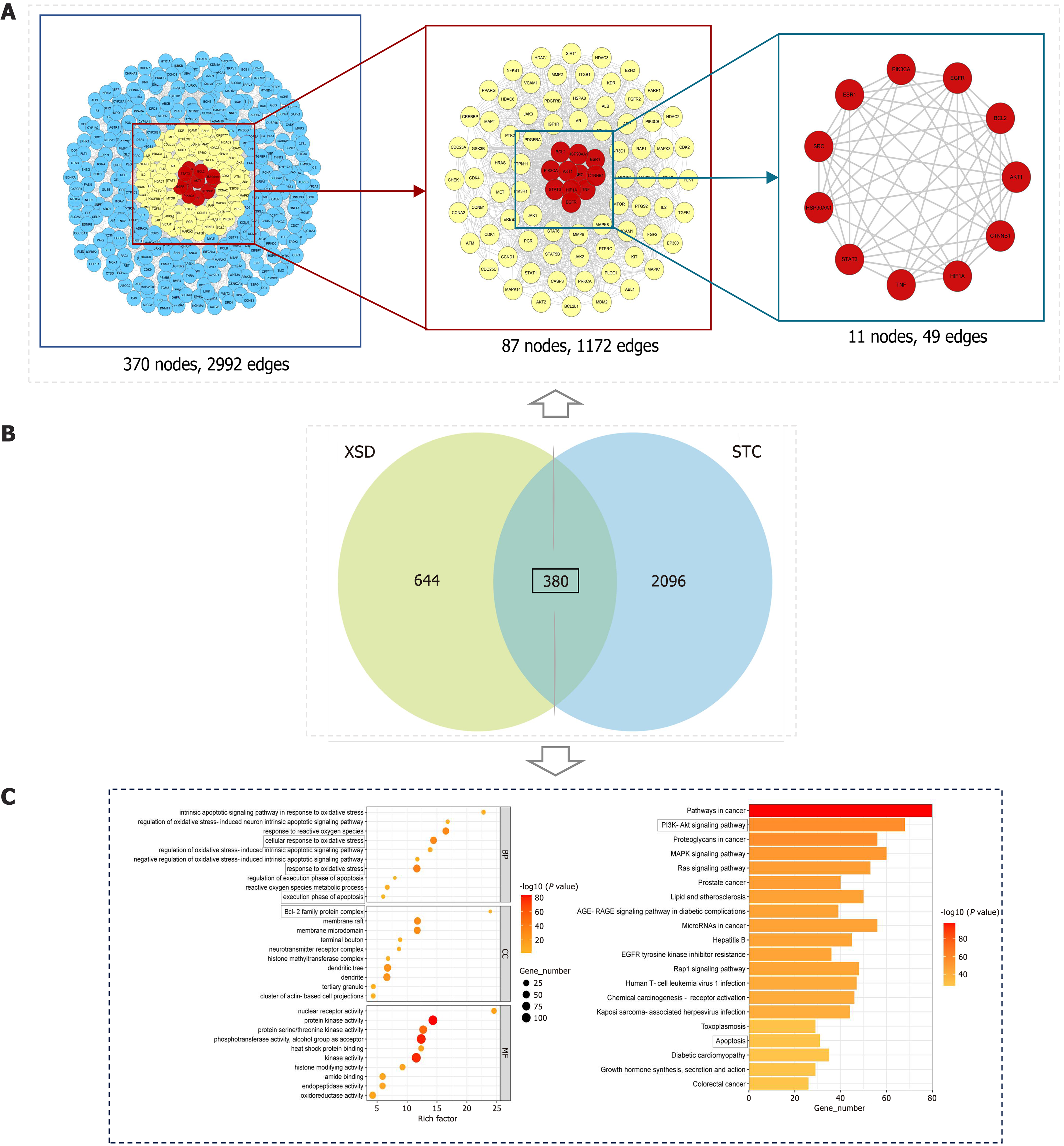
Figure 4 Network pharmacology flowchart.
A: Protein-protein interaction network construction and detection of Xuanshen decoction-slow transit constipation target genes; B: Venn diagram demonstrating the shared targets of Xuanshen decoction and slow transit constipation; C: Enrichment analysis. XSD: Xuanshen decoction; STC: Slow transit constipation.
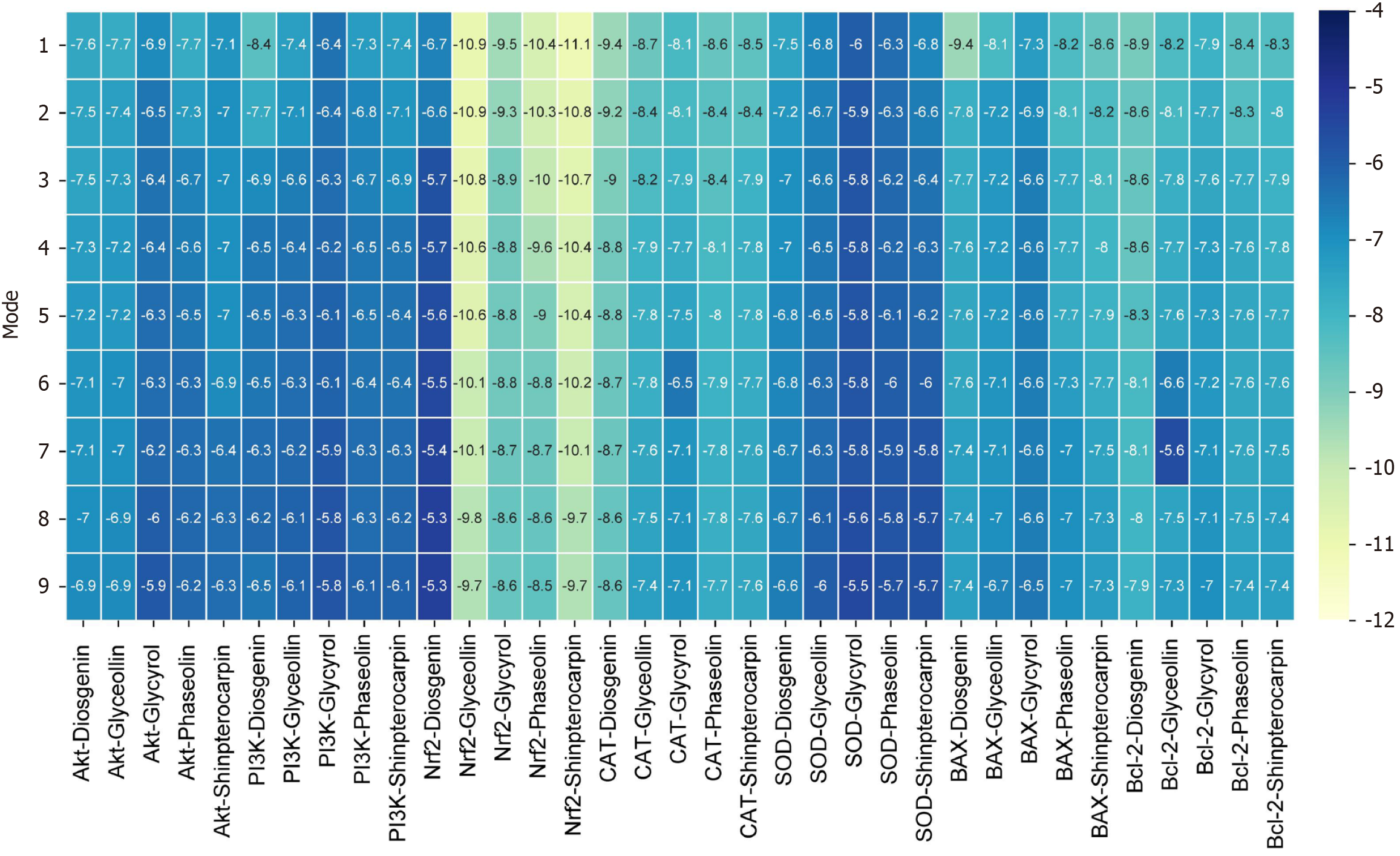
Figure 5 Schematic diagram of the binding energy of components and targets.
Mode: The coordination mode; Affinity: The binding energy; Akt: Protein kinase B; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; CAT: Catalase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase; BAX: B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein; Bcl2: B-cell lymphoma 2.
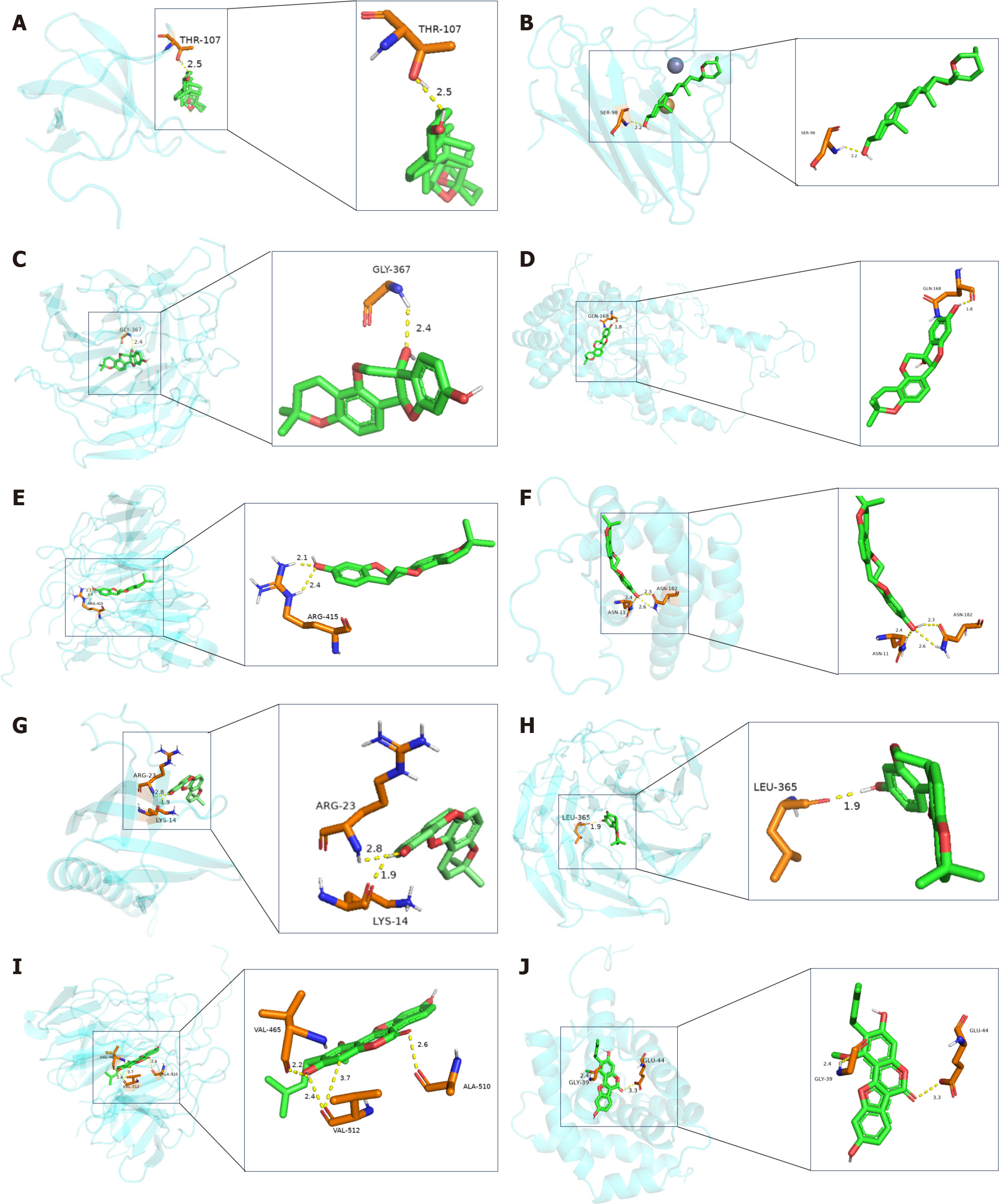
Figure 6 Molecular docking and visualization.
A: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase and diosgenin; B: Superoxide dismutase and diosgenin; C: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and glyceollin; D: Catalase and glyceollin; E: Nrf2 and shinpterocarpin; F: B-cell lymphoma 2 and shinpterocarpin; G: Protein kinase B and phaseolin; H: Nrf2 and phaseolin; I: Nrf2 and glycyrol; J: B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein and glycyrol.
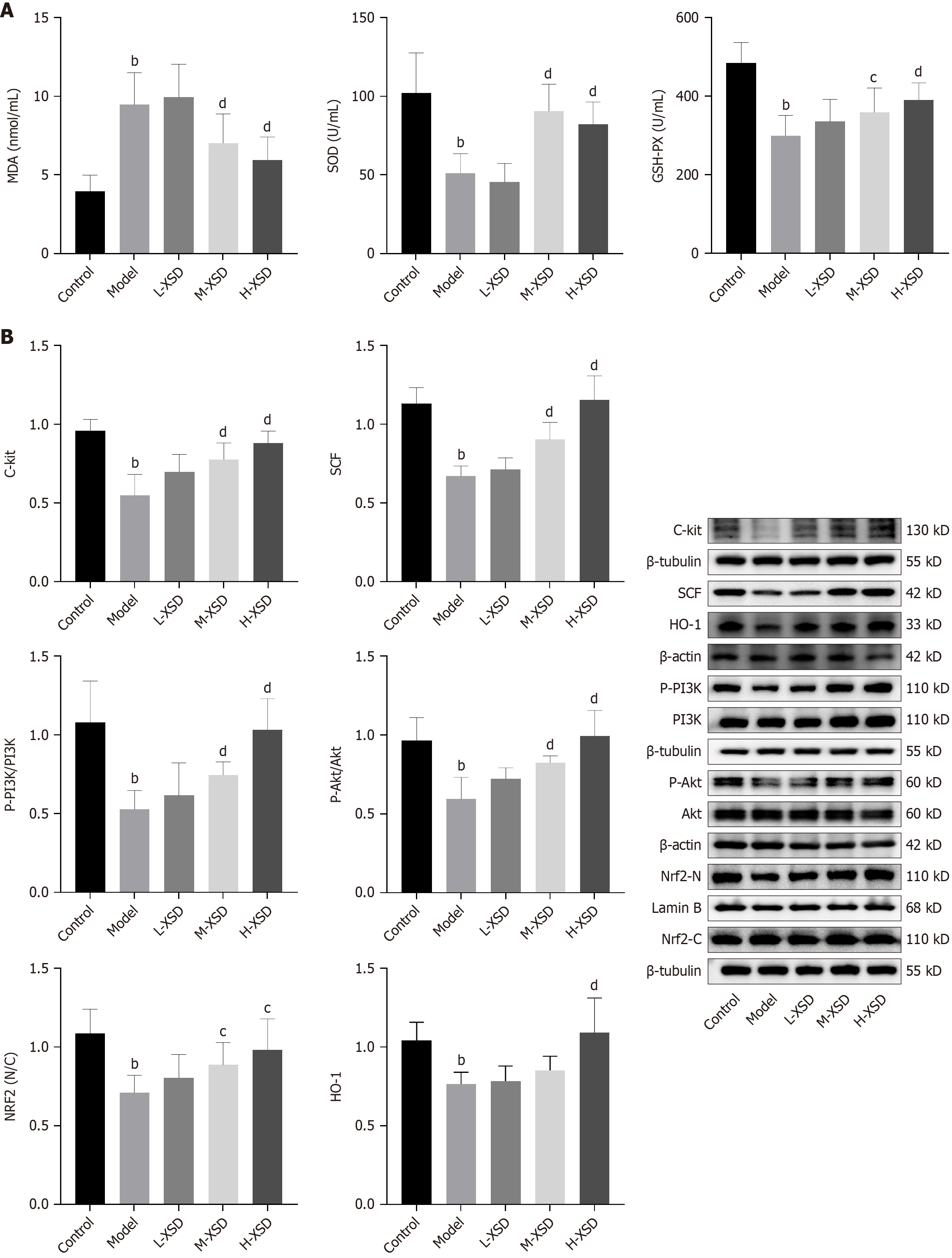
Figure 7 Impact of Xuanshen decoction on oxidative stress and phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 pathway in slow transit constipation Rats.
A: The oxidative stress level (n = 15); B: Western blotting (n = 6). bP < 0.01 vs control, cP < 0.05 vs model, and dP < 0.01 vs model. L-XSD: Low-dose Xuanshen decoction; M-XSD: Medium-dose Xuanshen decoction; H-XSD: High-dose Xuanshen decoction; GSH-PX: Glutathione peroxidase; C-KIT: Tyrosine-protein kinase Kit; SCF: Stem cell factor; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; P-PI3K: Phospho-phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; P-Akt: Phospho-Protein kinase B; Akt: Protein kinase B; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Nrf2-N: Nuclear-nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; Nrf2-C: Cytoplasmic nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2.
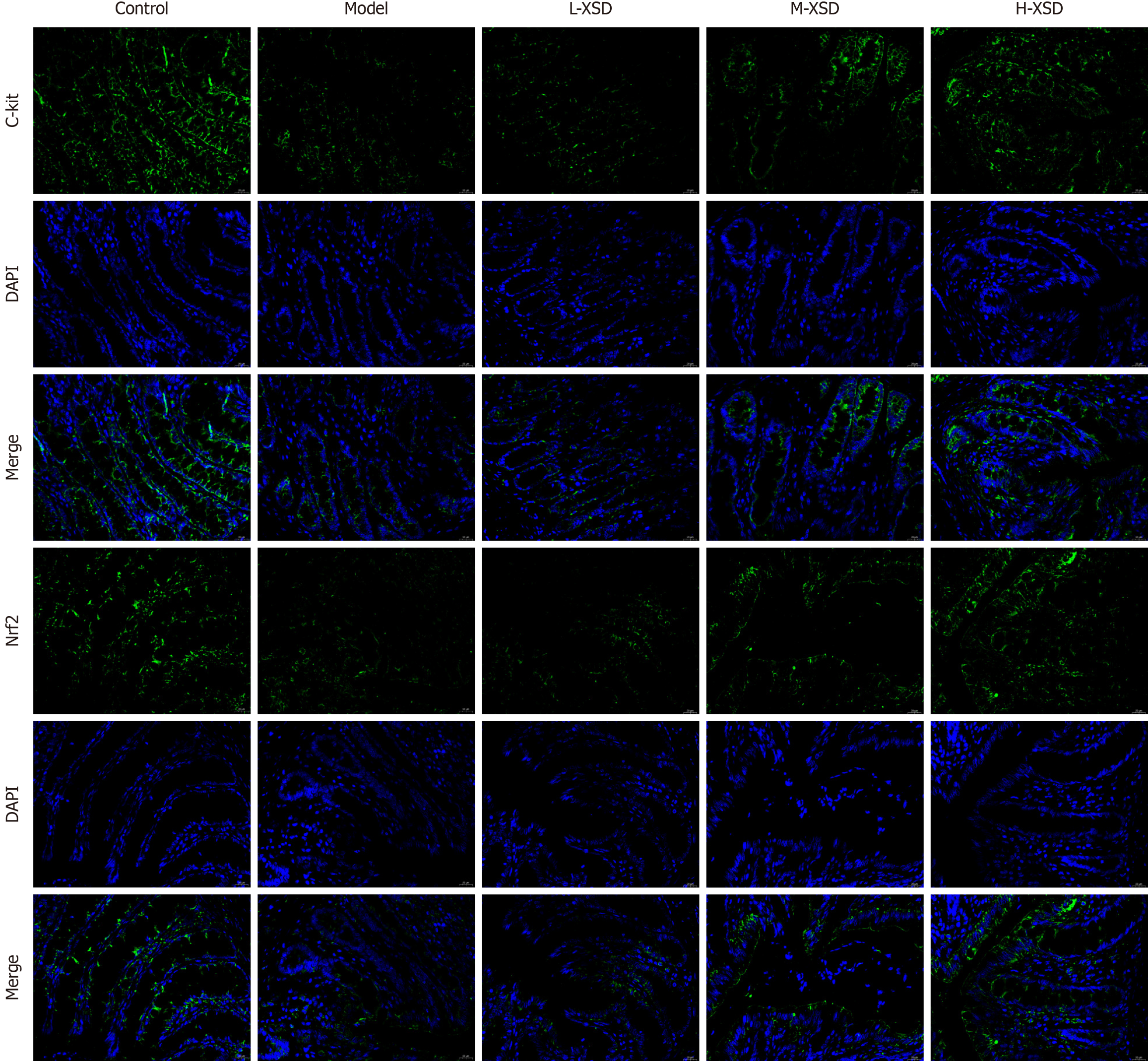
Figure 8 Immunofluorescence staining.
DAPI: 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole; Nrf2: Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2; L-XSD: Low-dose Xuanshen decoction; M-XSD: Medium-dose Xuanshen decoction; H-XSD: High-dose Xuanshen decoction.
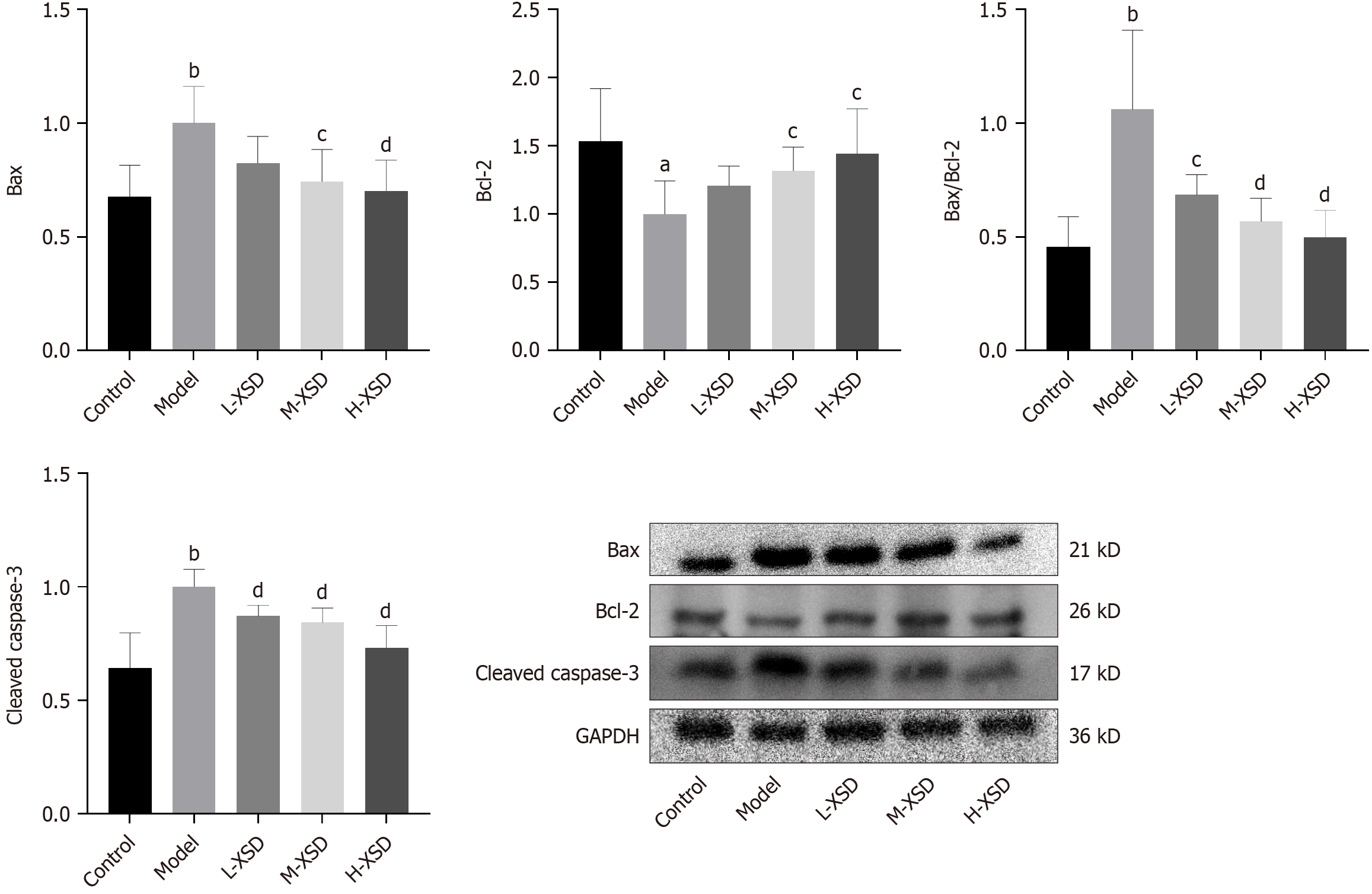
Figure 9 Apoptosis-related proteins in colonic tissues (n = 6).
aP < 0.05 vs control, bP < 0.01 vs control, cP < 0.05 vs model, and dP < 0.01 vs model. L-XSD: Low-dose Xuanshen decoction; M-XSD: Medium-dose Xuanshen decoction; H-XSD: High-dose Xuanshen decoction; Bax: B-cell lymphoma 2-associated X protein; Bcl-2: B-cell lymphoma 2; GAPDH: Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Citation: Zeng XL, Zhu LJ, Zhang Y, Yang XD, Zhu YJ. Unveiling Xuanshen decoction: A novel approach to combat slow transit constipation. World J Gastroenterol 2025; 31(30): 109187
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v31/i30/109187.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v31.i30.109187