Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2023; 29(11): 1708-1720
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1708
Published online Mar 21, 2023. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1708
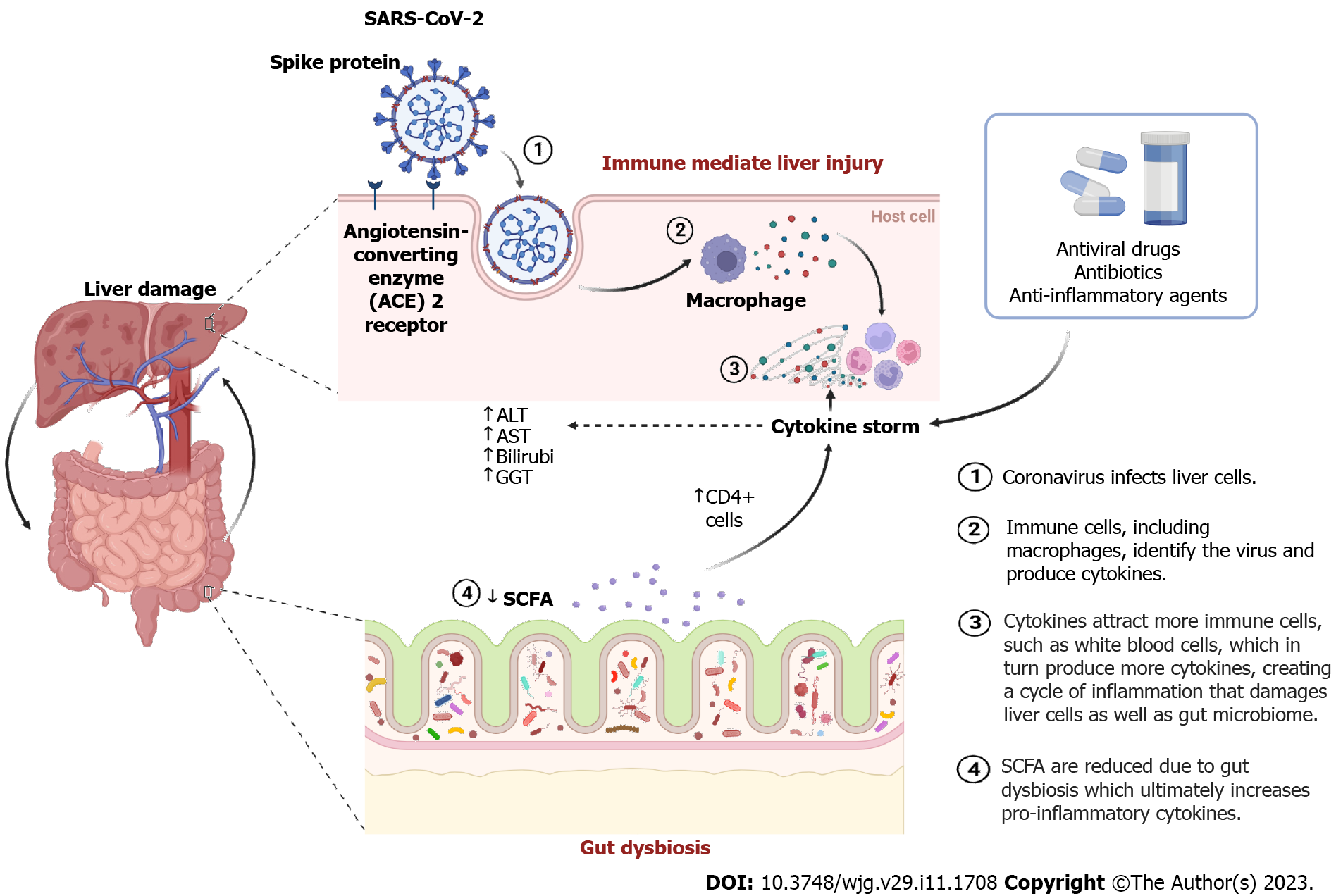
Figure 1 Potential causes of liver injury during coronavirus disease 2019.
Following severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection, liver injury may arise due to direct viral entry [via angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors on hepatocytes] or gut microbial dysbiosis leading to cytokine storm in the liver. ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; CD4+: Cluster of differentiation; GGT: Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase; SCFA: Short-chain fatty acids.
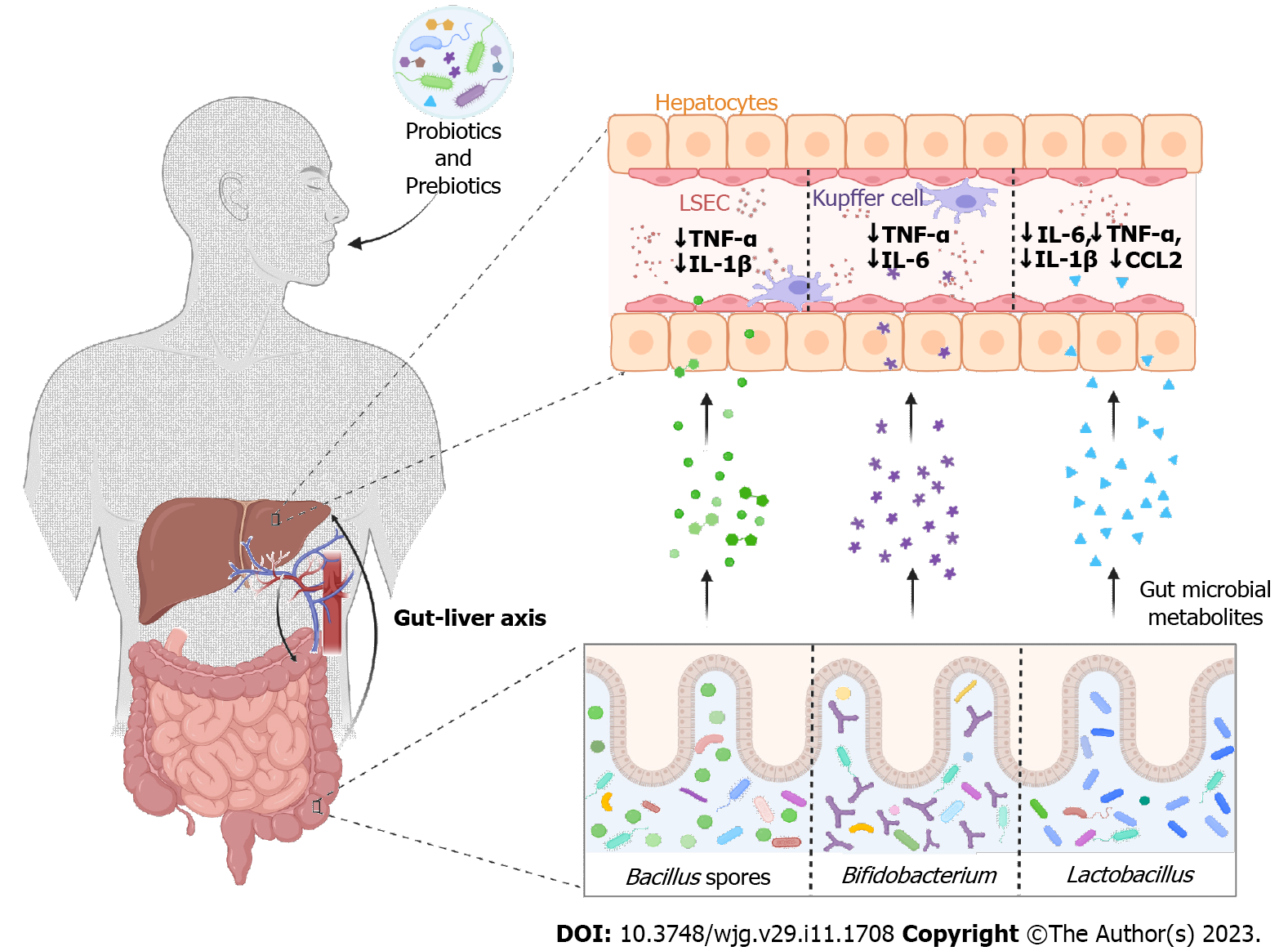
Figure 2 Modulation of gut microbiota and its role in the gut-liver axis during coronavirus disease 2019.
Probiotics and prebiotics could be used as potential therapeutics to lower coronavirus disease 2019 symptom severity by producing various bioactive metabolites, which are absorbed into the liver mainly via the hepatic portal vein, for regulation of hepatic function by reducing inflammatory cytokines. CCL2: Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; IL-1β: Interleukin-1 beta; IL-6: Interleukin 6; LSEC: Liver sinusoidal endothelial cells; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
- Citation: Ahsan K, Anwar MA, Munawar N. Gut microbiome therapeutic modulation to alleviate drug-induced hepatic damage in COVID-19 patients. World J Gastroenterol 2023; 29(11): 1708-1720
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v29/i11/1708.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v29.i11.1708