Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2020; 26(6): 670-685
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.670
Published online Feb 14, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.670
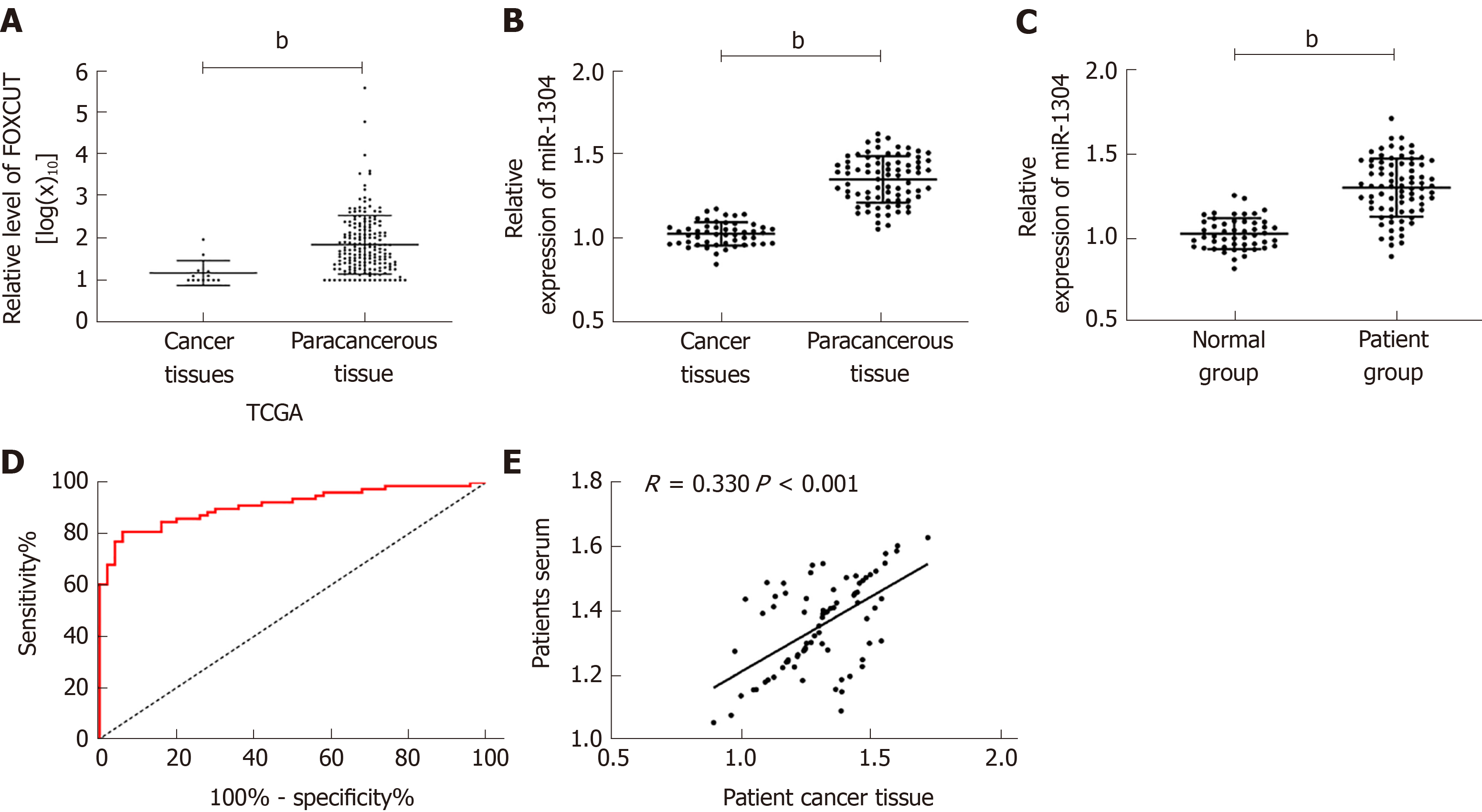
Figure 1 Expression of miR-1304 in patients with esophageal carcinoma and its diagnostic value.
A: Expression of miR-1304 in cancer tissues and tumor-adjacent tissues in The Cancer Genome Atlas database; B: Expression of miR-1304 in the tissues of patients; C: Expression of miR-1304 in the serum of patients; D, E: Diagnostic value of serum miR-1304 in esophageal carcinoma. When the cutoff value was 1.154, the specificity, sensitivity and Youden index were 94.00%, 80.77%, and 71.77%, respectively. bP < 0.001.
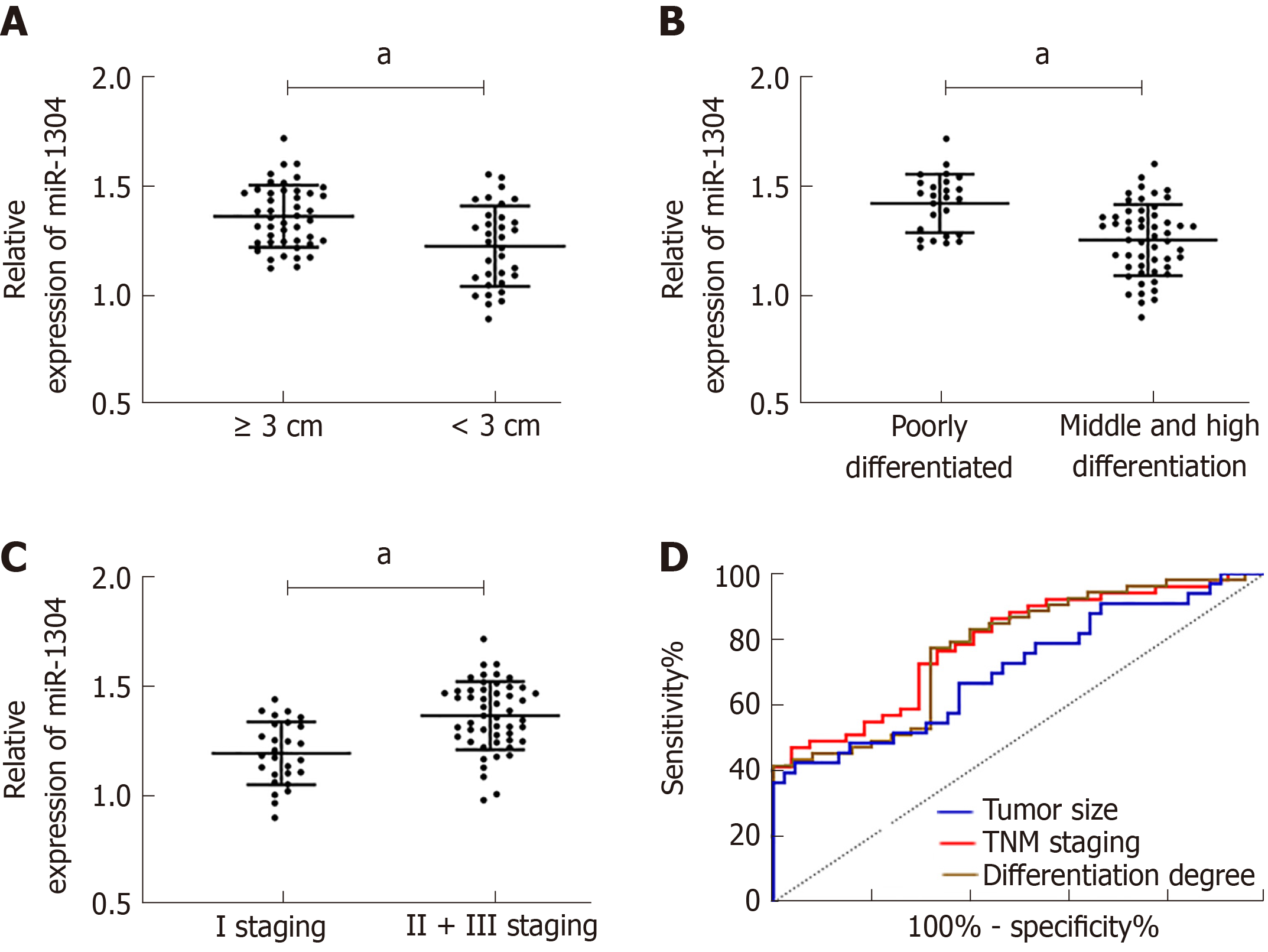
Figure 2 Relationship between miR-1304 and pathological data and its diagnostic value.
A: Patients with tumor size ≥ 3 cm showed increased expression of miR-1304; B: miR-1304 was highly expressed in patients with low differentiation; C: miR-1304 was highly expressed in patients with stage I + III disease; D: Receiver operating characteristic curves of miR-1304 for identifying tumor size, differentiation, and TNM stage. aP < 0.05.
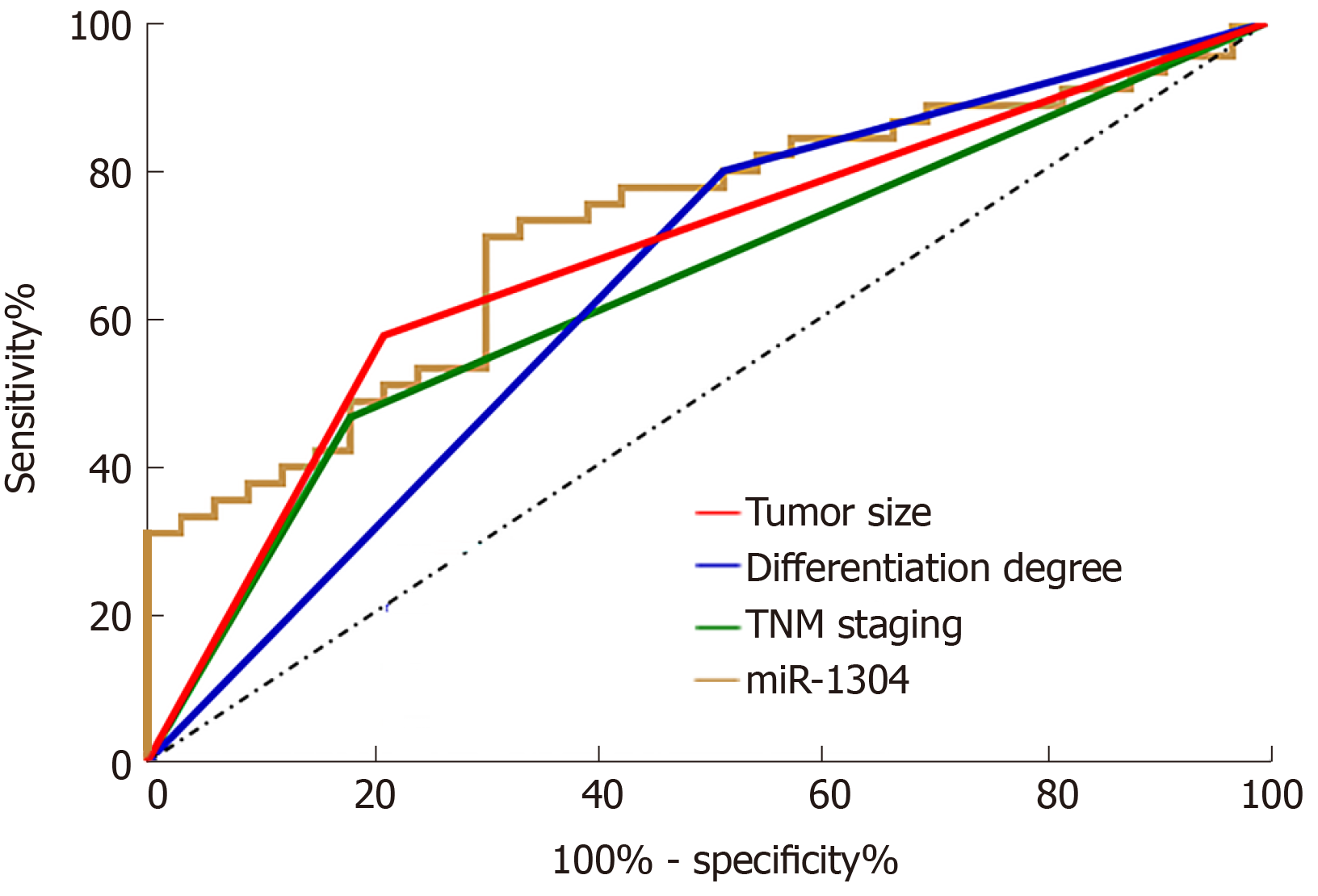
Figure 3 Diagnostic values of independent risk factors for recurrence.
The red line represents tumor size, and its area under the curve (AUC) was 0.683; the blue line represents differentiation, and its AUC was 0.642; the green line represents TNM stage, and its AUC was 0.642, and the light brown line represents miR-1304 and its AUC was 0.721.
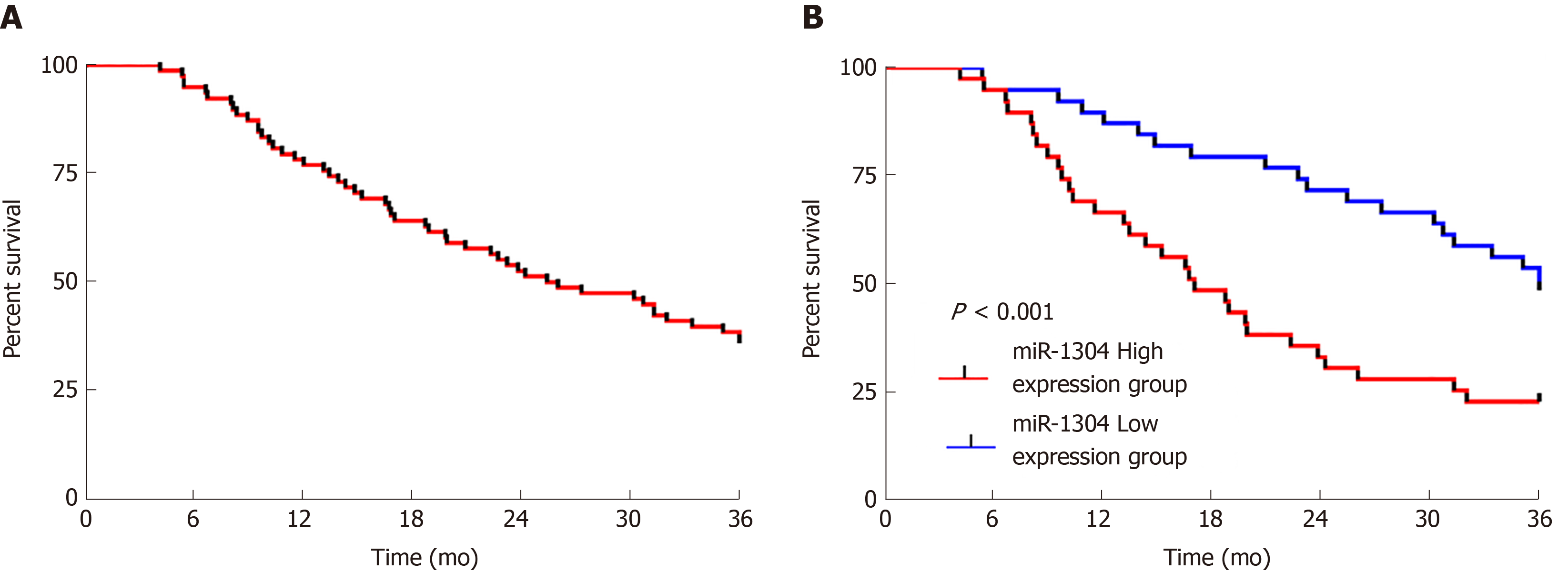
Figure 4 Three-year survival of esophageal carcinoma patients.
A: The 3-year overall survival rate of patients; B: Survival of the high and low miR-1304 expression groups.
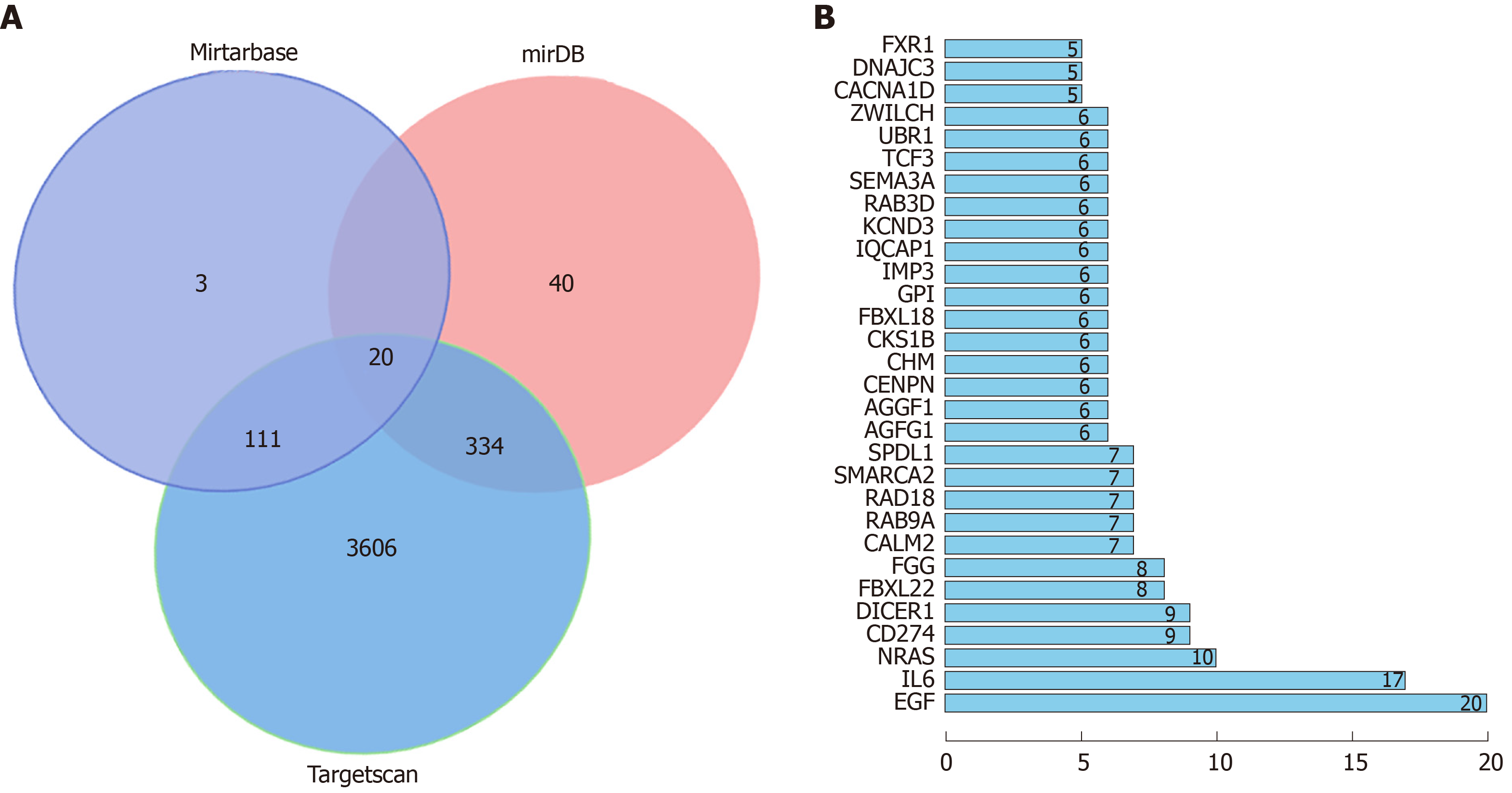
Figure 5 Bioinformatics analysis.
A: Venn diagram. Blue represents the potential target genes predicted by MiRTarBase; red represents the potential target genes predicted by miRDB, and green represents the potential target genes predicted by Targetscan; B: Distribution of the first 30 relationship pairs.
- Citation: Luo YG, Duan LW, Ji X, Jia WY, Liu Y, Sun ML, Liu GM. Expression of miR-1304 in patients with esophageal carcinoma and risk factors for recurrence. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(6): 670-685
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i6/670.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i6.670