Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2020; 26(45): 7131-7152
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131
Published online Dec 7, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131
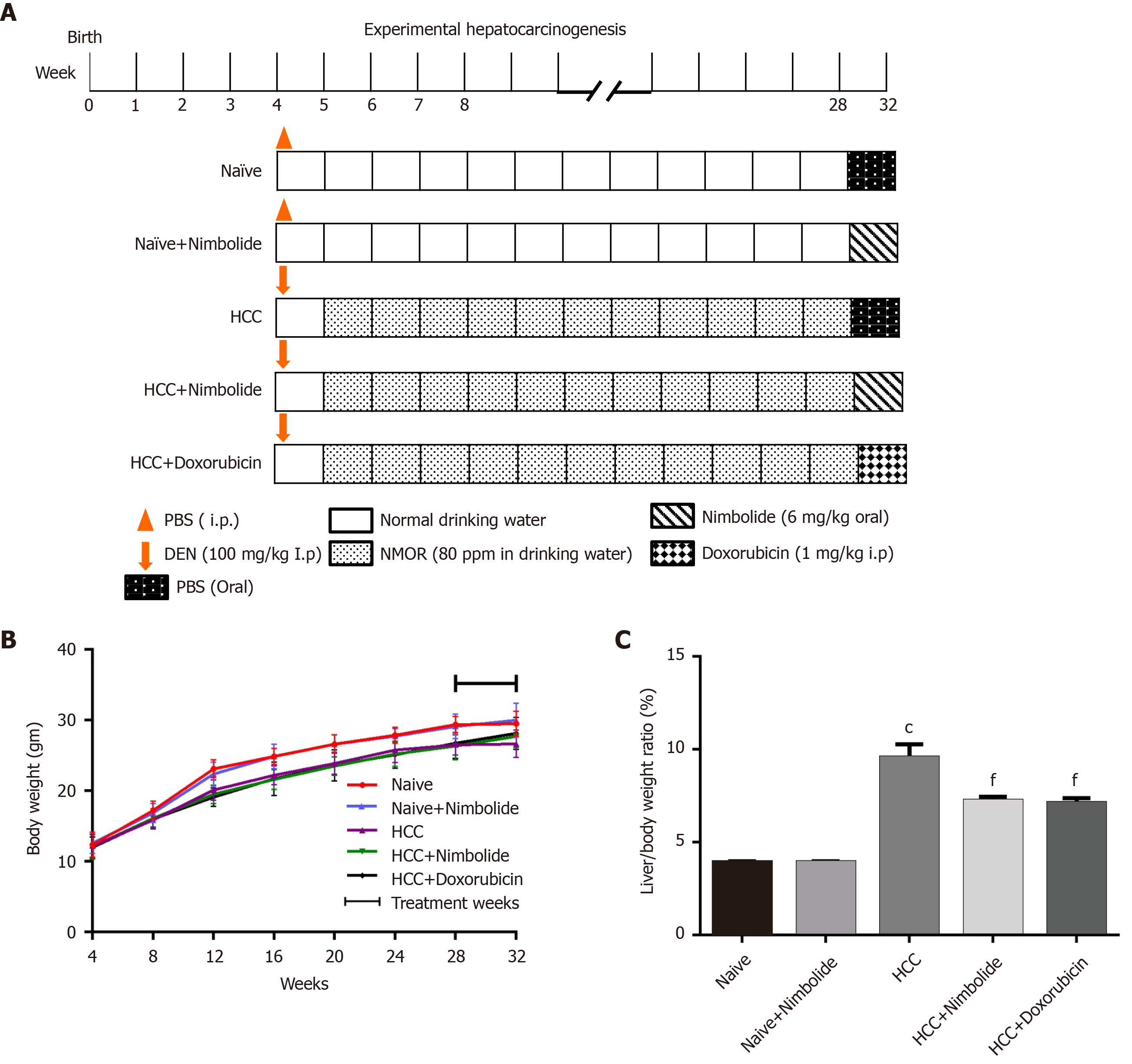
Figure 1 Effect of nimbolide on body weight and liver coefficient in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A: Flowchart for the experimental hepatocarcinogenesis model; B: Average weekly body weight of naïve and experimental mice; C: Liver coefficient of naïve and experimental mice. All the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6-10). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. cP < 0.0001 compared to naïve group; fP < 0.001 compared to hepatocellular carcinoma group. DEN: Diethylnitrosamine; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; NMOR: N-nitrosomorpholine; PBS: Phosphate buffer saline.
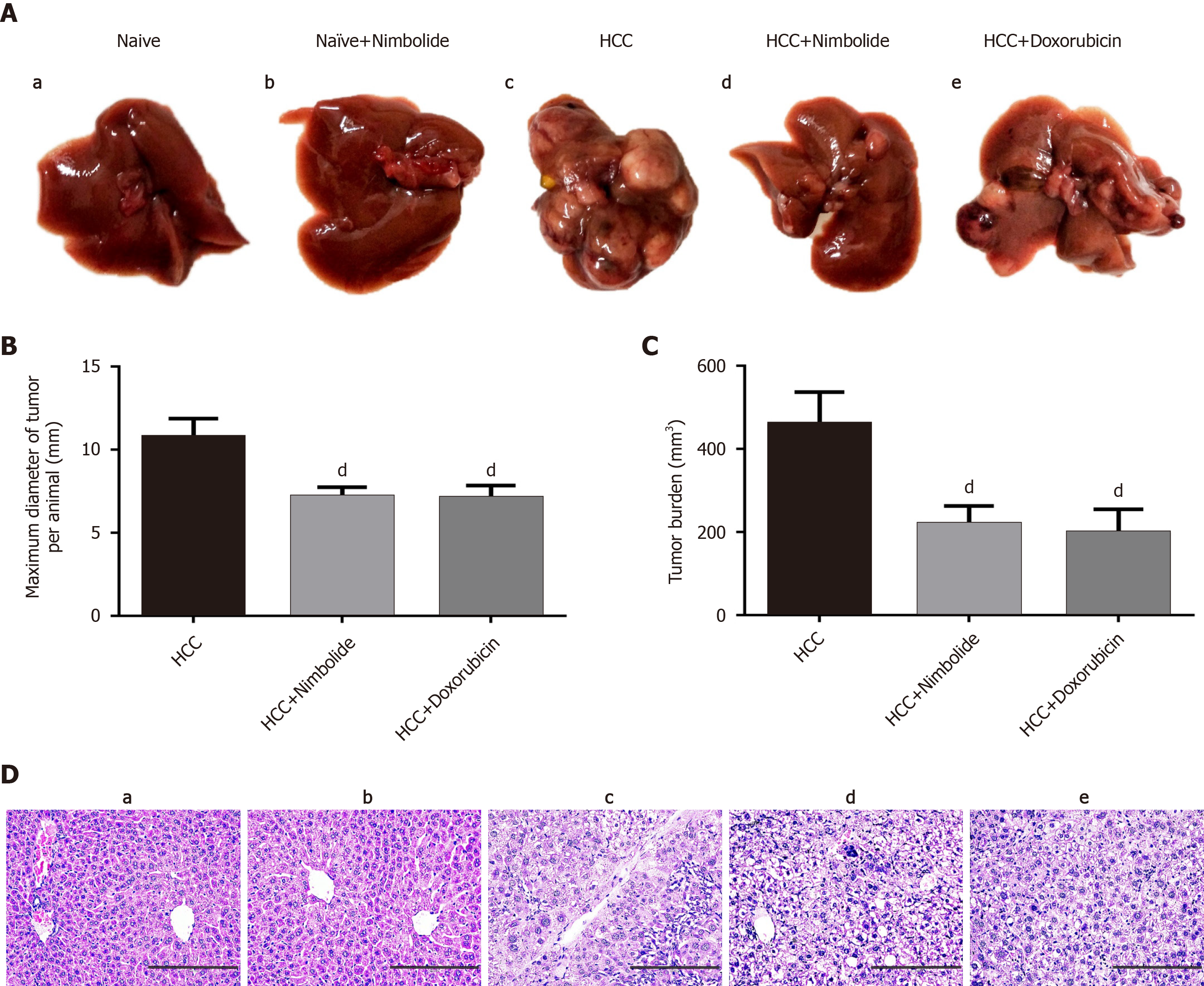
Figure 2 Nimbolide inhibits diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocarcinogenesis.
A: Macroscopic images of mice liver from naïve and experimental groups; B: Maximum tumor diameter in naïve and experimental groups; C: Tumor burden in naïve and experimental groups; D: Representative images of hematoxylin and eosin stained liver sections from naive and experimental groups (200 × magnification). Scale bar: 200 μm; all the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 6-7). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. dP < 0.05 compared to hepatocellular carcinoma group. HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
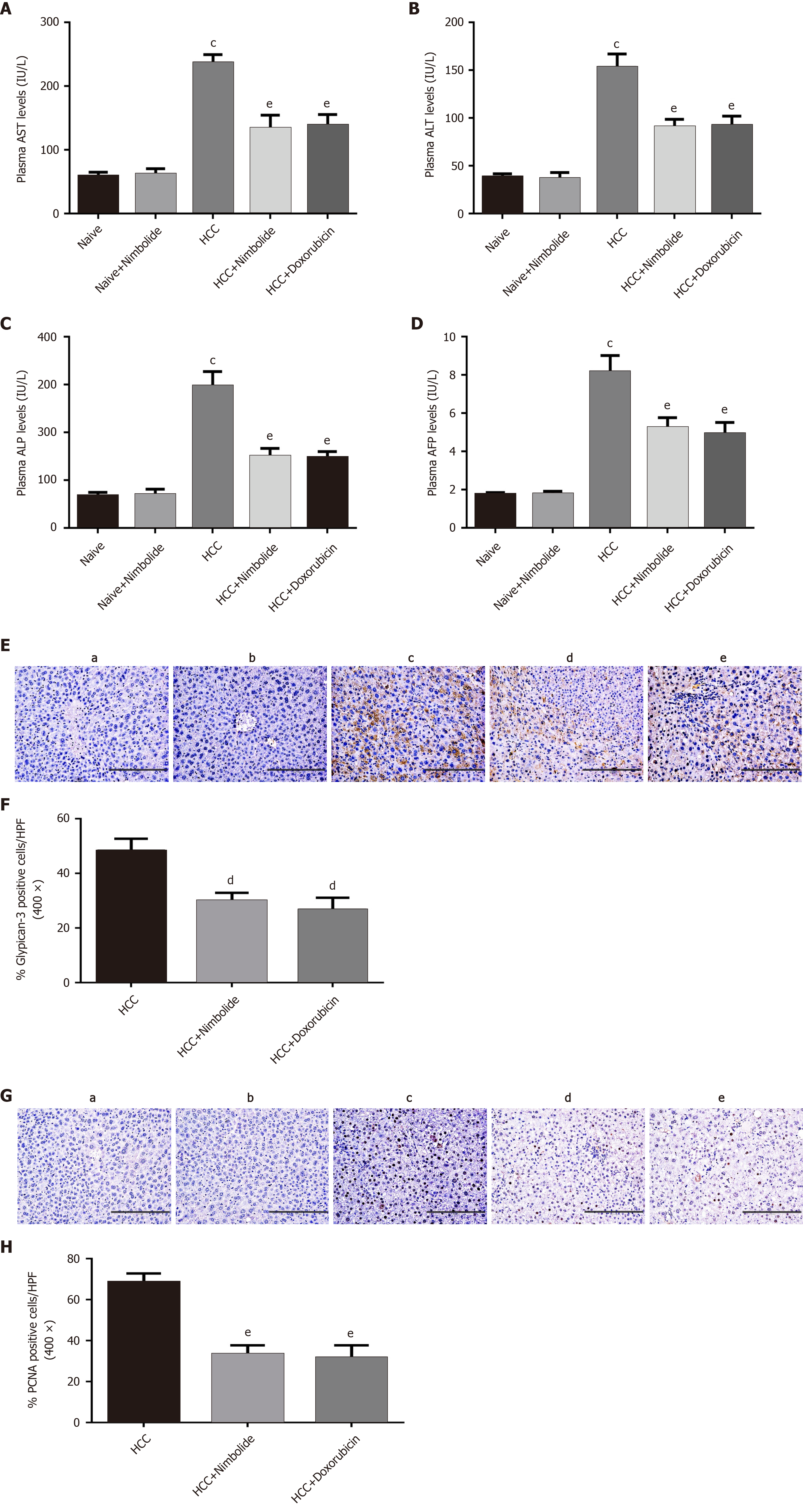
Figure 3 Effect of nimbolide on liver function parameters and tumor and cell proliferation markers in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A: Plasma aspartate aminotransferase level in naïve and experimental groups; B: Plasma alanine aminotransferase level in naïve and experimental groups; C: Plasma alkaline phosphatase level in naïve and experimental groups; D: Plasma alpha-fetoprotein level in naïve and experimental groups; E: Representative images of glypican-3 immunostaining of mice liver from naive and experimental groups (200 × magnification); F: Quantification of glypican-3 positive cells in experimental groups by counting five 400 × fields of each liver section; G: Representative images of proliferating hepatocytes by proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) immunostaining of mice liver from naive and experimental groups (200 × magnification); H: Quantification of PCNA positive nuclei in experimental groups by counting five 400 × fields of each liver section. Scale bar: 200 μm; all the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3-6). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. cP < 0.0001 compared to naïve group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01 compared to hepatocellular carcinoma group. AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; AFP: Alpha-fetoprotein; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; HPF: High-power fields; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
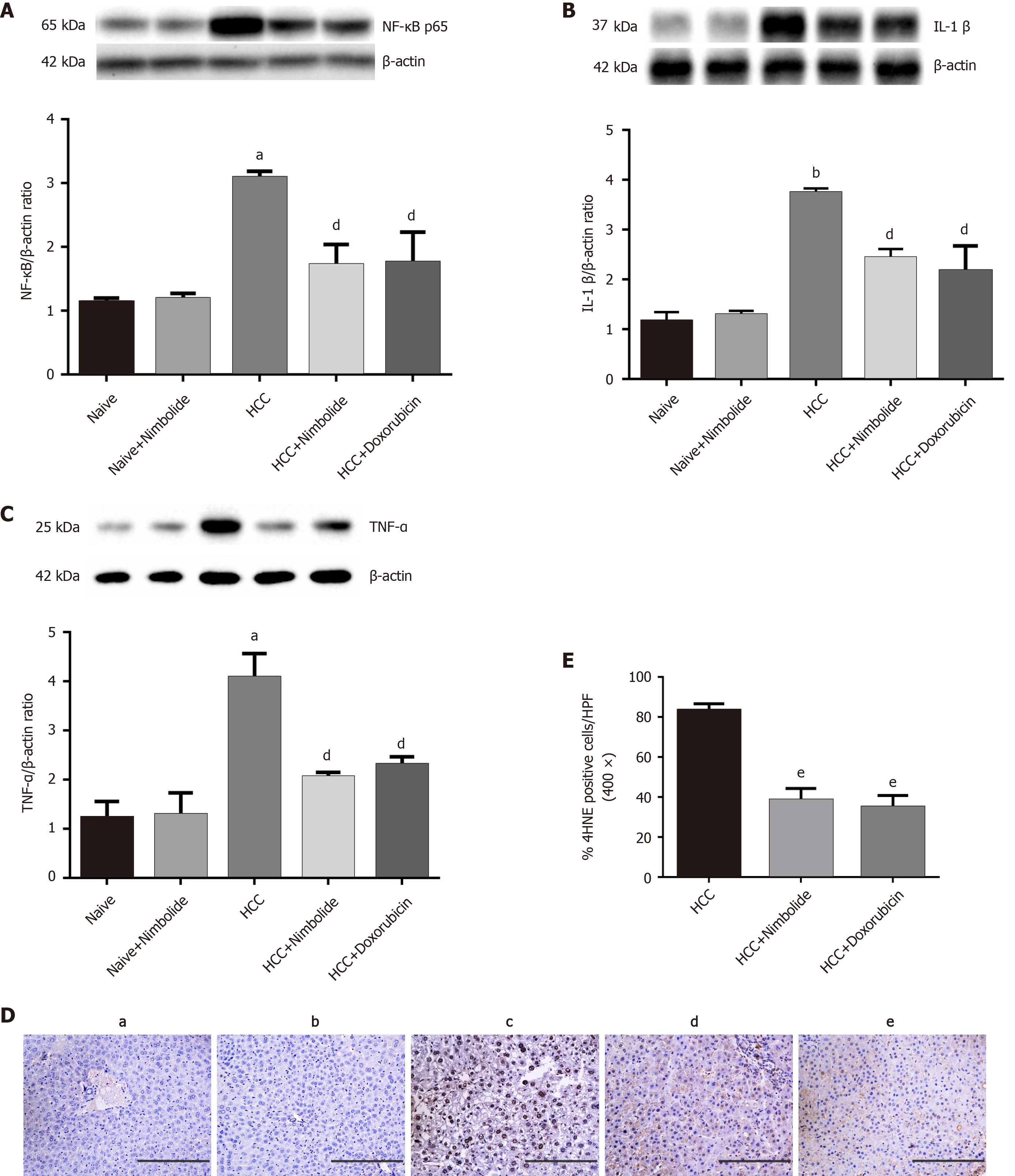
Figure 4 Nimbolide ameliorates hepatic inflammation and oxidative stress in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A-C: Hepatic protein expression levels of nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, interleukin 1 beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha by western blot in naive and experimental groups; D: Representative images of 4-Hydroxynonenal (4HNE) immunostaining of mice liver from naive and experimental groups (200 × magnification); E: Quantification of 4HNE positive nuclei in experimental groups by counting five 400 × fields of each liver section. Scale bar: 200 μm; all the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. aP < 0.01, bP < 0.001 compared to naïve group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01 compared to hepatocellular carcinoma group. NF-κB: Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells; IL-1β: Interleukin 1 beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; 4HNE: 4-Hydroxynonenal; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
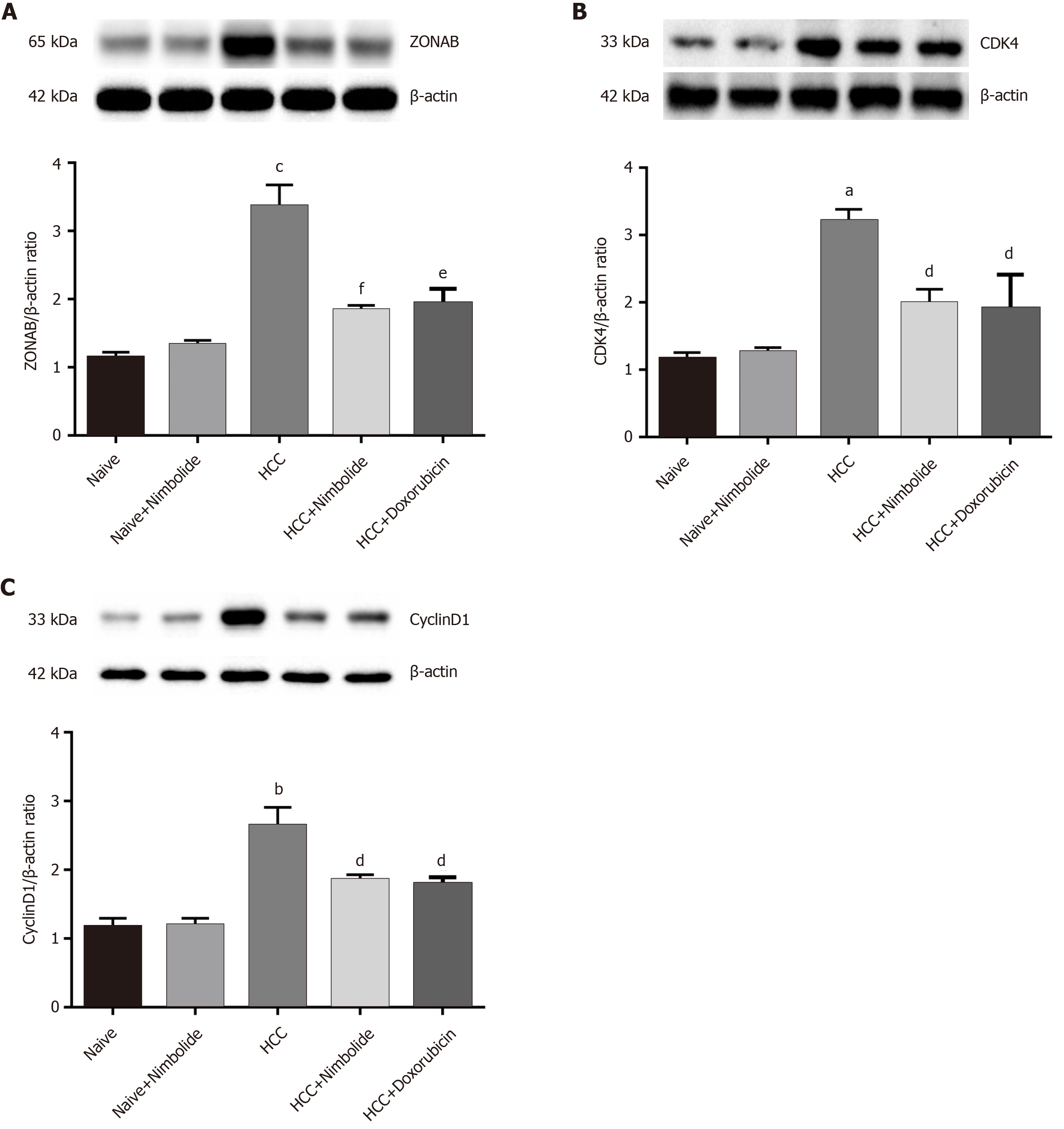
Figure 5 Nimbolide treatment attenuates hepatic zonula occludens 1 associated nucleic acid binding protein and cell cycle markers proteins expression in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A: Hepatic protein expression levels of zonula occludens 1 associated nucleic acid binding protein by western blot in naive and experimental groups; B: Hepatic protein expression levels of cyclin dependent kinase 4 by western blot in naive and experimental groups; C: Hepatic protein expression levels of CyclinD1 by western blot in naive and experimental groups. All the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. aP < 0.01, bP < 0.001, cP < 0.0001 compared to naïve group; dP < 0.05, eP < 0.01, fP < 0.001 compared to HCC group. ZONAB: Zonula occludens 1 associated nucleic acid binding protein; CDK4: Cyclin dependent kinase; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
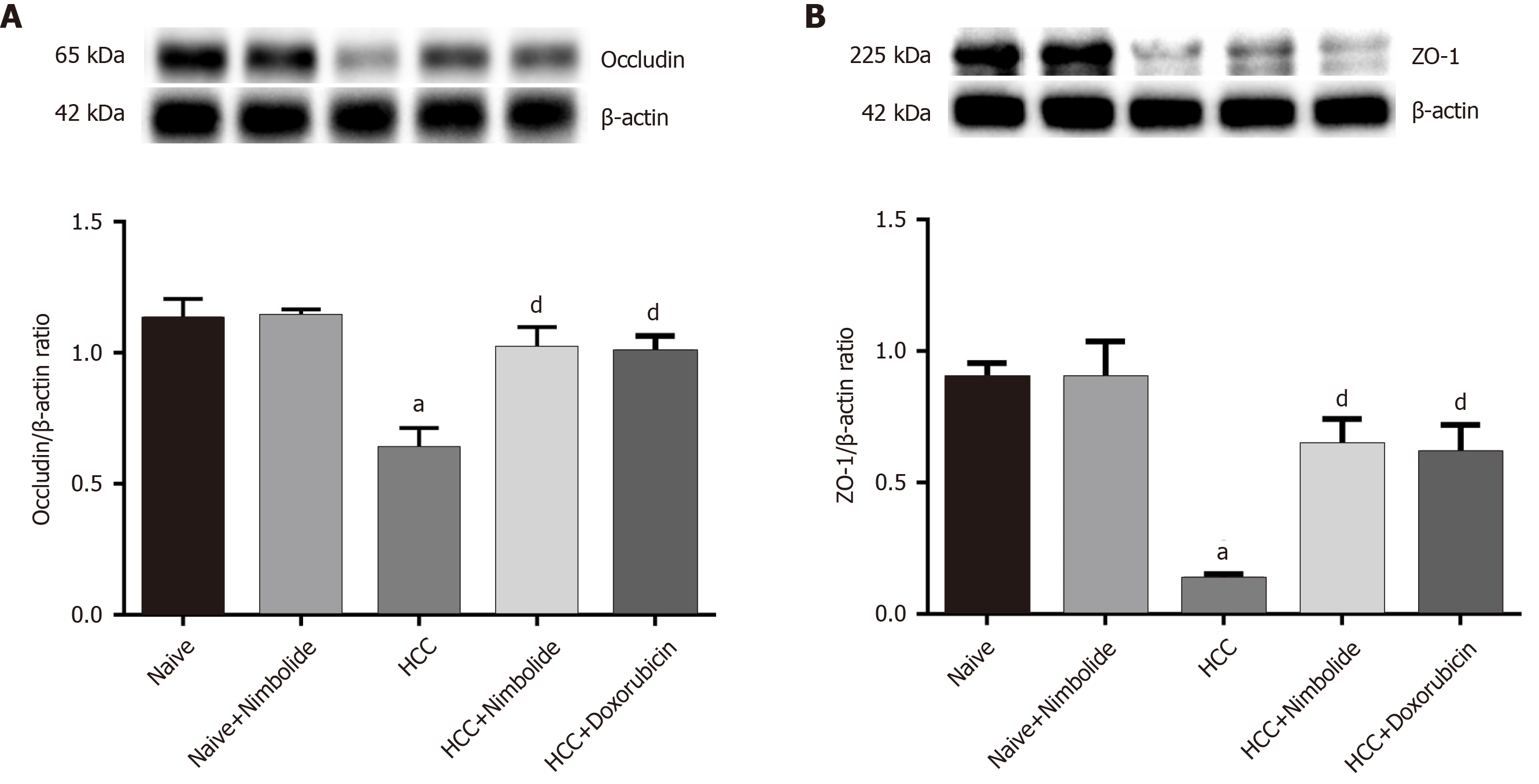
Figure 6 Nimbolide treatment restores hepatic tight junction protein expression in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
A and B: Hepatic protein expression levels of occludin and zonula occludens 1 by western blot in naive and experimental groups. All the data are expressed as mean ± SEM (n = 3). The comparison between the groups was analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison post-hoc test or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison post-hoc test. aP < 0.01 compared to naïve group; dP<0.05 compared to hepatocellular carcinoma group. ZO-1: Zonula occludens 1; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
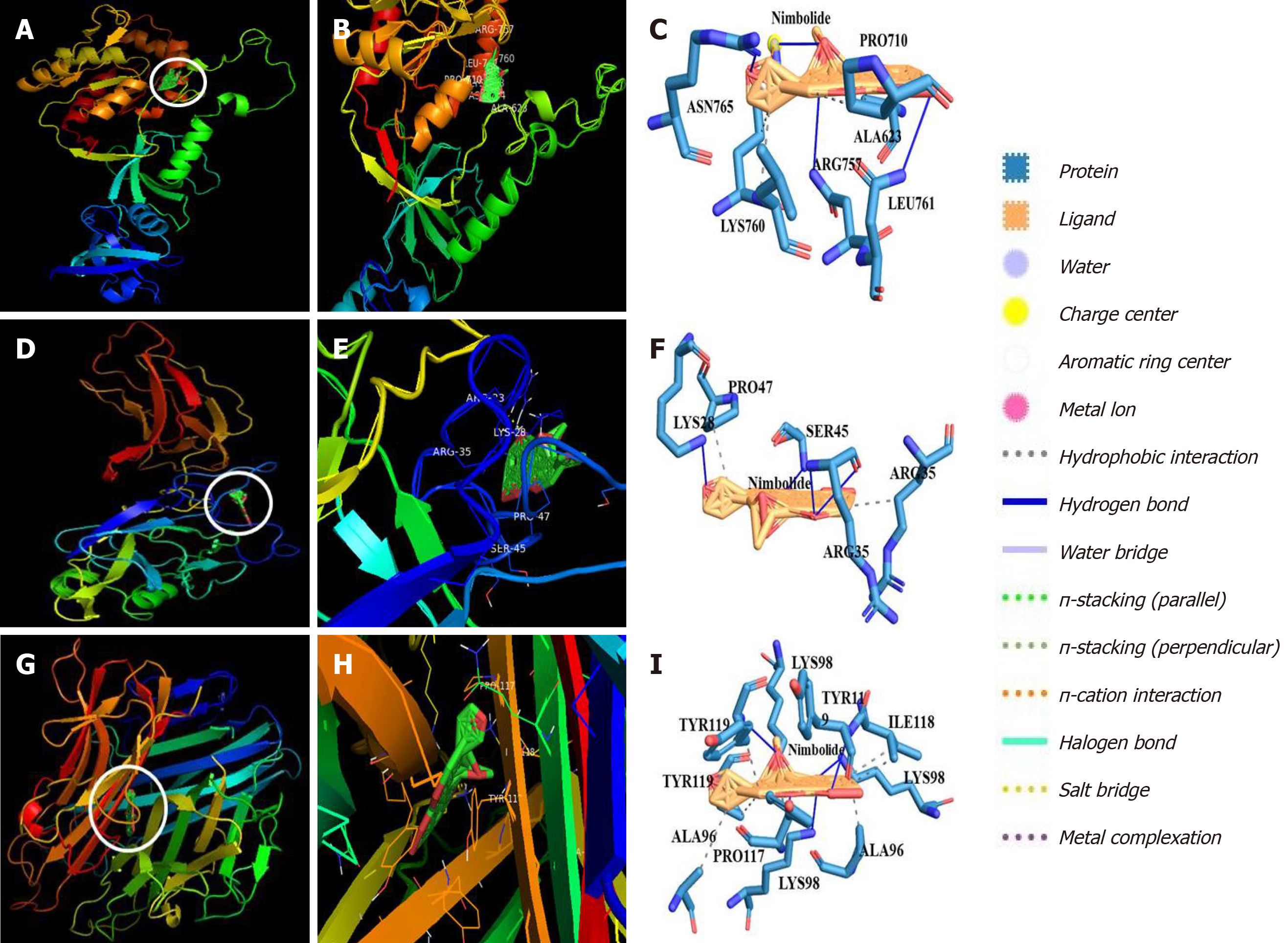
Figure 7 Molecular docking analysis of nimbolide with zonula occludens 1, nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells and tumor necrosis factor alpha.
A and B: Representation of nimbolide and zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1) docking complex; C: Interaction of nimbolide with amino acid residues of ZO-1; D and E: Representation of nimbolide and nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells (NF-κB) docking complex; F: Interaction of nimbolide with amino acid residues of NF-κB; G and H: Representation of nimbolide and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) docking complex; I: Interaction of nimbolide with amino acid residues of TNF-α.
Figure 8 Schematic representation of the mechanism of action of nimbolide in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced hepatocellular carcinoma mice.
Nimbolide treatment inhibits tumor growth in diethylnitrosamine and N-nitrosomorpholine induced Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) mice by targeting tight junctions (TJs) proteins [Zonula occludens-1 (ZO-1) and Occludin]. Nimbolide mediated up-regulation of ZO-1 represses the transcriptional activity of ZO-1 associated nucleic acid binding protein at a junctional site preventing its nuclear accumulation and thus preventing the induction of cell cycle related genes cyclin dependent kinase 4, cyclinD1 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Nimbolide treatment also restores barrier integrity by up-regulation TJs proteins which prevent translocation of growth factors and nutrients necessary for cell growth from apical to the basolateral domain. Further, nimbolide also targets the nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells pathway ameliorating inflammation in HCC mice. ZO-1: Zonula occludens 1; ZONAB: ZO-1 associated nucleic acid binding protein; CDK4: Cyclin dependent kinase; PCNA: Proliferating cell nuclear antigen; NF-κB: Nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells; IL-1β: Interleukin 1 beta; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Citation: Ram AK, Vairappan B, Srinivas BH. Nimbolide inhibits tumor growth by restoring hepatic tight junction protein expression and reduced inflammation in an experimental hepatocarcinogenesis. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(45): 7131-7152
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i45/7131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i45.7131