Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. May 28, 2020; 26(20): 2599-2617
Published online May 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2599
Published online May 28, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2599
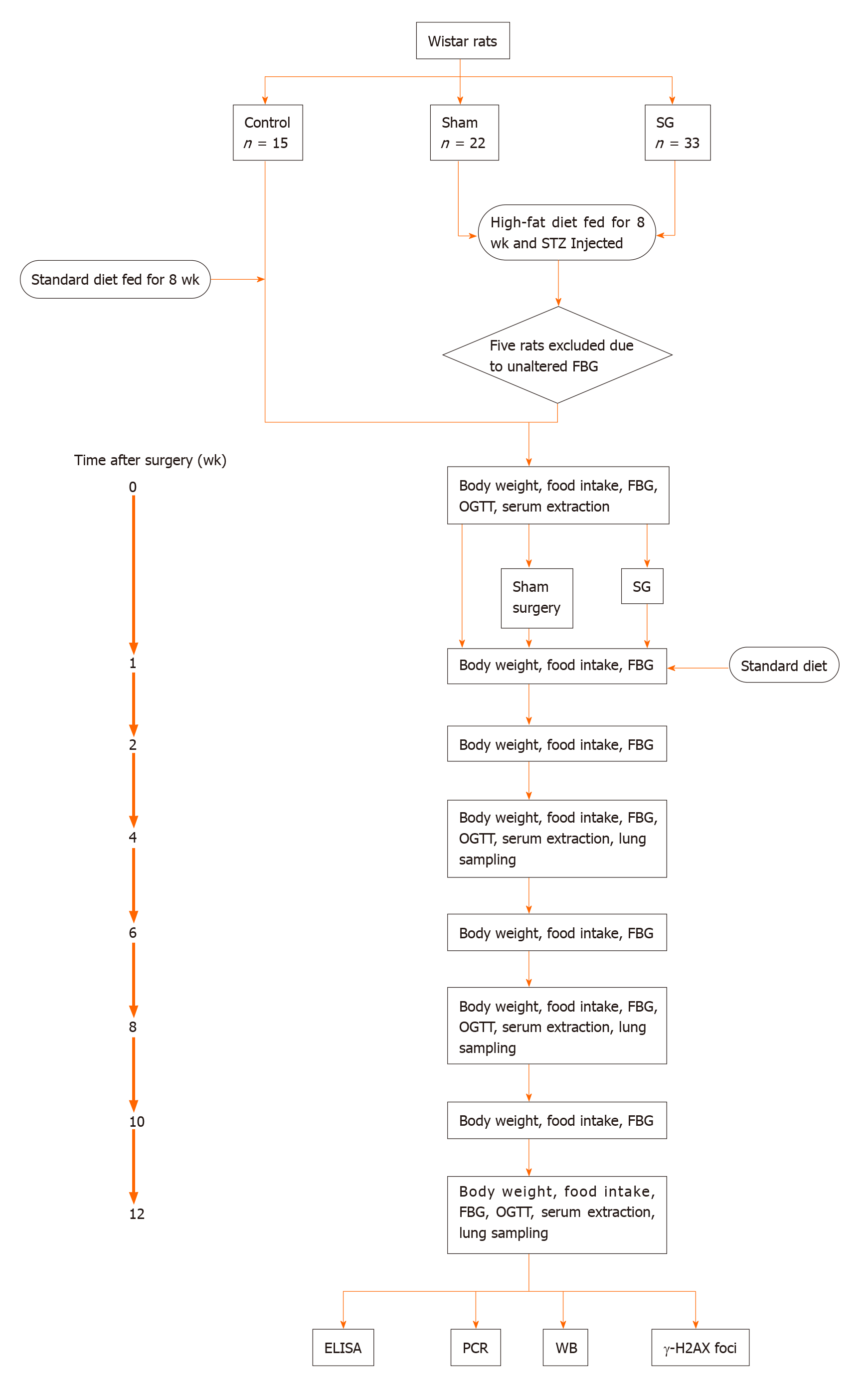
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study protocol.
ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; FBG: Fasting blood glucose; OGTT: Oral glucose tolerance test; PCR: Polymerase chain reaction; SG: Sleeve gastrectomy; STZ: Streptozotocin; WB: Western blot; γ-H2AX foci: H2A histone family member X focus assay.
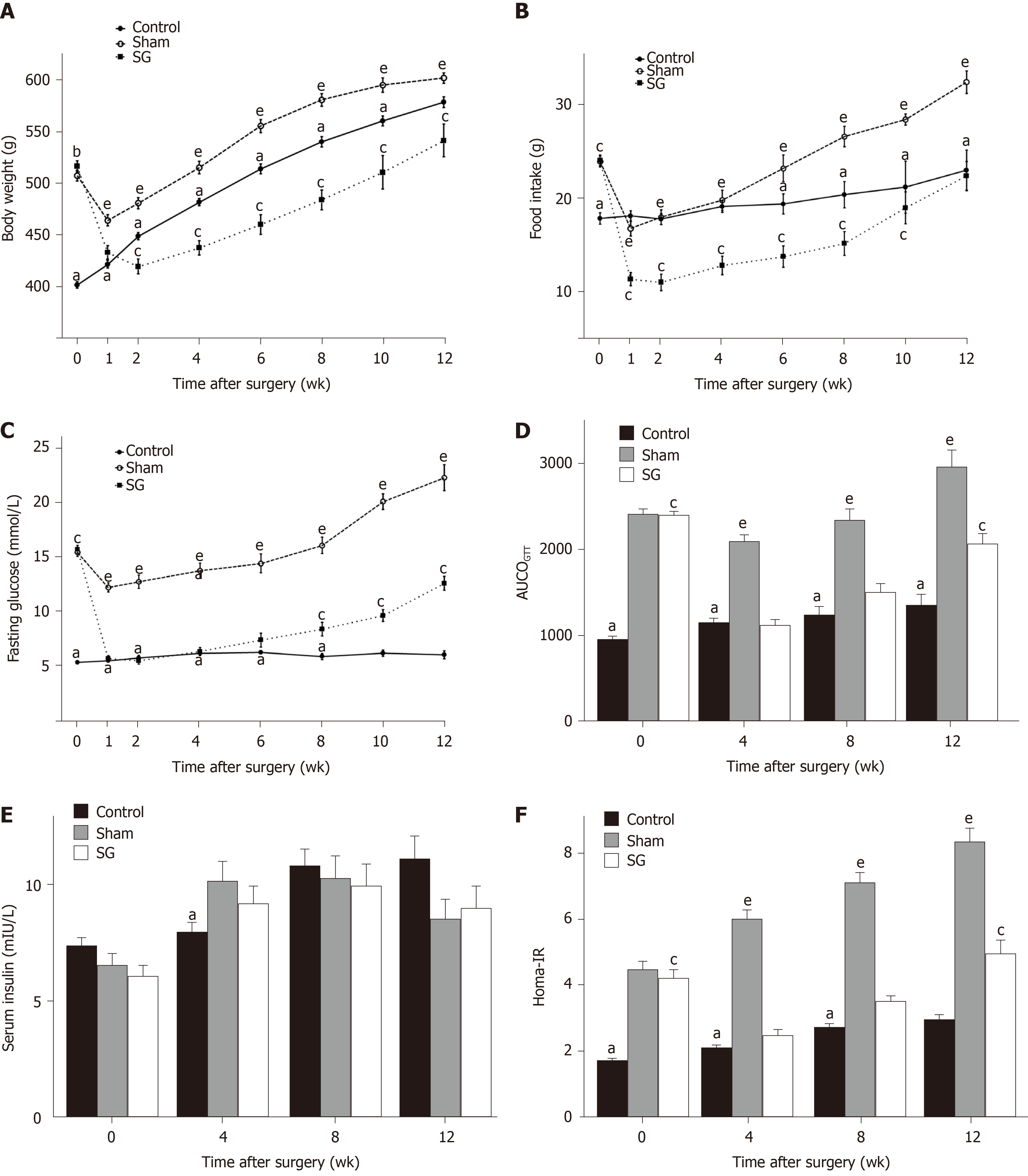
Figure 2 Comparisons of metabolic parameters among groups.
A: Body weight; B: Food intake; C: Fasting glucose level; D: Area under the curve of oral glucose tolerance test; E: Fasting serum insulin level; F: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance compared to sham-operated and control rats. aP < 0.05: Control vs sham; cP < 0.05: Control vs sleeve gastrectomy; eP < 0.05: Sham vs sleeve gastrectomy. AUCOGTT: Area under the curve of oral glucose tolerance test; Homa-IR: Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; SG: Sleeve gastrectomy.
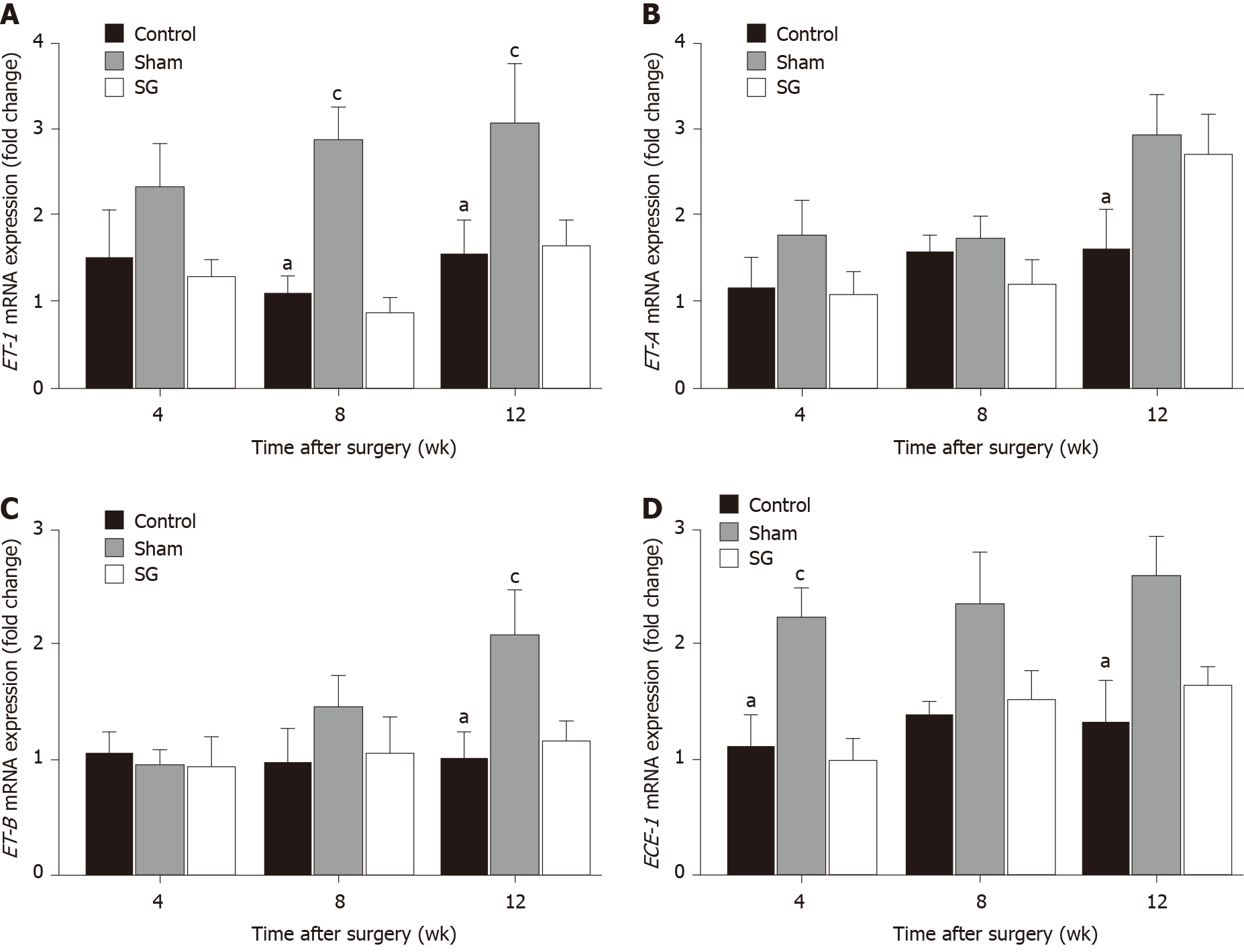
Figure 3 Expression of genes of the endothelin-1 axis.
aP < 0.05: Control vs sham; cP < 0.05: Sham vs sleeve gastrectomy. SG: Sleeve gastrectomy.
Figure 4 Protein expression of the endothelin-1 axis.
A: Immunoblotting of the proteins; B-E: Relative band intensity. aP < 0.05: Control vs sham; cP < 0.05: Control vs sleeve gastrectomy; eP < 0.05: Sham vs SG. ET: Endothelin; ECE: ET-converting enzyme; SG: Sleeve gastrectomy.
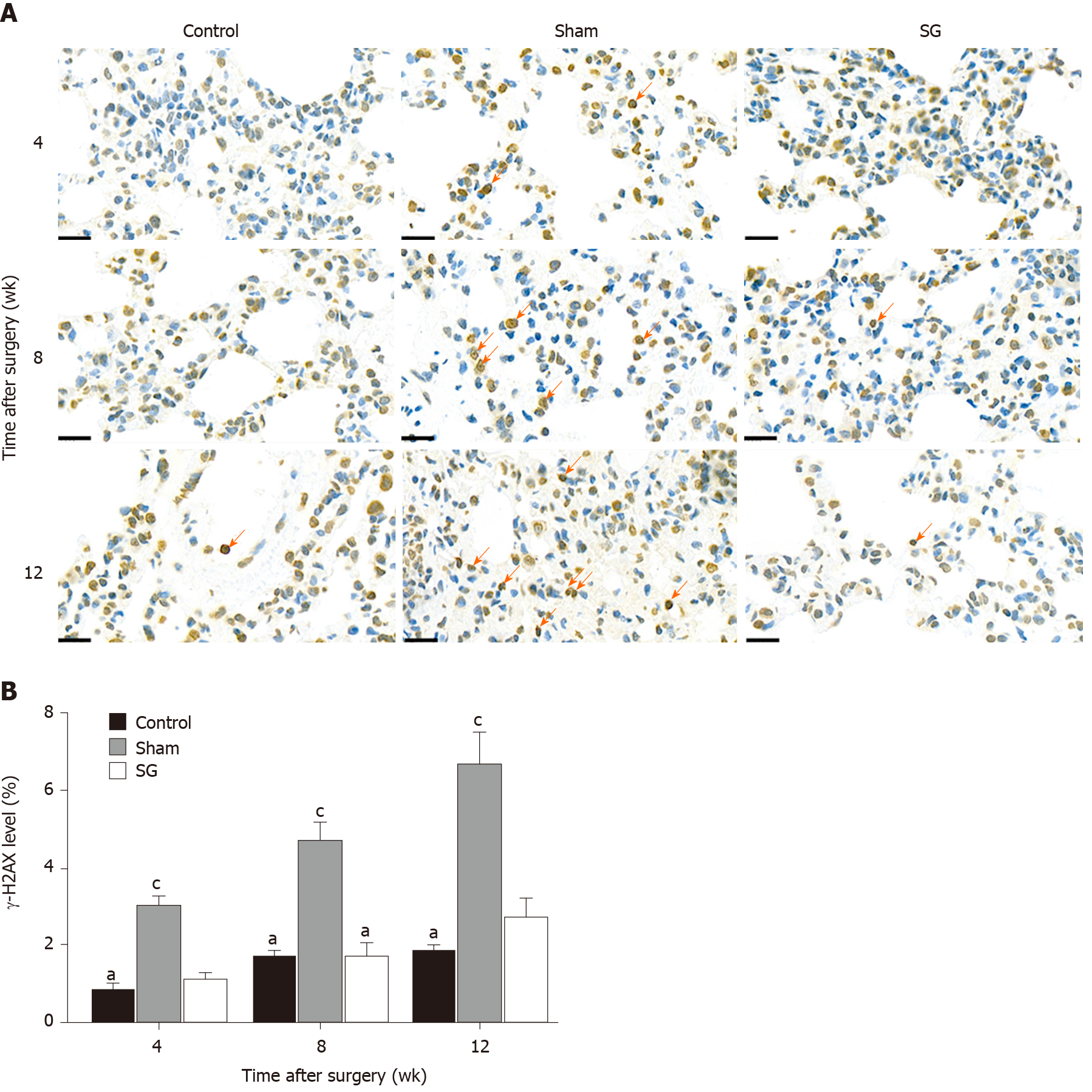
Figure 5 Immunohistochemical assessment of DNA damage using the γ-H2AX foci assay.
A: Representative images of γ-H2AX-positive cells (red arrows) at different time points (bar = 20 μm); B: Semi-quantification of the level of DNA damage. aP < 0.05: Control vs sham; cP < 0.05: Sham vs sleeve gastrectomy. SG: sleeve gastrectomy.
- Citation: Ruze R, Xiong YC, Li JW, Zhong MW, Xu Q, Yan ZB, Zhu JK, Cheng YG, Hu SY, Zhang GY. Sleeve gastrectomy ameliorates endothelial function and prevents lung cancer by normalizing endothelin-1 axis in obese and diabetic rats. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(20): 2599-2617
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i20/2599.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i20.2599