Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2020; 26(11): 1156-1171
Published online Mar 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i11.1156
Published online Mar 21, 2020. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i11.1156
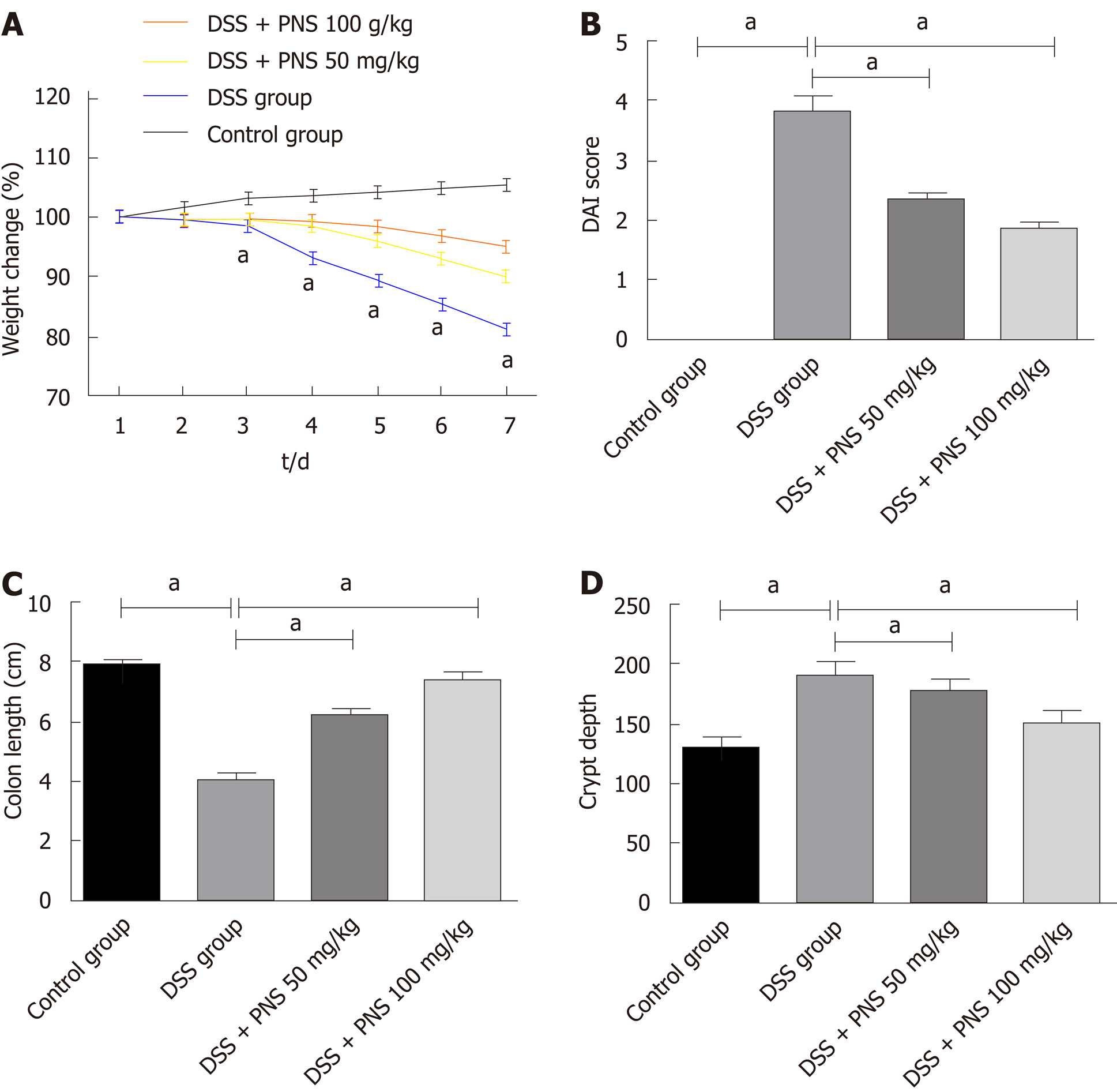
Figure 1 Panax notoginseng saponin alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced intestinal injury.
A: Weight changes of rats in the four groups; B: Comparison among the four groups in disease activity index; C: Comparison among the four groups in colon length; D: Comparison among the four groups in crypt depth. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
Figure 2 Panax notoginseng saponin improves histopathological scores of dextran sulfate sodium-induced rats.
A: Histopathological scores; B: Hematoxylin & eosin staining. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
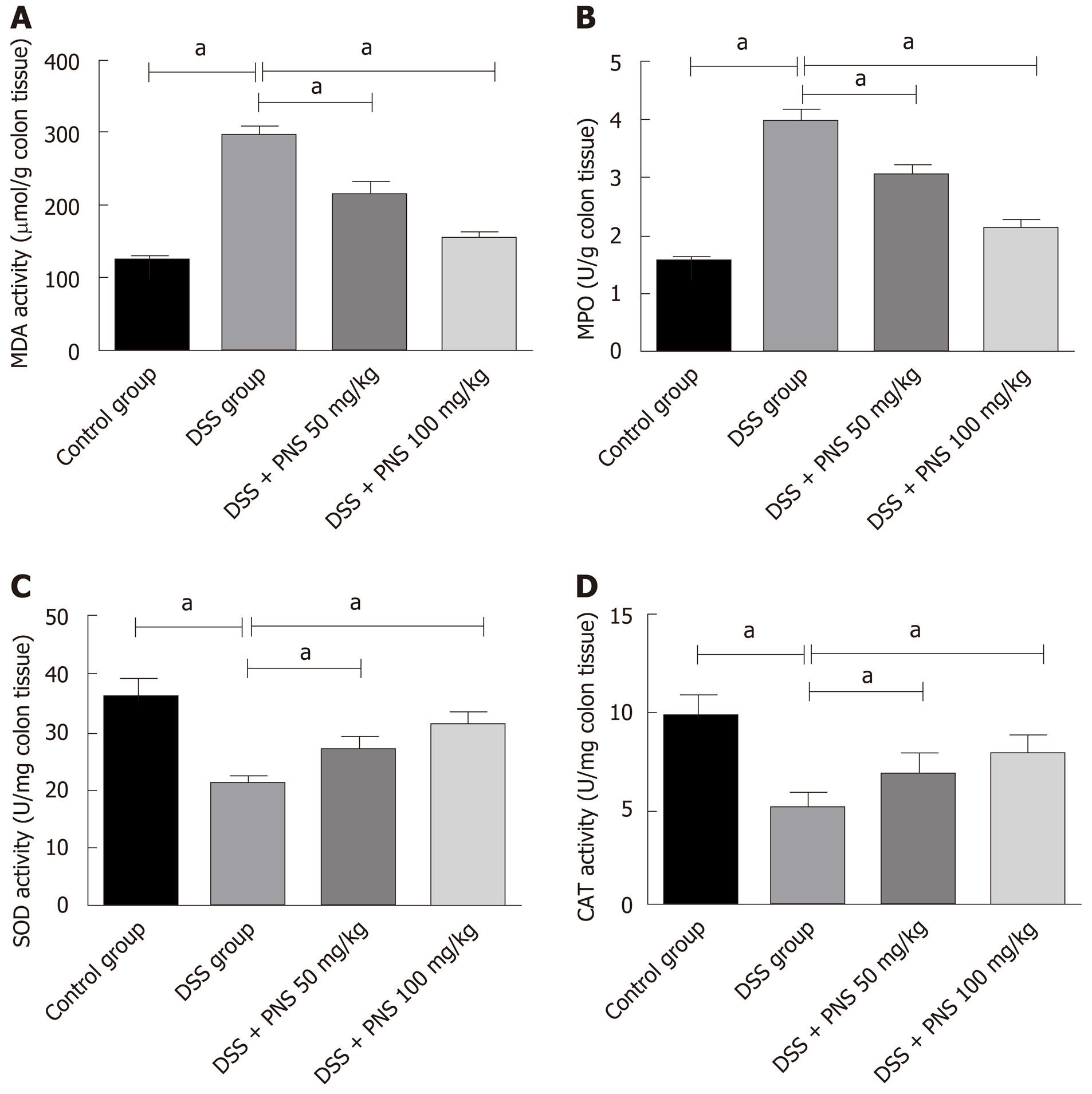
Figure 3 Panax notoginseng saponin alleviates intestinal oxidative damage in rats.
A: Comparison among the four groups in malondialdehyde; B: Comparison among the four groups in myeloperoxidase; C: Comparison among the four groups in superoxide dismutase; D: Comparison among the four groups in catalase. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; MDA: Malondialdehyde; MPO: Myeloperoxidase; CAT: Catalase; SOD: Superoxide dismutase.
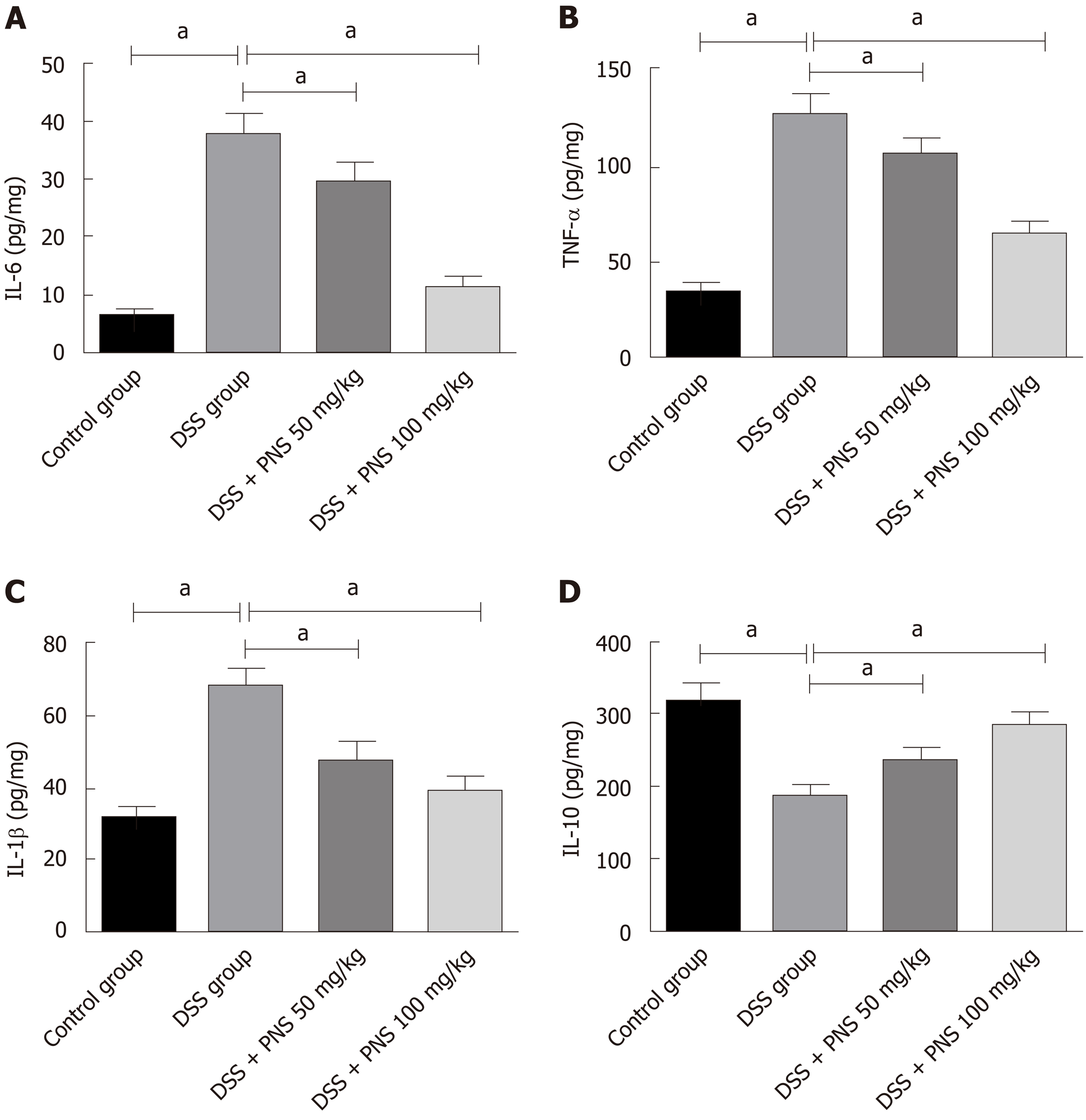
Figure 4 Panax notoginseng saponin alleviates intestinal inflammatory response in rats.
A: Comparison among the four groups in interleukin-6 (IL-6); B: Comparison among the four groups in tumor necrosis factor-α; C: Comparison among the four groups in IL-1β; D: Comparison among the four groups in IL-10. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium; IL: Interleukin; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α.
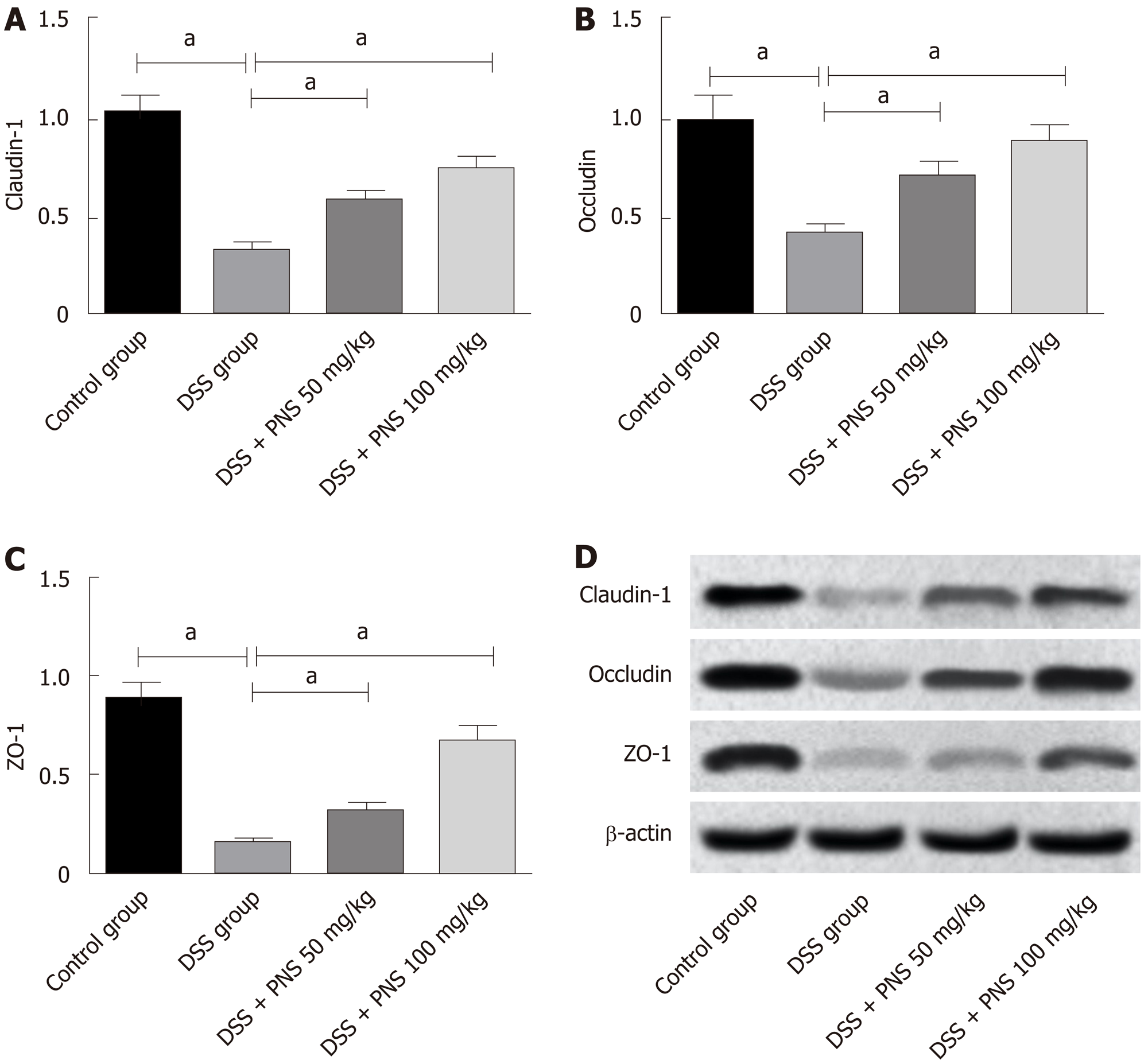
Figure 5 Effects of panax notoginseng saponin on tight junction proteins in the intestinal mechanical barrier of rats.
A: Comparison of claudin-1 among the four groups; B: Comparison of occluding among the four groups; C: Comparison in ZO-1 among the four groups; D: Western blot protein map. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
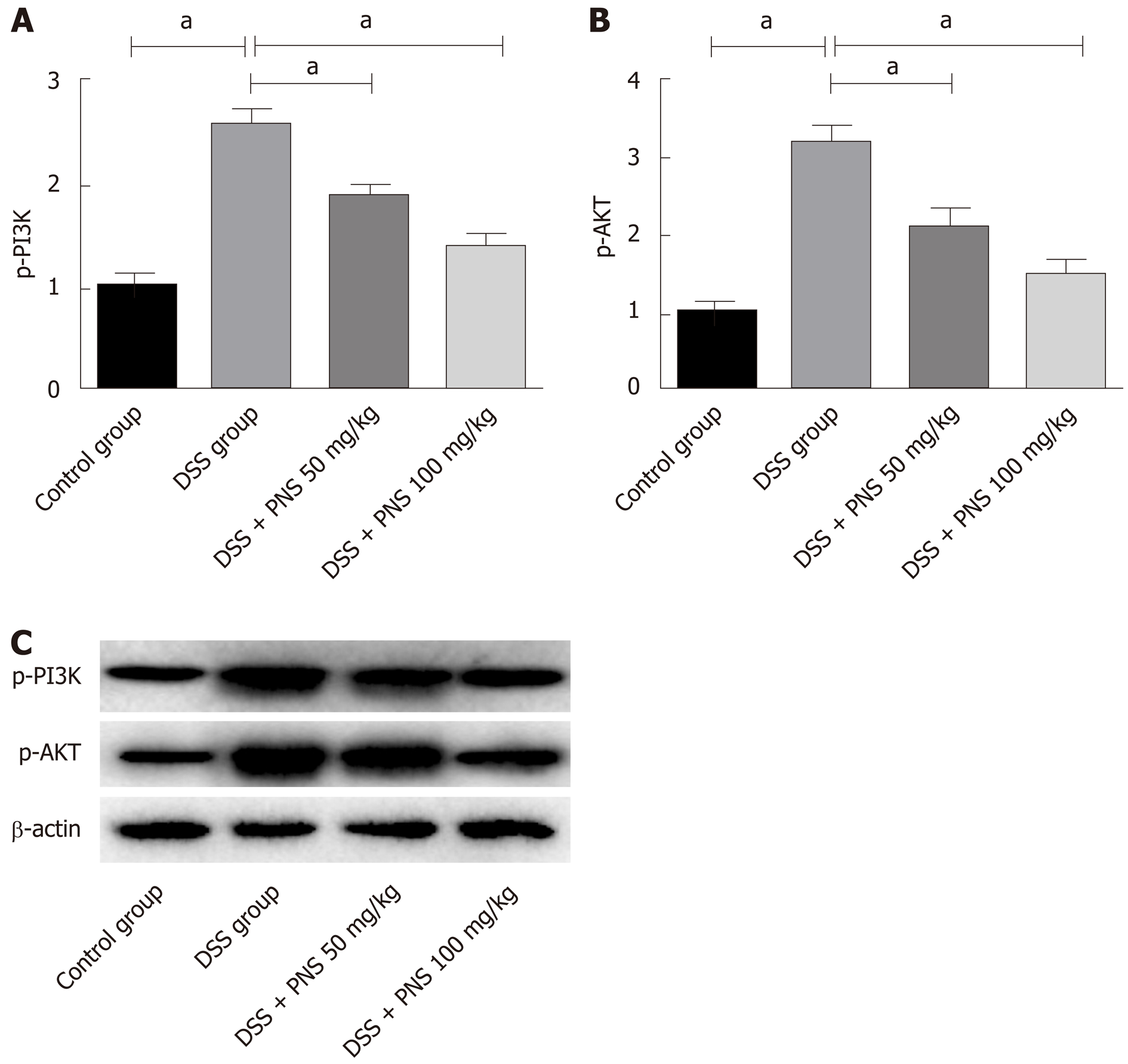
Figure 6 Effects of panax notoginseng saponin on phosphoinositide-3-kinase protein kinase B signaling pathway.
A: Comparison of p-PI3 among the four groups; B: Comparison of p-AKT among the four groups; C: Western blot protein map. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
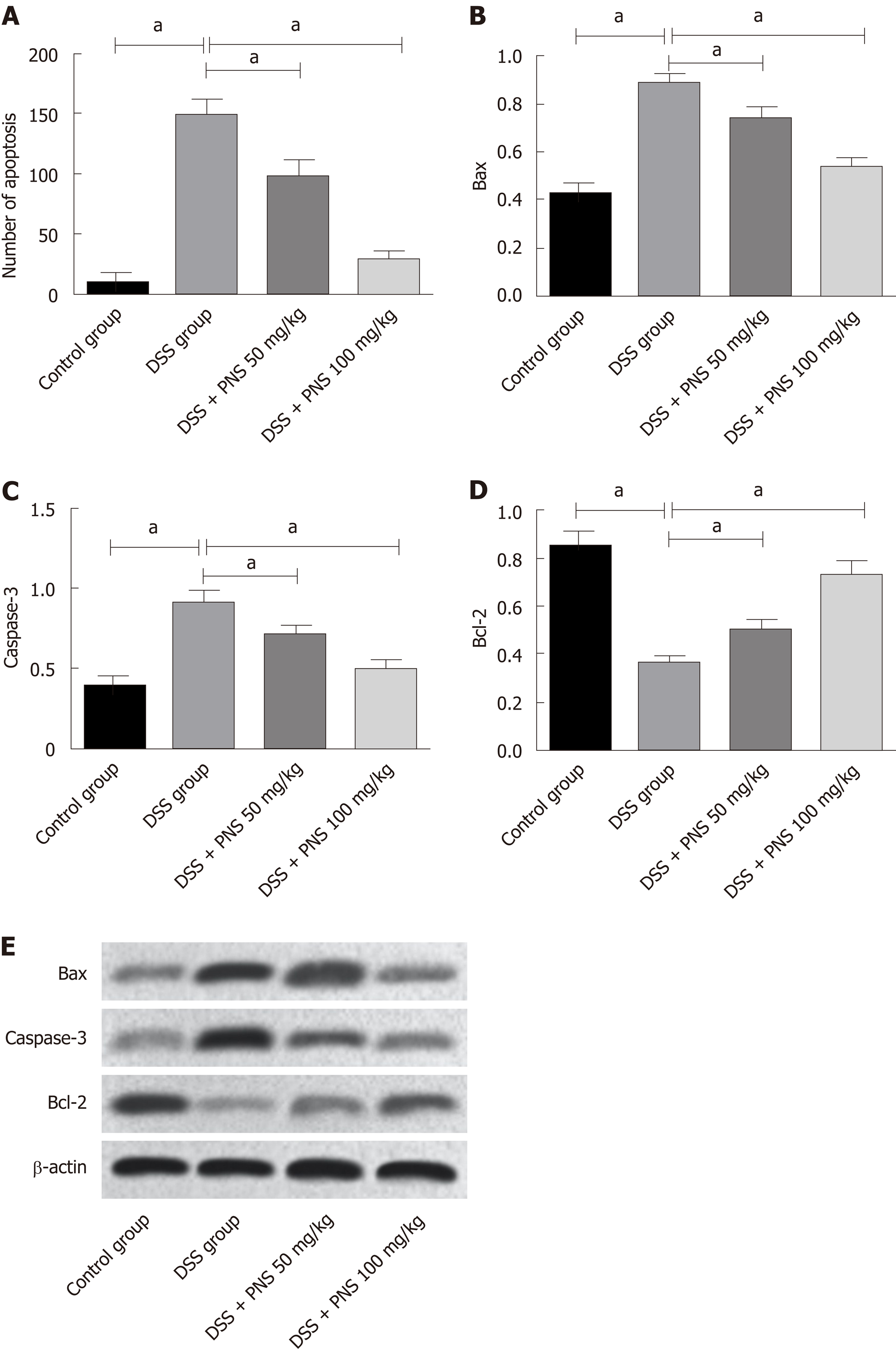
Figure 7 Effects of panax notoginseng saponin on apoptosis in the colon tissues of rats.
A: The number of apoptotic TUNEL-positive cells in rats from the four groups; B: Comparison among the four groups in Bax; C: Comparison among the four groups in Caspase-3; D: Comparison among the four groups in Bcl-2; E: Western blot protein map. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
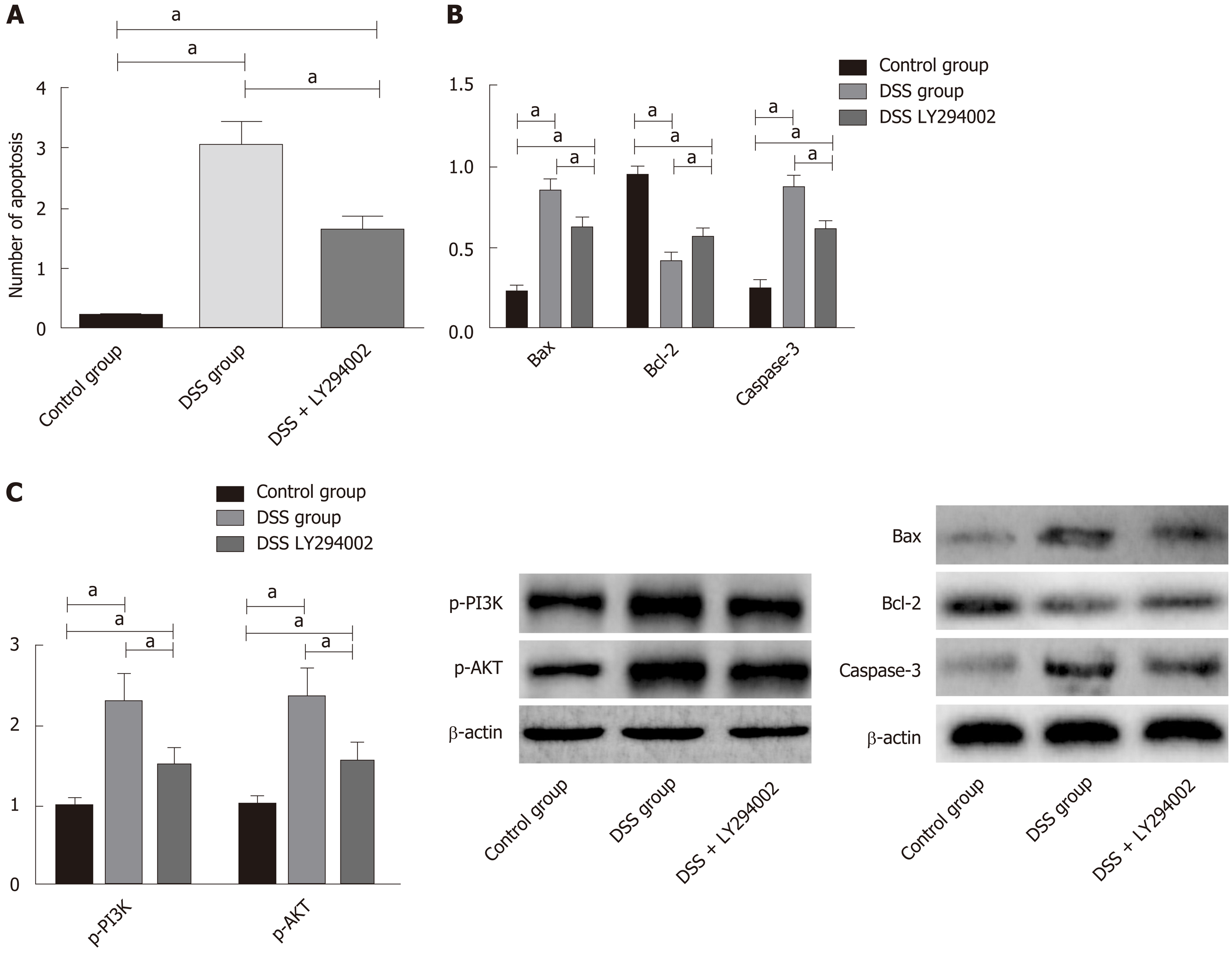
Figure 8 Effects of inhibiting the phosphoinositide-3-kinase protein kinase B signaling pathway on apoptosis of colon tissue cells in colitis rats.
A: Effects of inhibiting the phosphoinositide-3-kinase protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signaling pathway on apoptosis rates of colon tissue cells; B: Effects of inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway on the phosphorylation of PI3K and AKT in the colon tissues of rats; C: Effects of inhibiting the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway on apoptosis-related proteins in colon tissues. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
Figure 9 Macrophage changes in spleen and colon tissues.
A: Percentage of CD11b+F4/80-labeled macrophages in spleen and colon tissues; B: CD16/32-labeled MI macrophages in spleen and colon tissues; C: CD206-labeled M2 macrophages in spleen and colon tissues; D, E: Flow cytometry. aP < 0.05. PNS: Panax notoginseng saponin; DSS: Dextran sulfate sodium.
- Citation: Lu QG, Zeng L, Li XH, Liu Y, Du XF, Bai GM, Yan X. Protective effects of panax notoginseng saponin on dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in rats through phosphoinositide-3-kinase protein kinase B signaling pathway inhibition. World J Gastroenterol 2020; 26(11): 1156-1171
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v26/i11/1156.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v26.i11.1156