Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 7, 2019; 25(45): 6653-6667
Published online Dec 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6653
Published online Dec 7, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6653
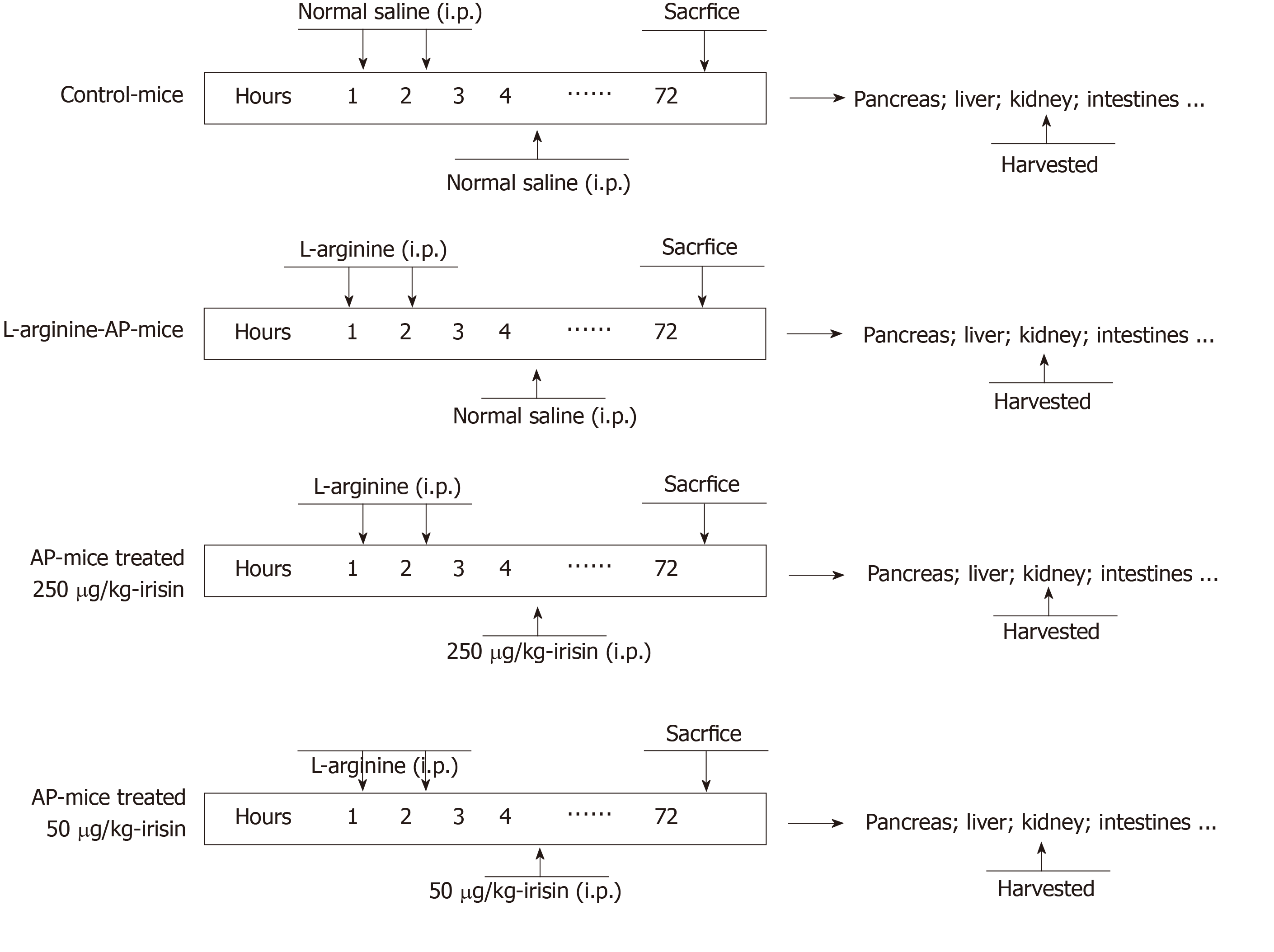
Figure 1 Mouse acute pancreatitis model schedule.
Arginine-acute pancreatitis was induced by two hourly intraperitoneal injections of 4.0 g/kg L-arginine. At 2 h after the last injection of L-arginine, normal saline (vehicle) or 50 μg/kg or 250 μg/kg irisin were administered through intraperitoneal injection. The animals were sacrificed 69 h after irisin treatment (i.e. 72 h after the first injection of L-arginine). Blood and tissue samples were collected. Model schedule for each group of mice. n = 6. AP: Acute pancreatitis; i.p.: Intraperitoneal injection.
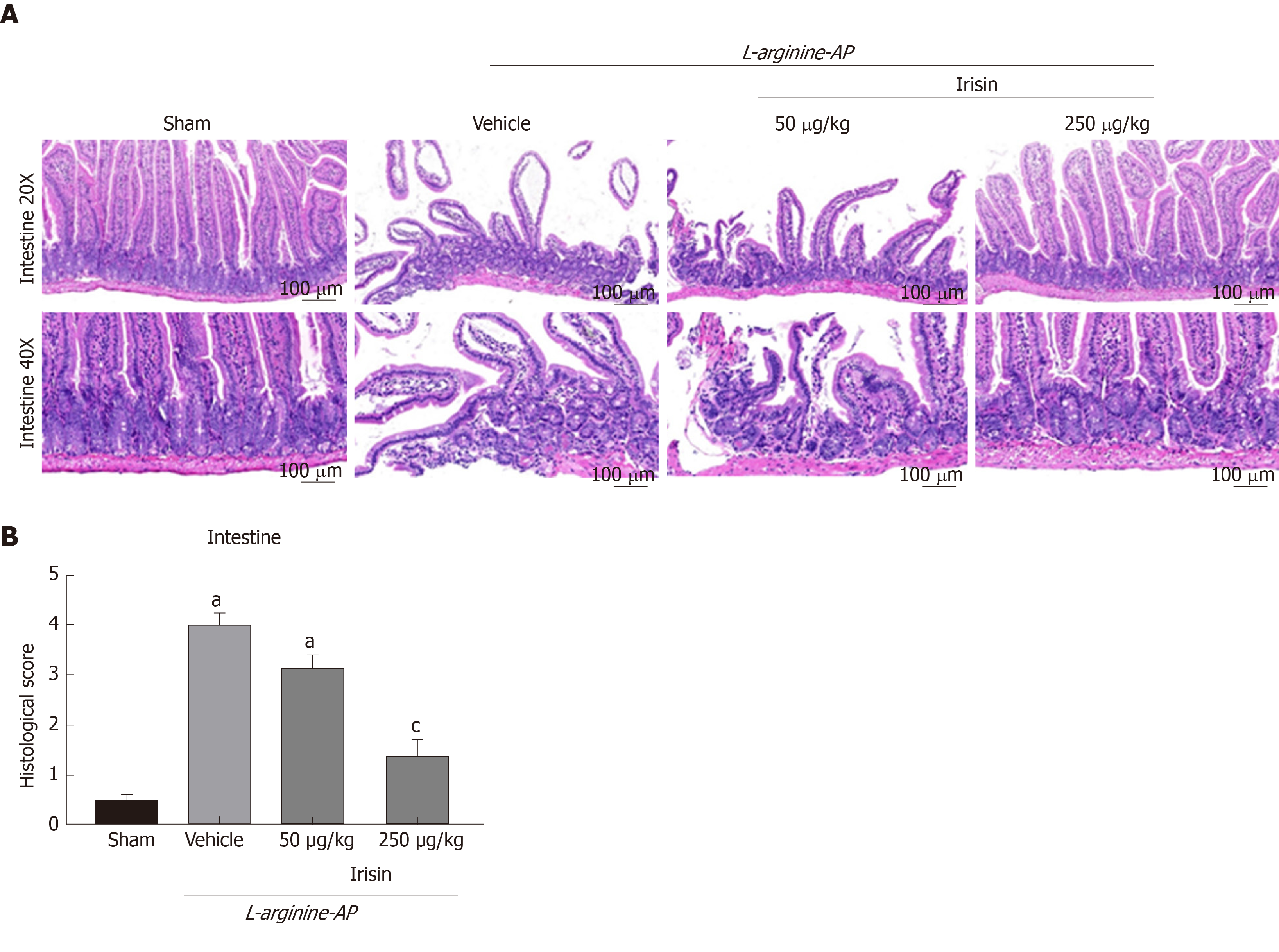
Figure 2 Irisin administration attenuates intestinal injury in experimental acute pancreatitis.
A: Representative photos of hematoxylin and eosin staining; B: Intestinal injury scores. n = 6, mean ± standard error of mean; aP < 0.05 vs sham group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle group. AP: Acute pancreatitis.
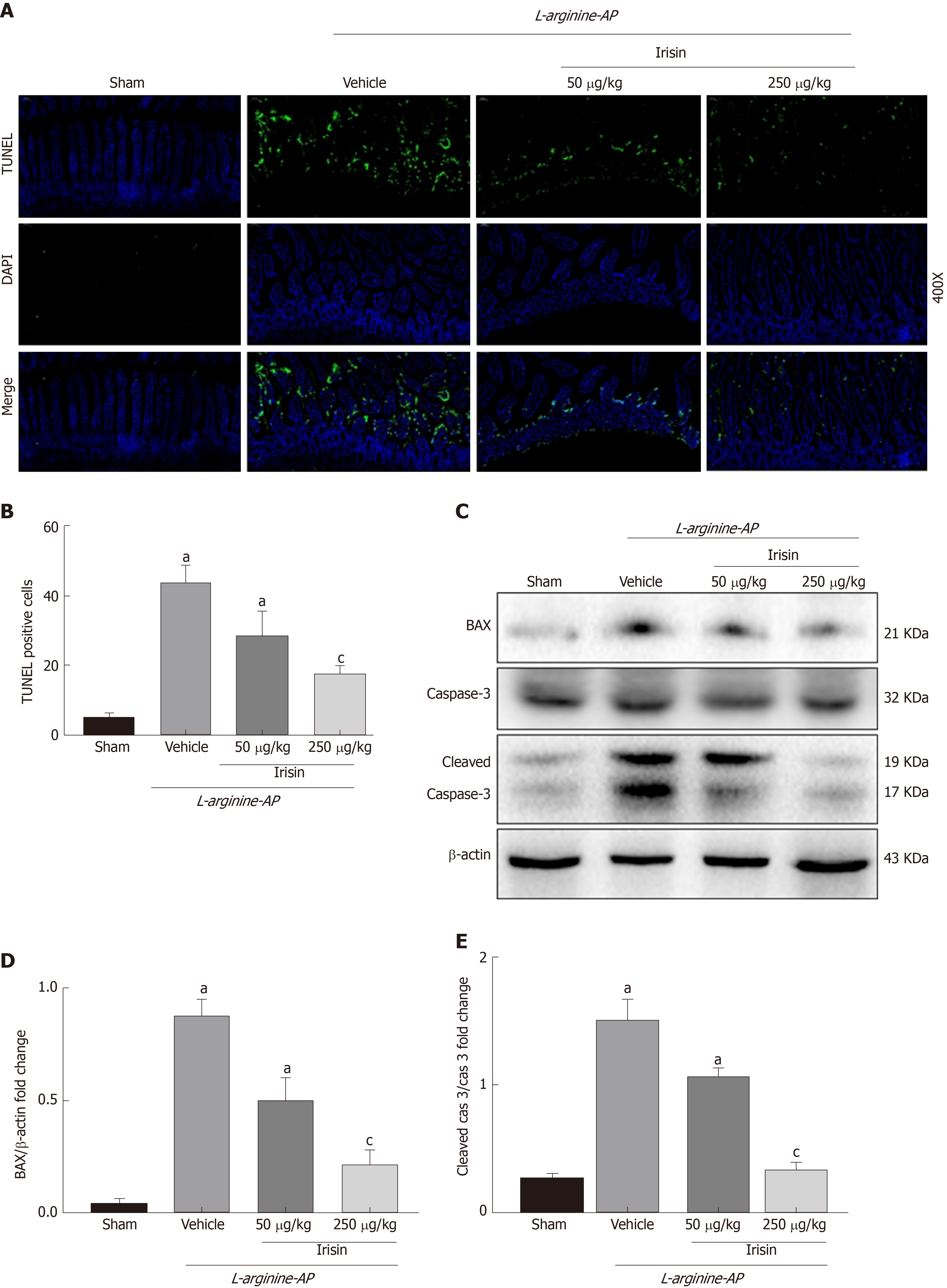
Figure 3 Irisin administration alleviates intestinal apoptosis in experimental acute pancreatitis.
A: Representative photos of TUNEL staining (green) and corresponding nuclear counterstaining (blue) in the intestines; B: Quantitative analysis of TUNEL-positive cells; C-E: Western blot analysis of the expression of BAX, caspase-3 and cleaved caspase-3 in the intestines. n = 6, mean ± standard error of mean; aP < 0.05 vs sham group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle group. AP: Acute pancreatitis; TUNEL: TdT-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling.
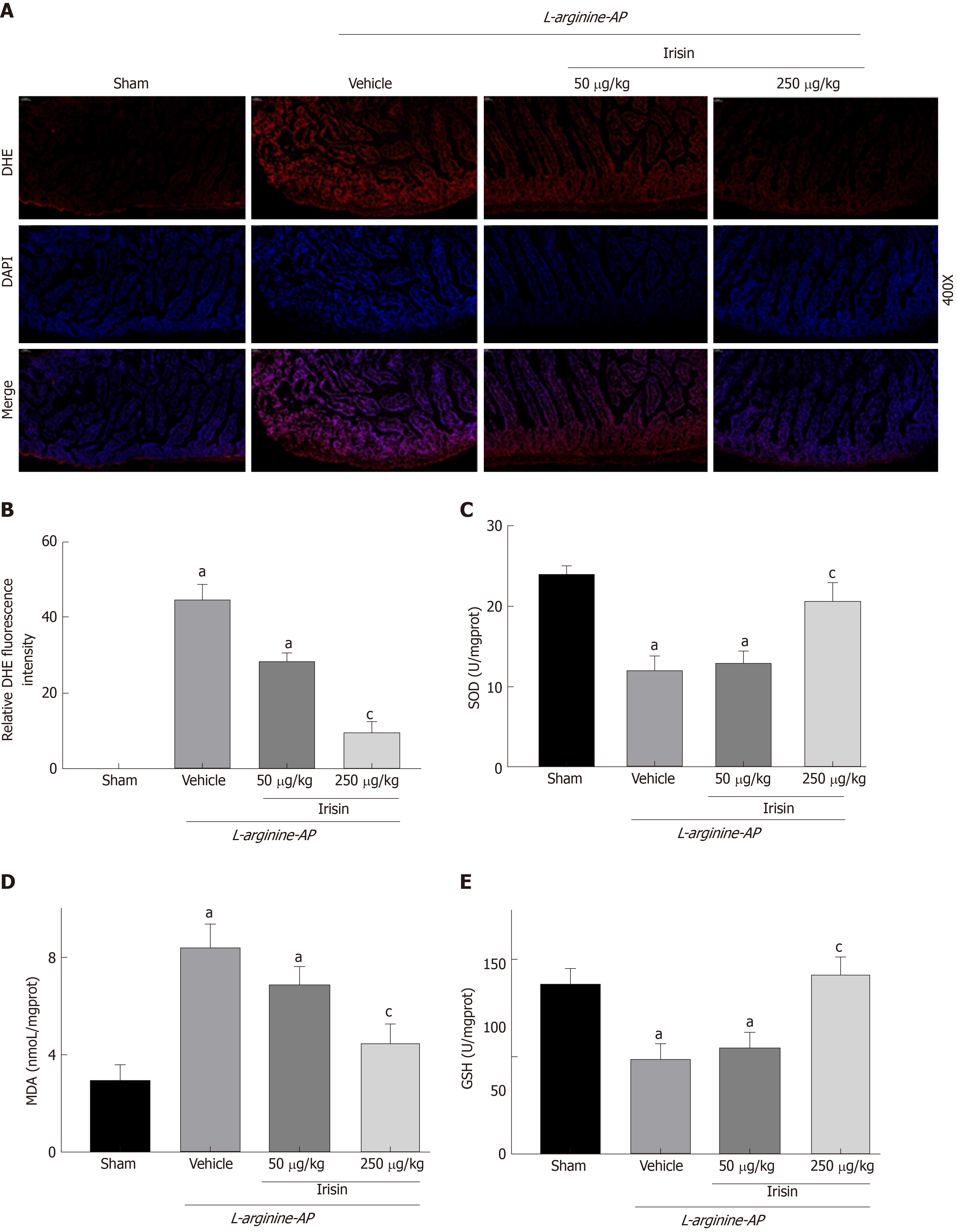
Figure 4 Irisin reduces intestinal oxidative stress in experimental acute pancreatitis.
A: Representative images of dihydroethidium (DHE) fluorescence staining in the intestines; B: Relative fluorescence intensity of DHE fluorescence staining in the intestines; C: Superoxide dismutase levels in the intestinal tissue; D: Malondialdehyde levels in the intestinal tissue; E: Glutathione levels in the intestinal tissue. n = 6, mean ± standard error of mean; aP < 0.05 vs sham group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle group. AP: Acute pancreatitis; DHE: Dihydroethidium; MDA: Malondialdehyde; GSH: Glutathione; SOD: Superoxide dismutase.
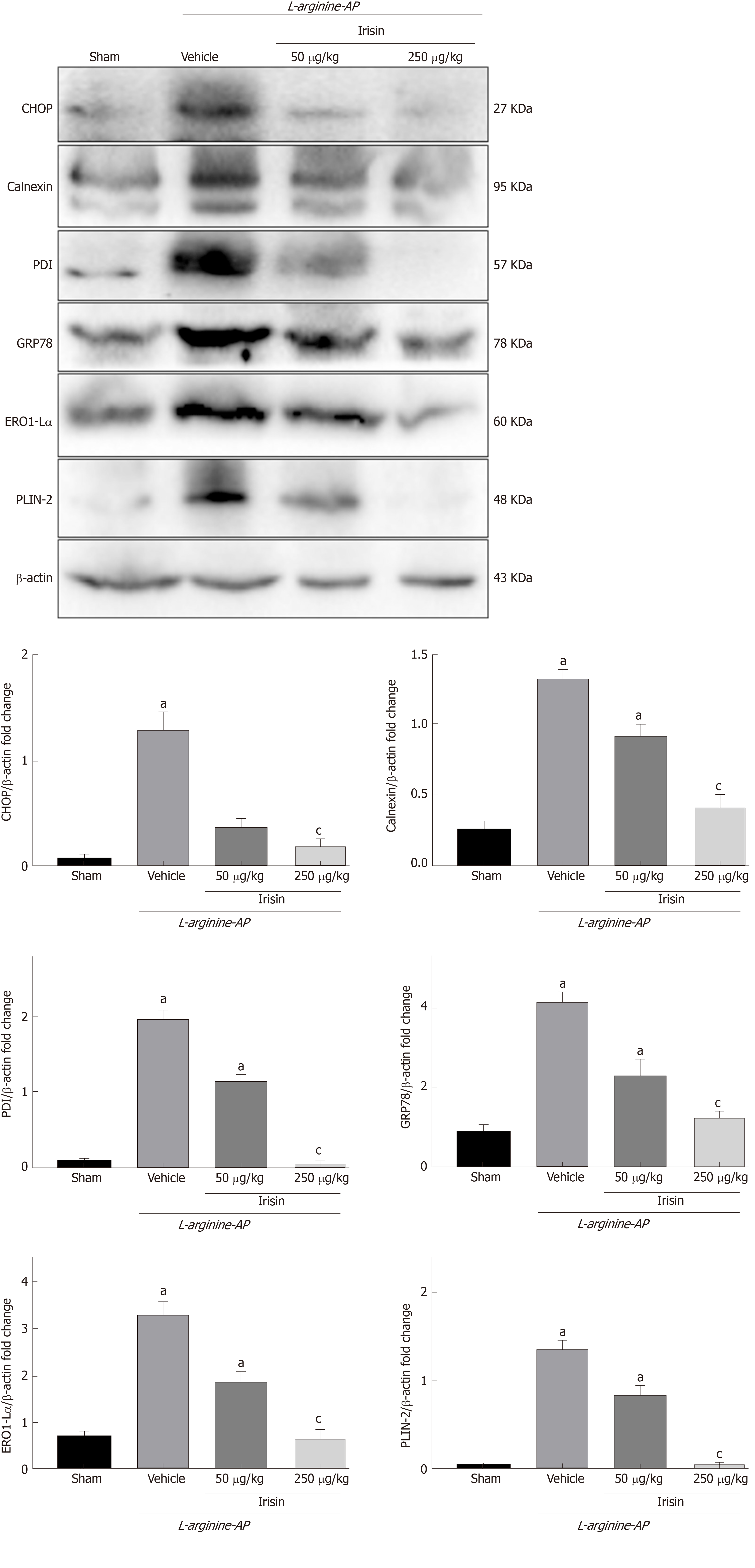
Figure 5 Irisin alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress in experimental acute pancreatitis.
Western blot analysis of the expression of glucose-regulated protein 78, protein disulfide isomerase, endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase 1-Lα, calnexin, C/EBP homologous protein and perilipin-2 in the intestines. n = 6, mean ± standard error of mean; aP < 0.05 vs sham group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle group. AP: Acute pancreatitis; GRP78: Glucose-regulated protein 78; PDI: Protein disulfide isomerase; Ero1-Lα: Endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductase 1-Lα; CHOP: C/EBP homologous protein; PLIN2: Perilipin-2.
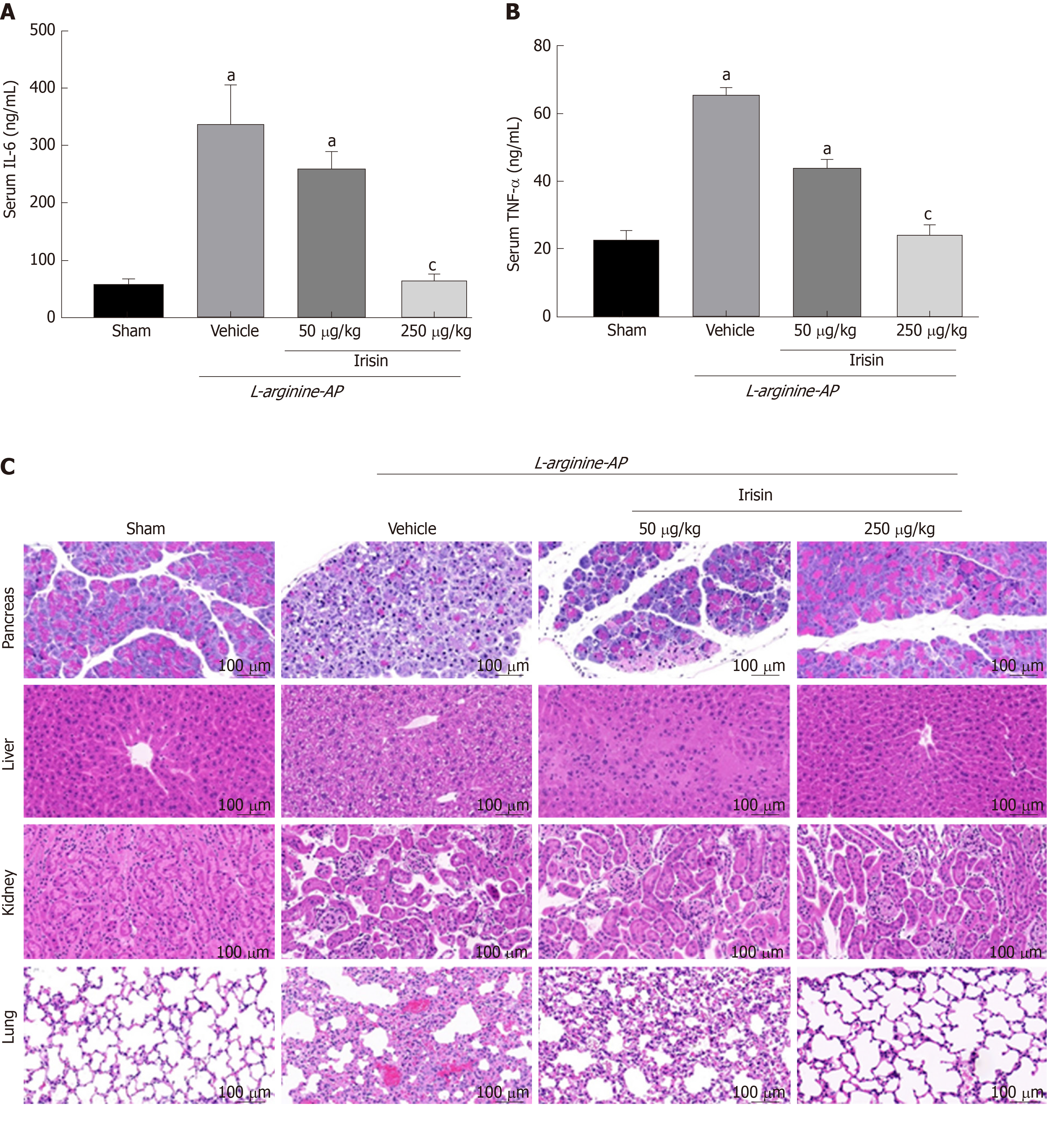
Figure 6 Protective effects of irisin on multiple organ damage in acute pancreatitis.
A: Serum IL-6 levels; B: Serum TNF-α levels; C: Representative photos of hematoxylin and eosin staining; D: Renal, hepatic, pancreatic and pulmonary injury scores. n = 6, mean ± standard error of mean; aP < 0.05 vs sham group; cP < 0.05 vs vehicle group. AP: Acute pancreatitis; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
- Citation: Ren YF, Wang MZ, Bi JB, Zhang J, Zhang L, Liu WM, Wei SS, Lv Y, Wu Z, Wu RQ. Irisin attenuates intestinal injury, oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress in mice with L-arginine-induced acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(45): 6653-6667
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i45/6653.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6653