Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2019; 25(31): 4512-4533
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4512
Published online Aug 21, 2019. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4512
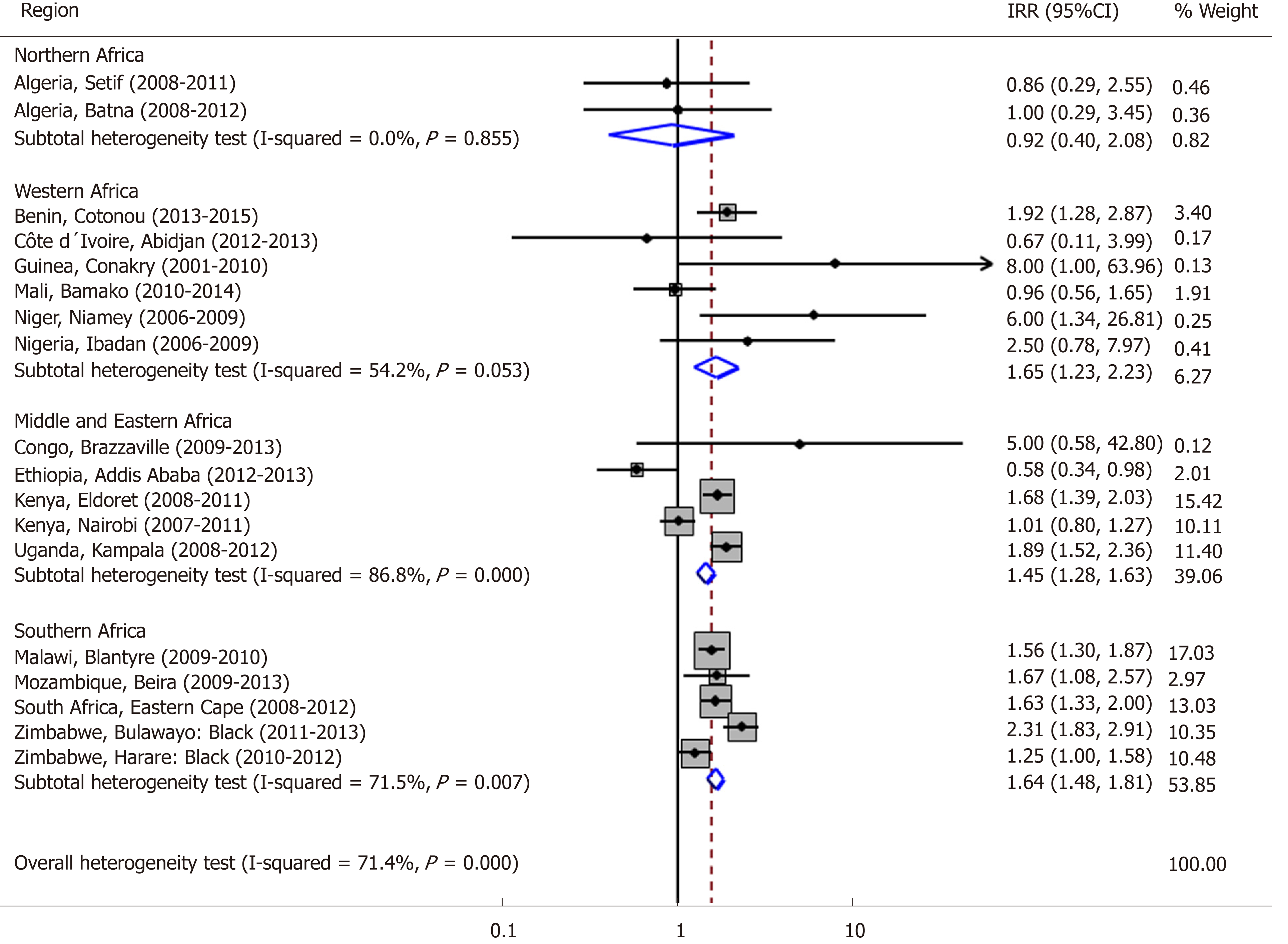
Figure 1 Forest plot displaying the inverse-variance weighted fixed-effect meta-analysis of the age-standardized incidence rate ratio for oesophageal cancer in males vs females by region in 18 urban populations in Africa, 2009-2013.
IRR: Incidence rate ratio; CI: Confidence interval.
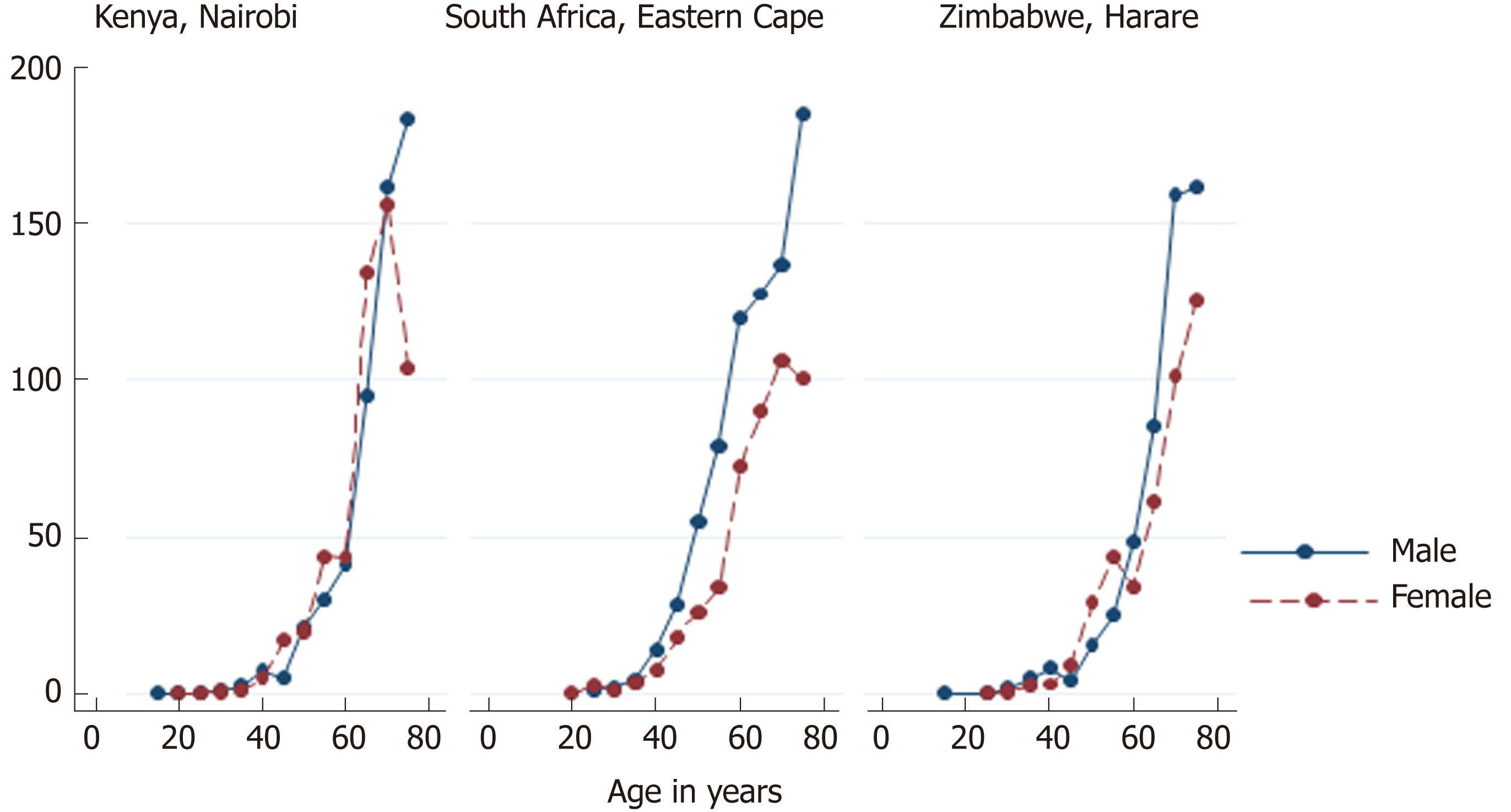
Figure 2 Age-specific incidence rates for esophageal cancer among males and females in Africa, 2009-2013[18].
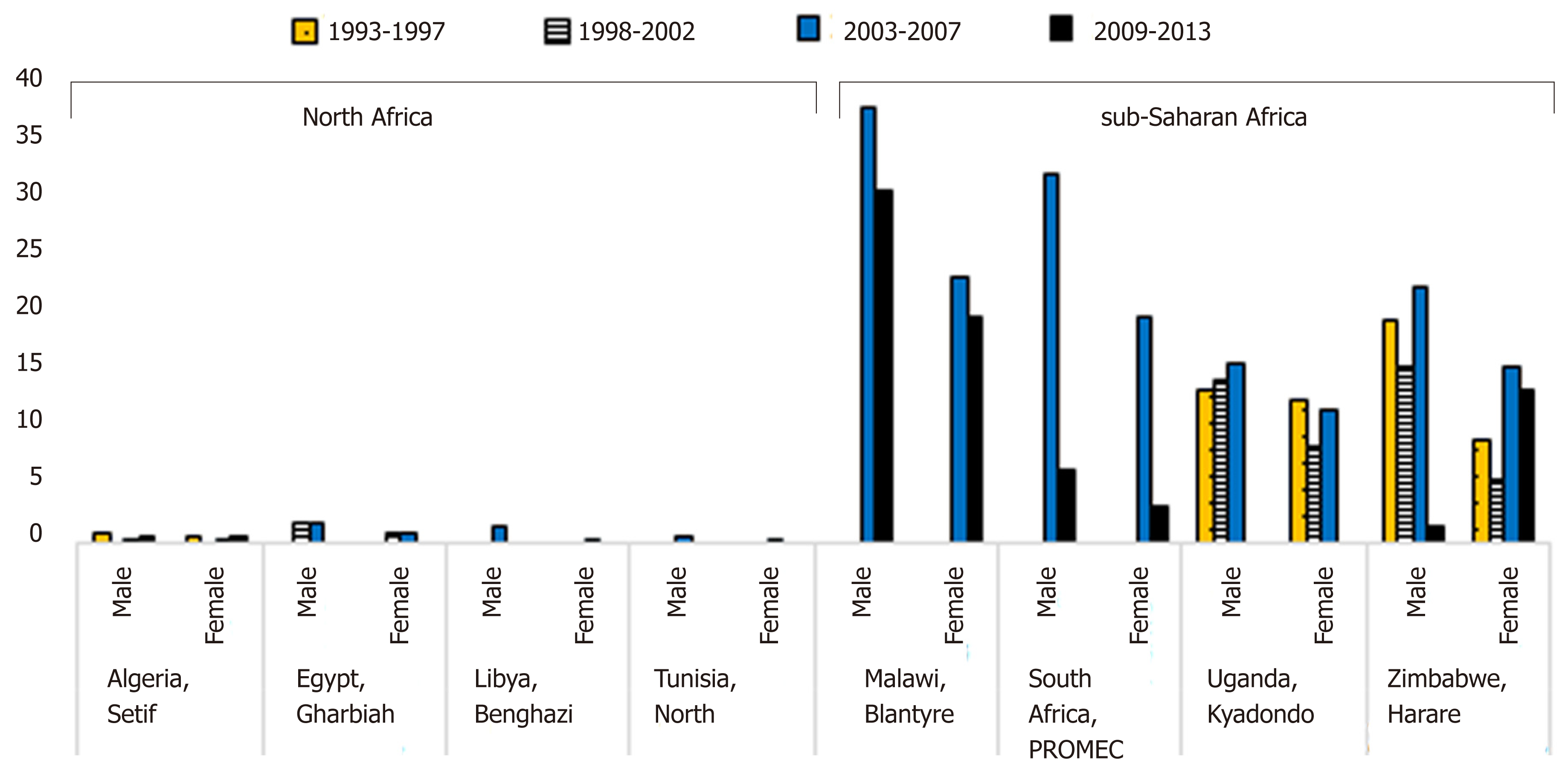
Figure 3 Age-standardized incidence trends for esophageal cancer by calendar year and gender in Africa, 1993-2013[17].
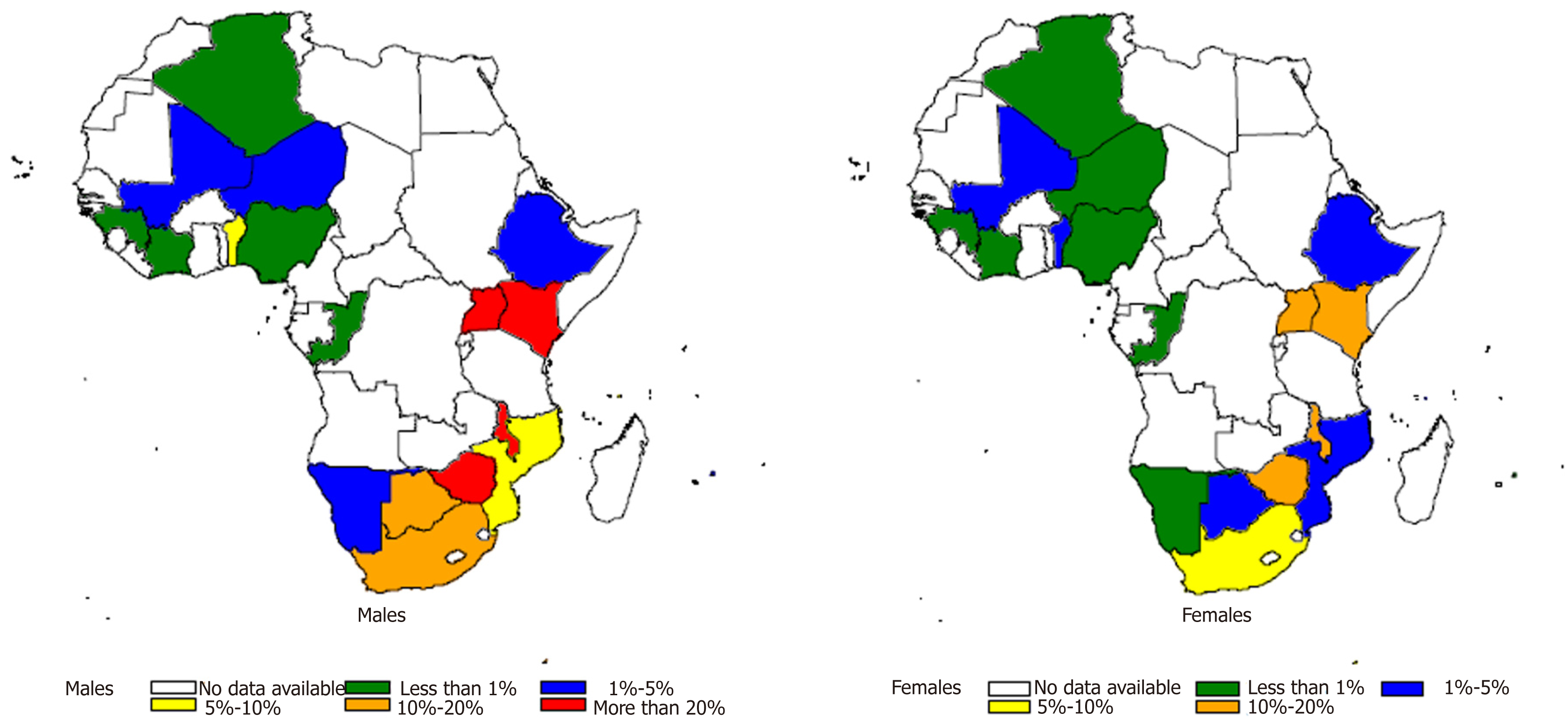
Figure 4 Age-standardized incidence rates for males and females by country in Africa, 2009-2013[18].
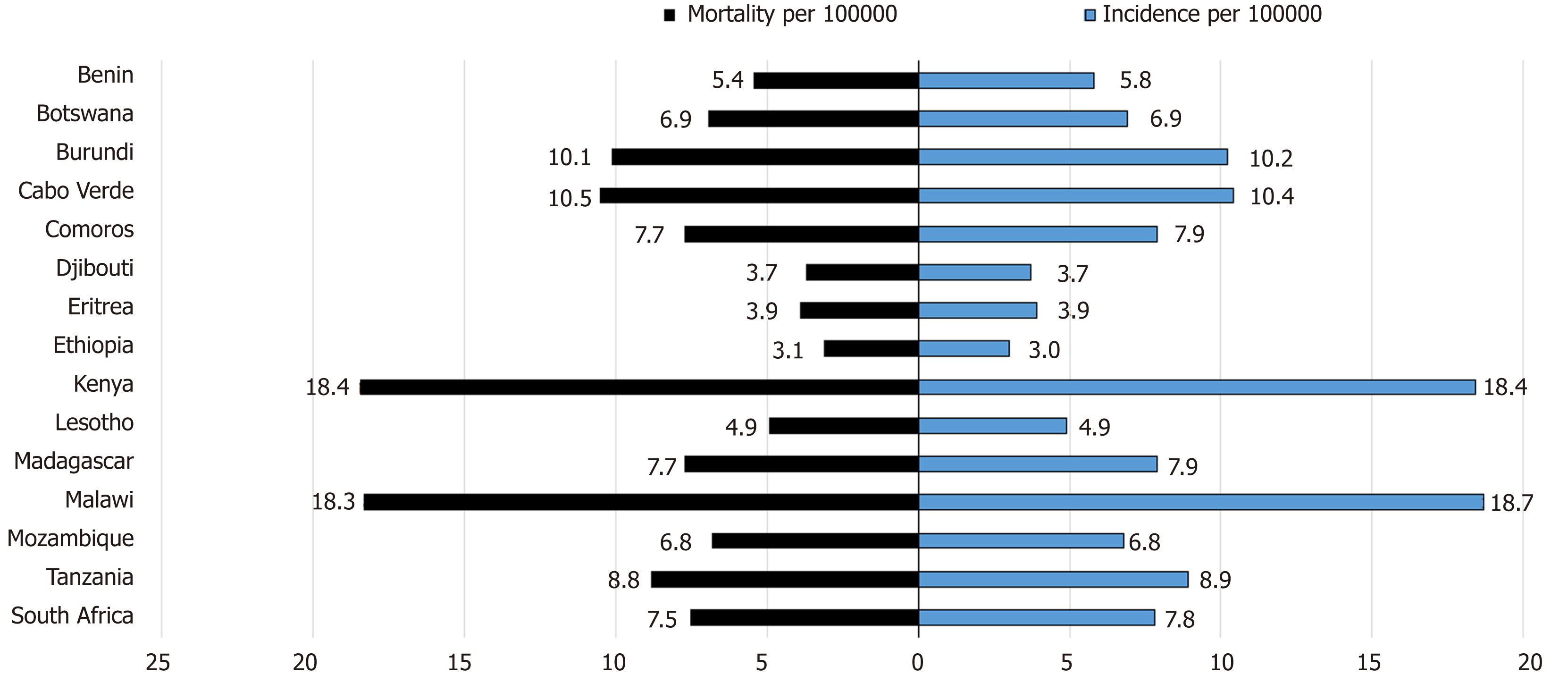
Figure 5 Estimated age-standardized mortality and incidence rates for both males and females from selected African countries, 2018.
Data Source: International Agency for Research on Cancer[21].
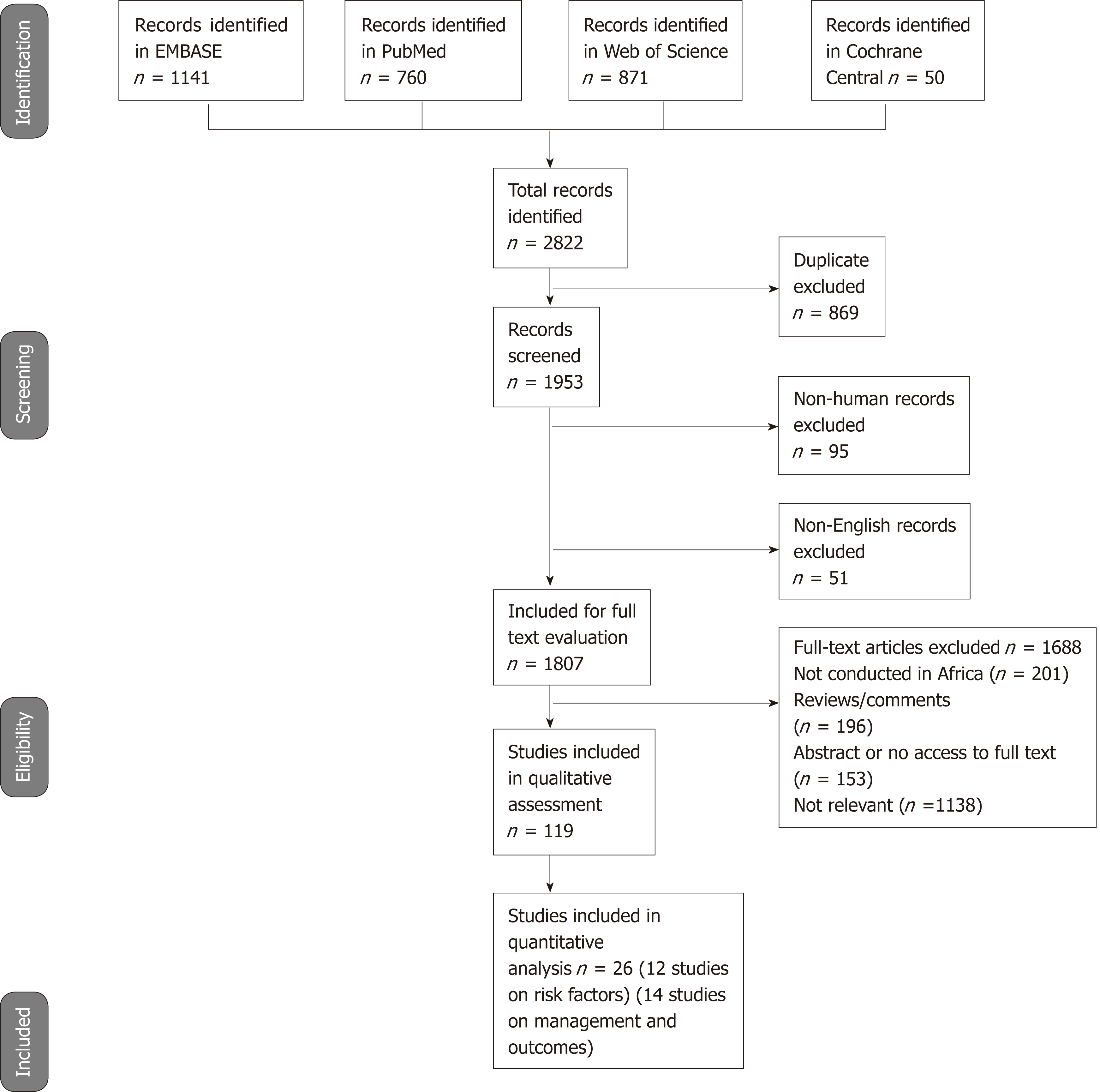
Figure 6 Flow diagram for literature review.
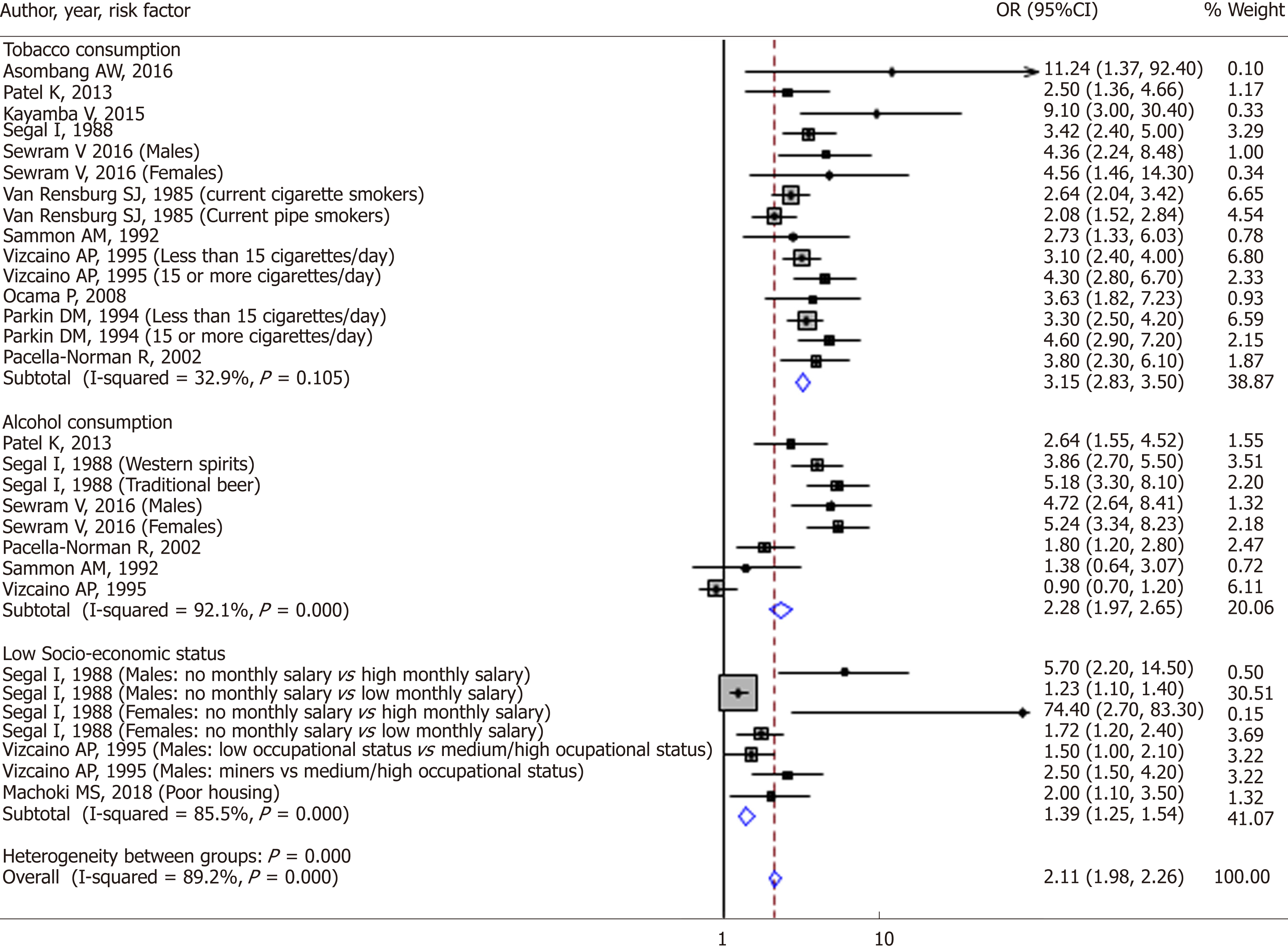
Figure 7 Forest plot displaying the inverse-variance weighted fixed-effect meta-analysis of risk factors for esophageal cancer in Africa.
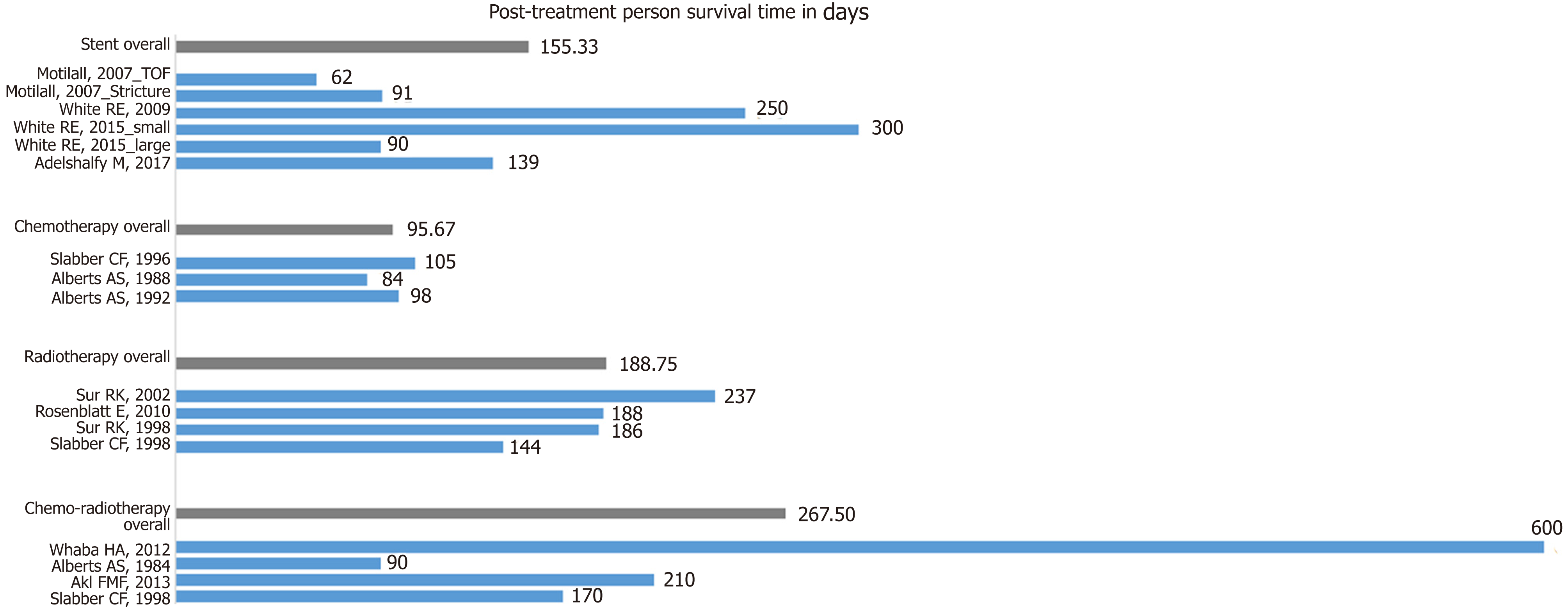
Figure 8 Shows the median post-treatment survival times in days for Stent, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, chemo-radiation and respective treatment of esophageal cancer in Africa.
- Citation: Asombang AW, Chishinga N, Nkhoma A, Chipaila J, Nsokolo B, Manda-Mapalo M, Montiero JFG, Banda L, Dua KS. Systematic review and meta-analysis of esophageal cancer in Africa: Epidemiology, risk factors, management and outcomes. World J Gastroenterol 2019; 25(31): 4512-4533
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v25/i31/4512.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v25.i31.4512