Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2018; 24(47): 5366-5378
Published online Dec 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i47.5366
Published online Dec 21, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i47.5366
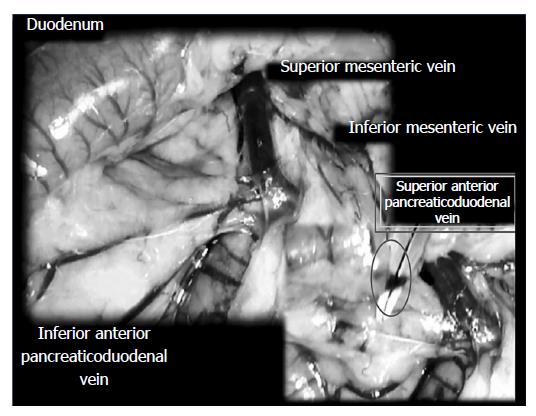
Figure 1 Model illustration of major venous obstruction and duodenal lesions in rat.
The major venous obstruction and duodenal lesions in rat, and therapy solution with the stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157, model illustration. Superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein (SAPDV) was occluded by ligation (Premilene 7/0, Braun), 5 arcade vessels at duodenal serosa within the SAPDV tributaries, the 30-mm blood-flow disturbed duodenum segment was the marked area; inferior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein and superior mesenteric vein as bypassing loop.
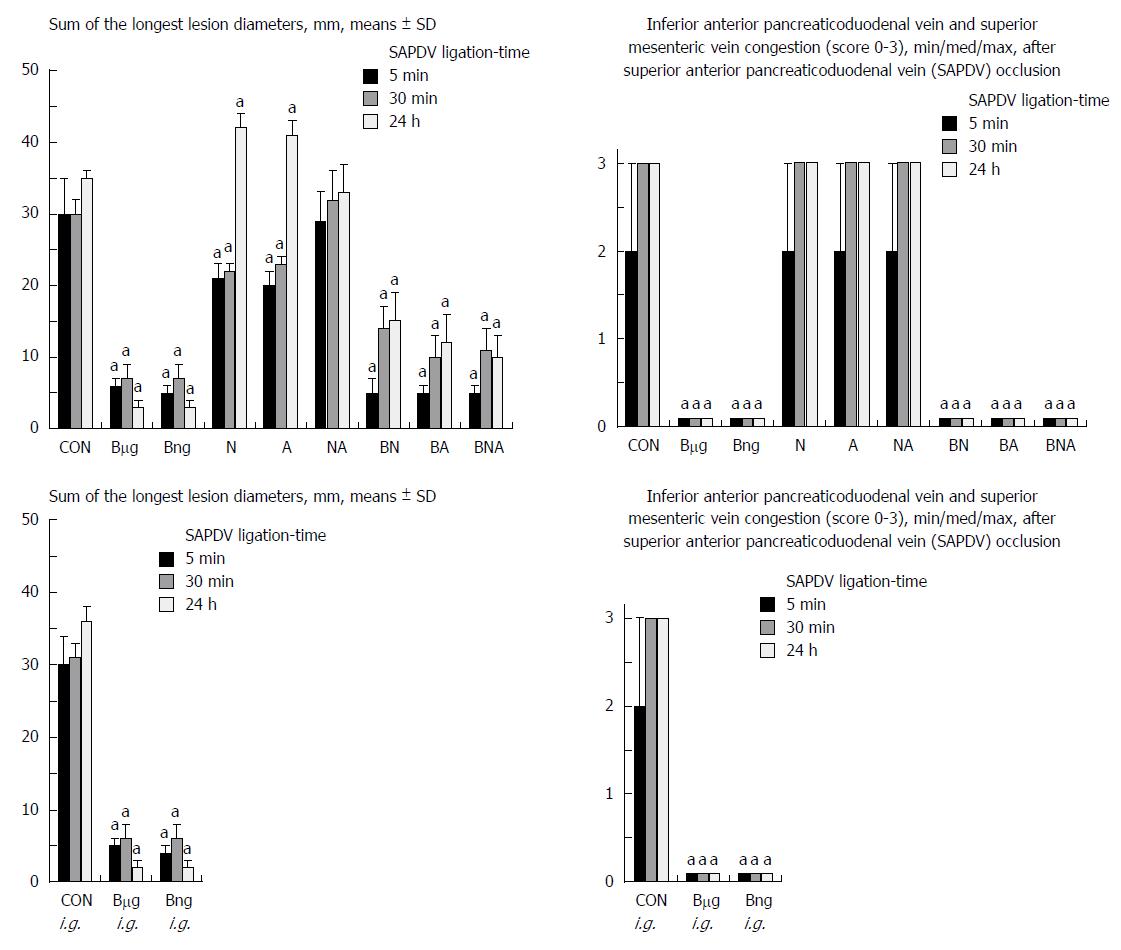
Figure 2 Duodenal lesions as a sum of the longest lesions diameters (left); Inferior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein and superior mesenteric vein congestion, scored 0-3 (right).
The gross appearance of the tissue was recorded using a USB microscope camera. At 1 min post-injury, medication [BPC 157, 10 μg/kg (Bμg), 10 ng/kg (Bng), L-NAME, 5 mg/kg (N), L-arginine, 100 mg/kg (A) alone and /or together (NA, BN, BA, BNA) 1 mL bath/rat] or an equal volume of a saline was applied to the duodenum of the superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein (SAPDV)-ligated rats (upper); alternatively, at 1 min post-injury, medication was Bμg i.g., Bng i.g., 1 mL inistillation into the stomach or an equal volume of a saline instilled into the stomach of the SAPDV-ligated rats (CON i.g.) (lower). The rats were sacrificed 5 min, 30 min or 24 h later. aP < 0.05 vs saline. Bng: BPC 157, 10 ng/kg; Bμg: BPC 157, 10 μg/kg; N: L-NAME, 5 mg/kg; A: L-arginine, 100 mg/kg; NA: L-NAME+L-arginine; BN: BPC 157+L-NAME; BA: BPC 157+L-arginine; BNA: BPC 157+L-NAME+L-arginine; SAPDV: Superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein.
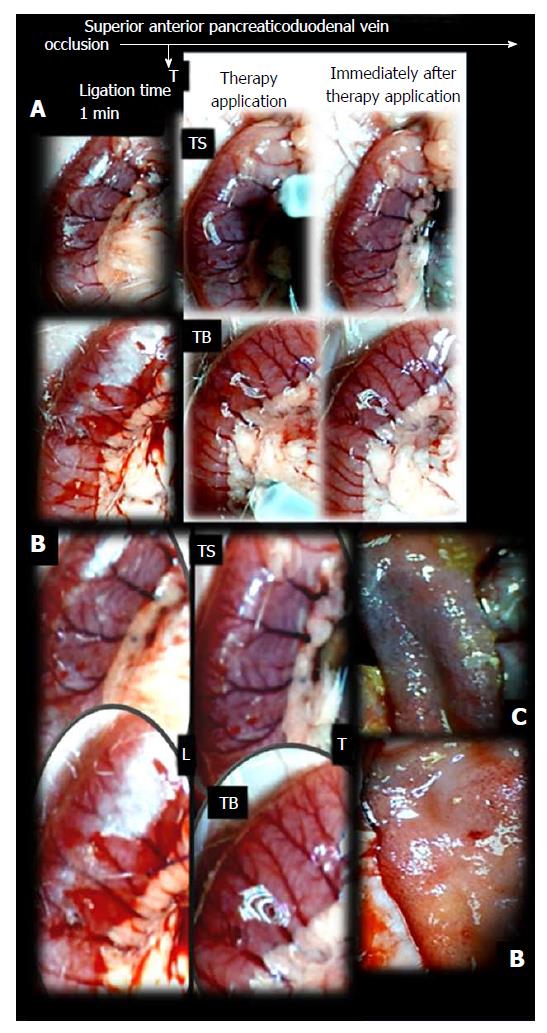
Figure 3 Characteristic appearance of the duodenum in superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein-ligated rats.
A: The characteristic appearance of the duodenum in superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein (SAPDV)-ligated rats after ligation (before therapy), and then with therapy: during and immediately after medication bath [saline (upper); BPC 157 (lower) application; duodenum opening before sacrifice at 5 min ligation-time; USB microscope camera]. Therapy with saline bath. Congested duodenal serosa and duodenal arcades with few vessels branching before, during and after medication saline bath. The congested haemorrhagic area was observed upon duodenal opening after saline bath treatment in rats that underwent obstruction of the SAPDV for 5 min. Therapy with BPC 157 bath. Immediately with BPC 157 medication applied as a bath apparently not congested serosa and vessels with increased branching replaced congested duodenal serosa and duodenal arcades with few vessel branching. Area without apparent congestion and haemorrhage was observed upon duodenal opening after BPC 157 bath treatment in rats that underwent obstruction of the SAPDV for 5 min; B: High magnification of presentation with ligation, and presentation of the moment immediately with therapy application, as saline bath as medication, or BPC 157 bath medication. L: Ligation; T: Therapy; TS: Therapy with saline bath; TB: Therapy with BPC 157 bath; C: Congested haemorrhagic area; B: Area without apparent congestion and haemorrhage.
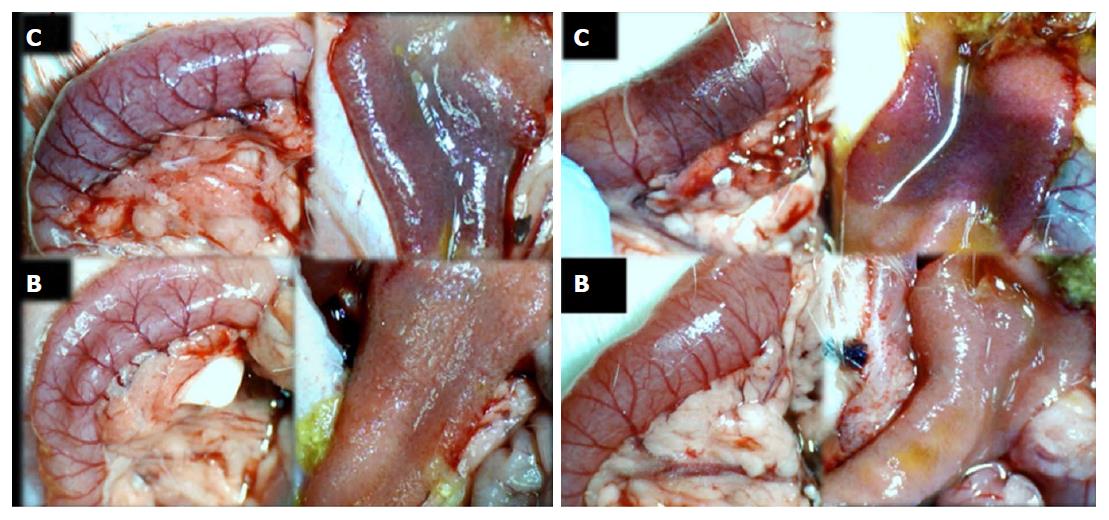
Figure 4 Characteristic appearance of the duodenum in superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein-ligated rats at 30 min (left) or 24 h (right) ligation-time.
After medication bath [saline (upper) (C); BPC 157 (lower) (B) application]; duodenum opening before sacrifice at 30 min (left) or 24 h (right) ligation-time; USB microscope camera. Control: 30 min. Congested duodenal serosa and duodenal arcades with few vessel branching. Congested haemorrhagic upon duodenal opening. 24 h. Severely congested duodenal serosa and duodenal arcades with few vessel branching. Severely congested haemorrhagic upon duodenal opening. BPC 157 therapy: 30 min. Not congested serosa and vessels with increased branching. Area without apparent congestion and haemorrhage was observed upon duodenal opening: 24 h. Not congested serosa and vessels with increased branching. Area without apparent congestion and haemorrhage was observed upon duodenal opening. C: Control; B: BPC 157.
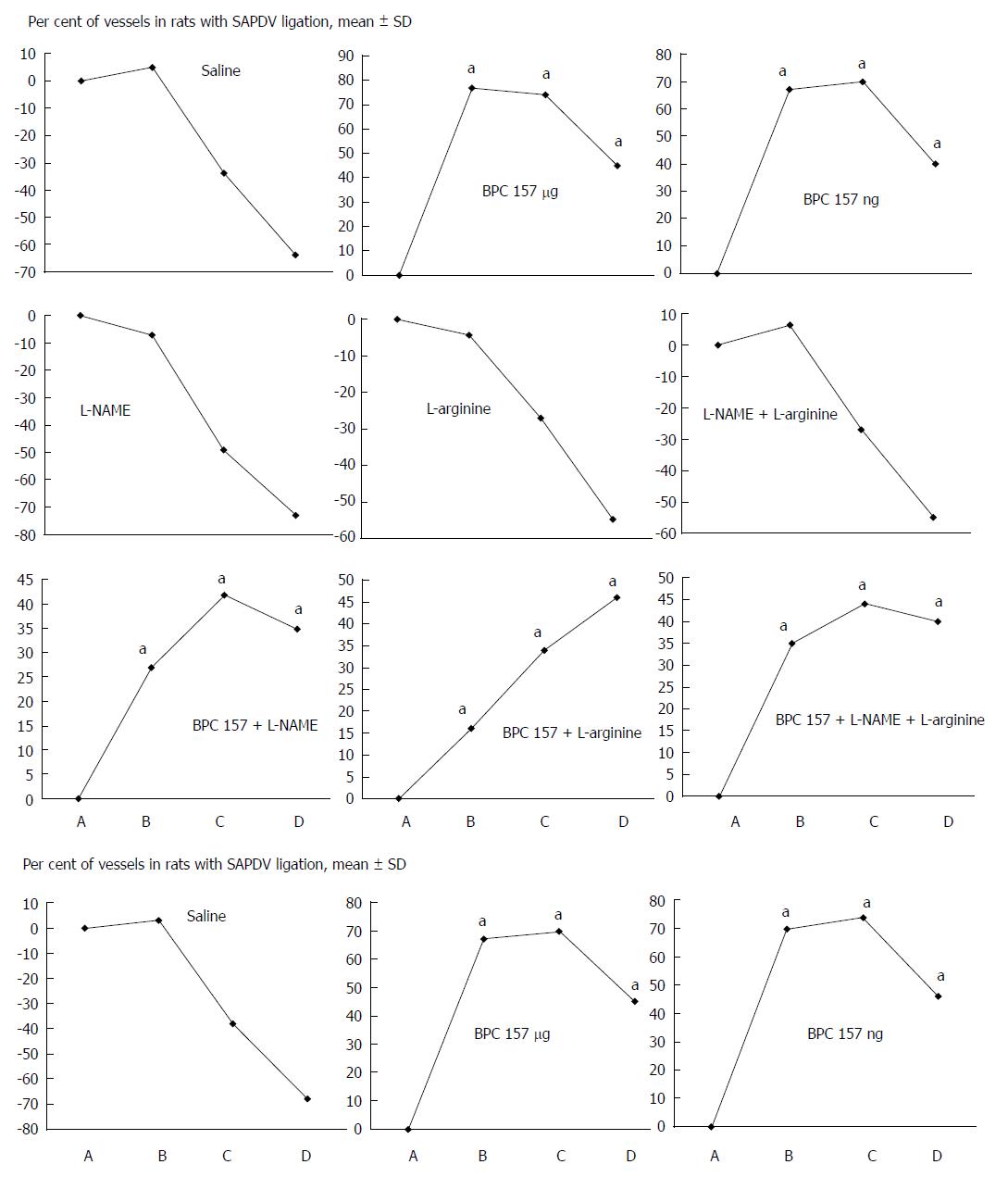
Figure 5 Percent of vessels present between 5 arcade vessels on the ventral side of the duodenum in different time points.
Percent of vessels present between 5 arcade vessels on the ventral side of the duodenum 1 min following ligation before therapy (as 100%) (A); mean ± SD. The gross appearance of the tissue was recorded using a USB microscope camera. The following time points were assessed: A: After ligation and before therapy (1 min); B: 5 min after the application of medication; C: 30 min after the application of medication; D: 24 h after the application of medication. At 1 min post-injury, medication [BPC 157, 10 μg/kg (BPC 157 μg), 10 ng/kg (BPC 157 ng), L-NAME, 5 mg/kg (L-NAME), L-arginine, 100 mg/kg (L-arginine) alone and/or together (L-NAME+L-arginine, BPC 157+L-NAME,BPC 157+L-arginine, BPC 157+L-NAME+L-arginine) 1 mL bath/rat] or an equal volume of a saline was applied to the duodenum of the SAPDV-ligated rats (upper); alternatively, at 1 min post-injury, medication was BPC 157 μg, BPC 157 ng, 1 mL inistillation into the stomach or an equal volume of a saline (saline) instilled into the stomach of the superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein-ligated rats (lower). The rats were sacrificed 5 min, 30 min or 24 h later. For clarity, the SD is not shown on the graph; the SD was never higher than 10% of the mean. aP < 0.05 vs saline. BPC 157 μg: BPC 157, 10 μg/kg; BPC 157 ng: BPC 157, 10 ng/kg; L-NAME: L-NAME, 5 mg/kg; L-arginine: L-arginine, 100 mg/kg.
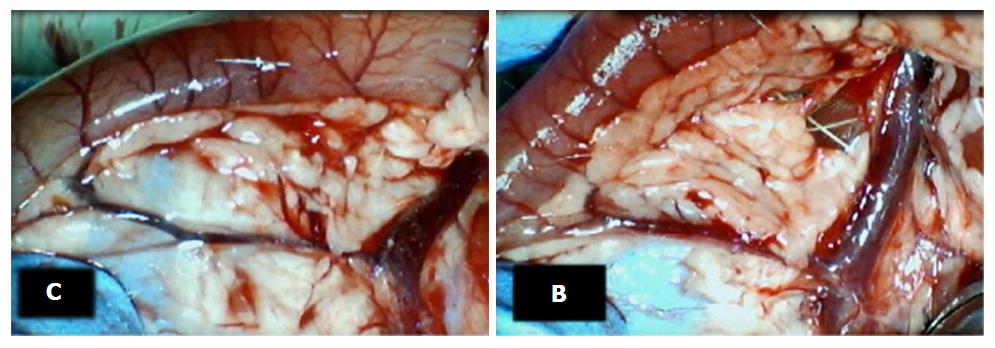
Figure 6 Characteristic appearance of inferior anterior pancreaticoduodenal and superior mesenteric vein presentation in superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein-ligated rats at 24 h ligation time.
Control, left (C). Congested inferior anterior pancreaticoduodenal and superior mesenteric vein presentation along with duodenal serosa and arcade vessels. during and immediately after medication bath [saline (C); BPC 157, right (B)]. Presentation close to normal, unlike congested inferior anterior pancreaticoduodenal and superior mesenteric vein presentation along with duodenal serosa and arcade vessels in controls. C: Control; B: BPC 157.
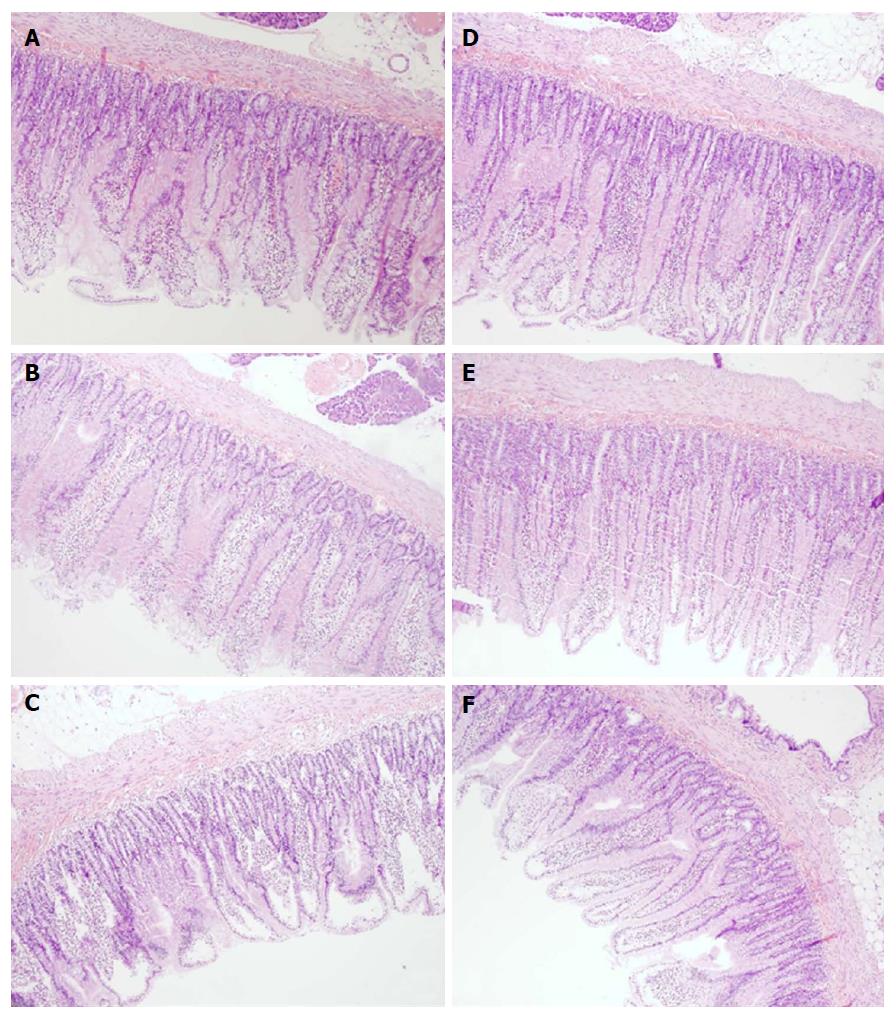
Figure 7 Microscopical presentation of duodenal lesions.
Microscopically (Hex10), in controls the lesions progressed from mild villous edema with mild lymphocytic infiltrate (5 min ligation time) (A) toward denuded villous tops with marked villous edema and submucosal capillary congestion (30 min ligation time) (B) to the substantial subepithelial space with abundant lifting of epithelial layer from lamina propria extending down sides of villi, villous edema with capillary congestion, submucosal congestion and lymphocytic infiltrate (24 h ligation time) (C). BPC 157 rats (D, E, F) exhibited always intestinal preservation with only mild villous edema and mild lymphocytic infiltrate. Elevation of epithelium from lamina propria was found only on the apical portion of villi (24 h ligation time, F).
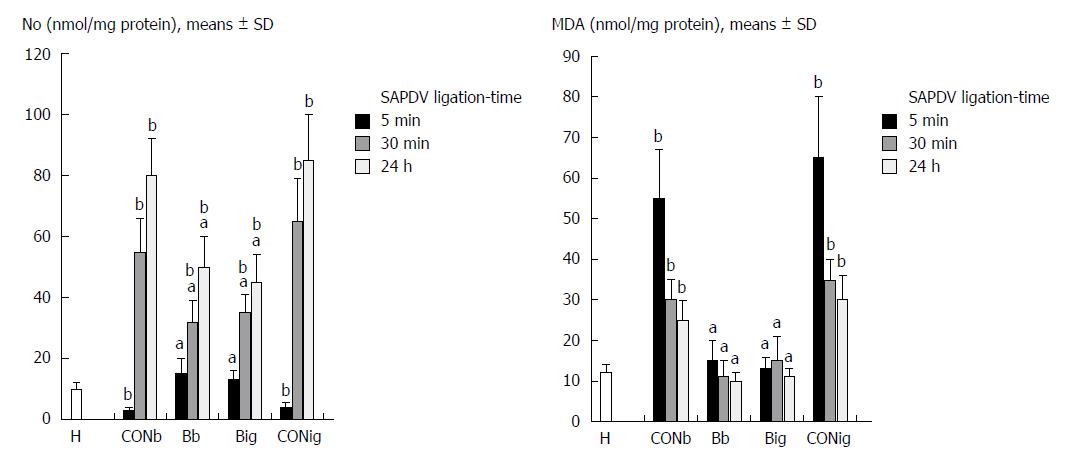
Figure 8 Nitric oxide levels and malondialdehyde levels in the duodenal tissue of superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein-ligated rats at 5 min, 30 min and 24 h ligation.
BPC 157 [10 μg/kg, 1 mL bath/rat (Bb), 1 mL instilled into the stomach (Big)] or an equal volume of a saline bath (CONb) or instillation in the stomach (CONig) (controls) was applied to superior anterior pancreaticoduodenal vein-ligated rats. aP < 0.05 vs saline; bP < 0.05 vs healthy duodenum. H: Healthy duodenum; Bb: BPC 157 10 μg/kg, 1 mL bath/rat; Big: BPC 157 10 μg/kg, 1 mL instilled into the stomach; CONb: 1 mL saline bath; CONig: 1 mL saline instillation in the stomach; NO: Nitric oxide; MDA: Malondialdehyde.
- Citation: Amic F, Drmic D, Bilic Z, Krezic I, Zizek H, Peklic M, Klicek R, Pajtak A, Amic E, Vidovic T, Rakic M, Milkovic Perisa M, Horvat Pavlov K, Kokot A, Tvrdeic A, Boban Blagaic A, Zovak M, Seiwerth S, Sikiric P. Bypassing major venous occlusion and duodenal lesions in rats, and therapy with the stable gastric pentadecapeptide BPC 157, L-NAME and L-arginine. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(47): 5366-5378
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i47/5366.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i47.5366