Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2018; 24(10): 1093-1106
Published online Mar 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i10.1093
Published online Mar 14, 2018. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i10.1093
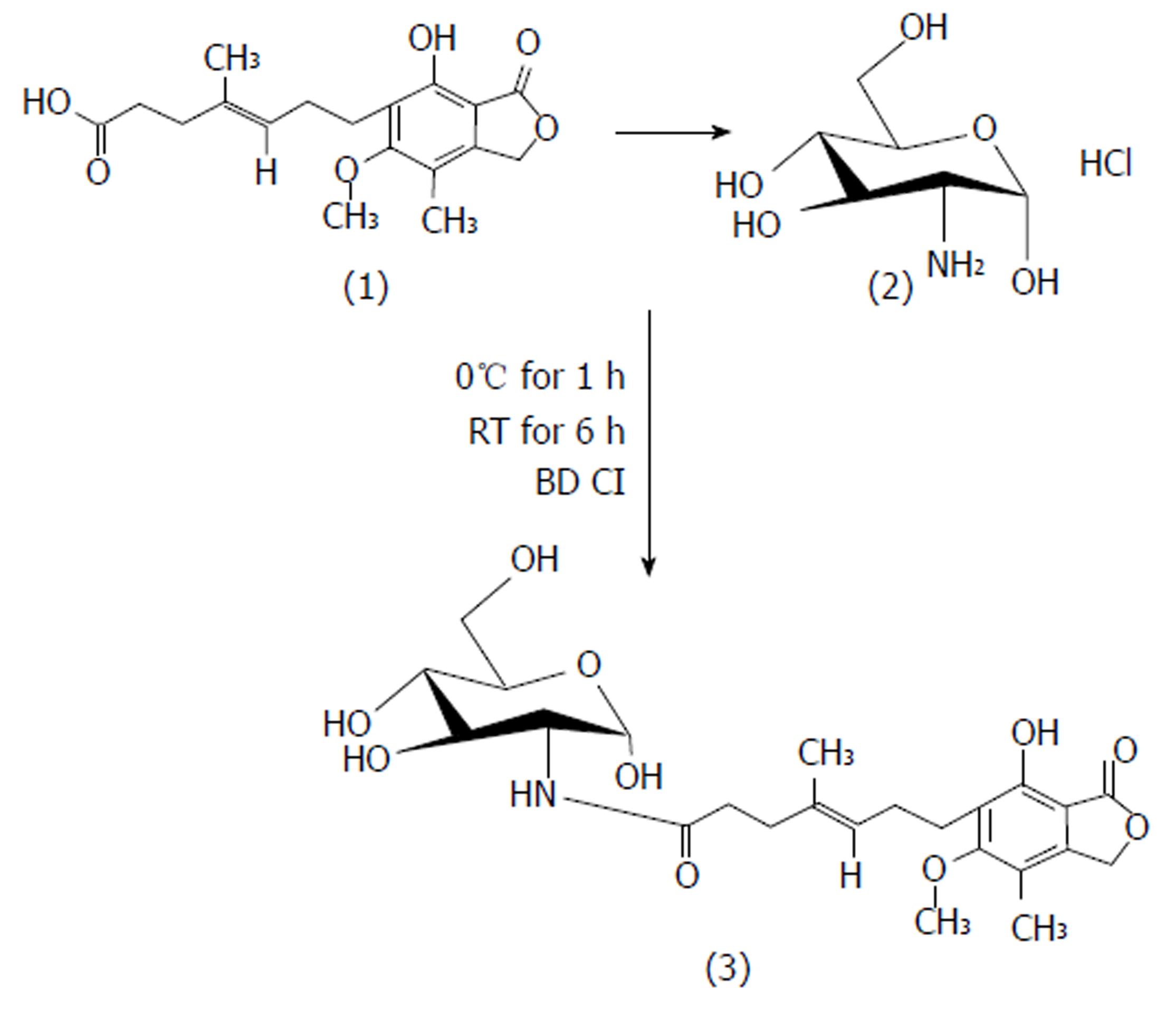
Figure 1 Scheme of synthesis.
(1) Mycophenolic acid: (2) D-glucosamine and (3) Prodrug of mycophenolic acid and D-glucosamine.
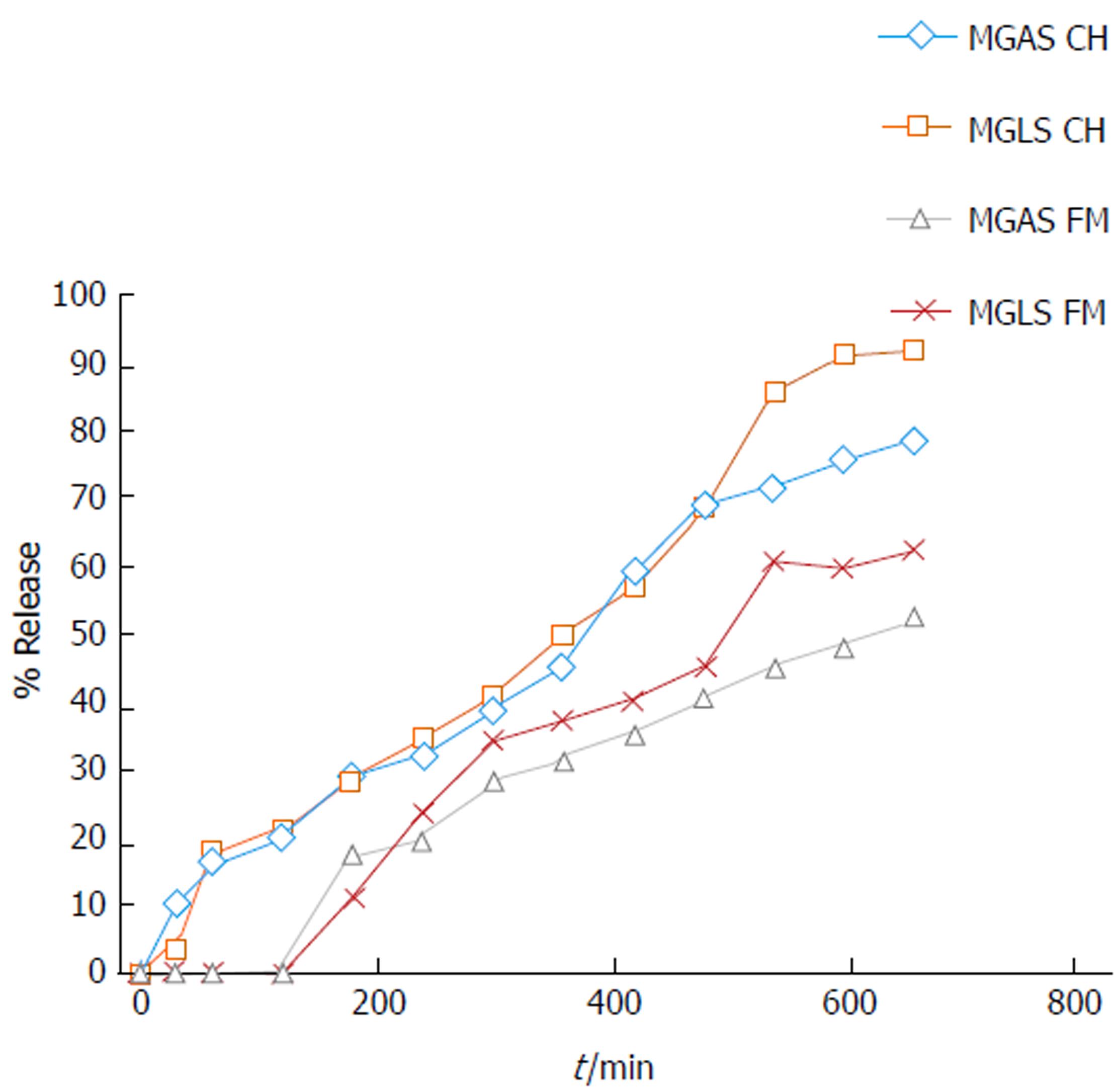
Figure 2 In vitro release of mycophenolic acid from prodrugs in different incubation media.
MPA: Mycophenolic acid; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine; CH: Colon homogenate; FM: Faecal matter.
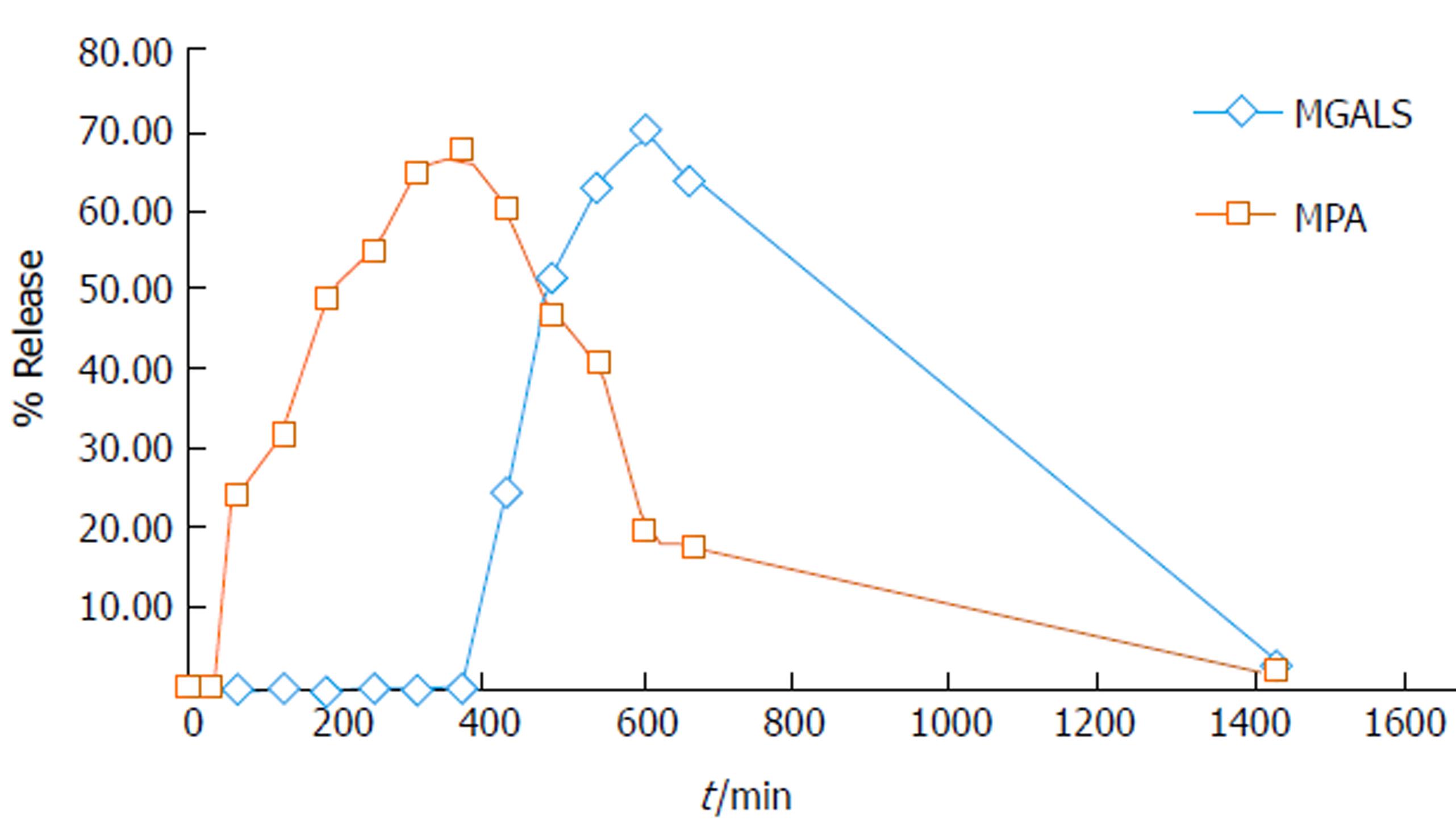
Figure 3 In vivo kinetics.
MPA: Mycophenolic acid; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine.
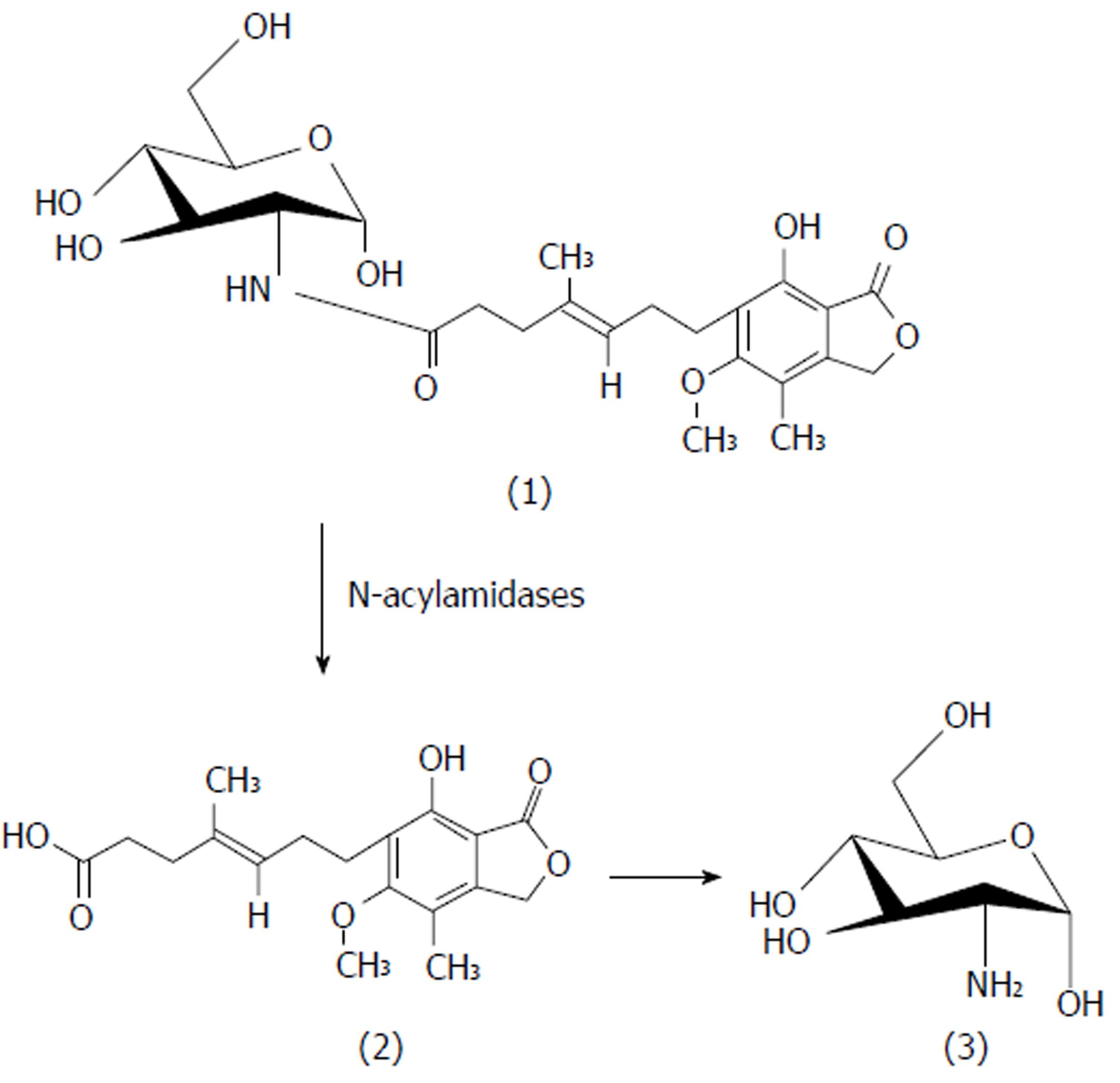
Figure 4 Mode of activation of mycophenolic acid and D-glucosamine prodrug.
(1) MGLS prodrug; (2) Mycophenolic acid; and (3) D-glucosamine. MPA: Mycophenolic acid; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine.
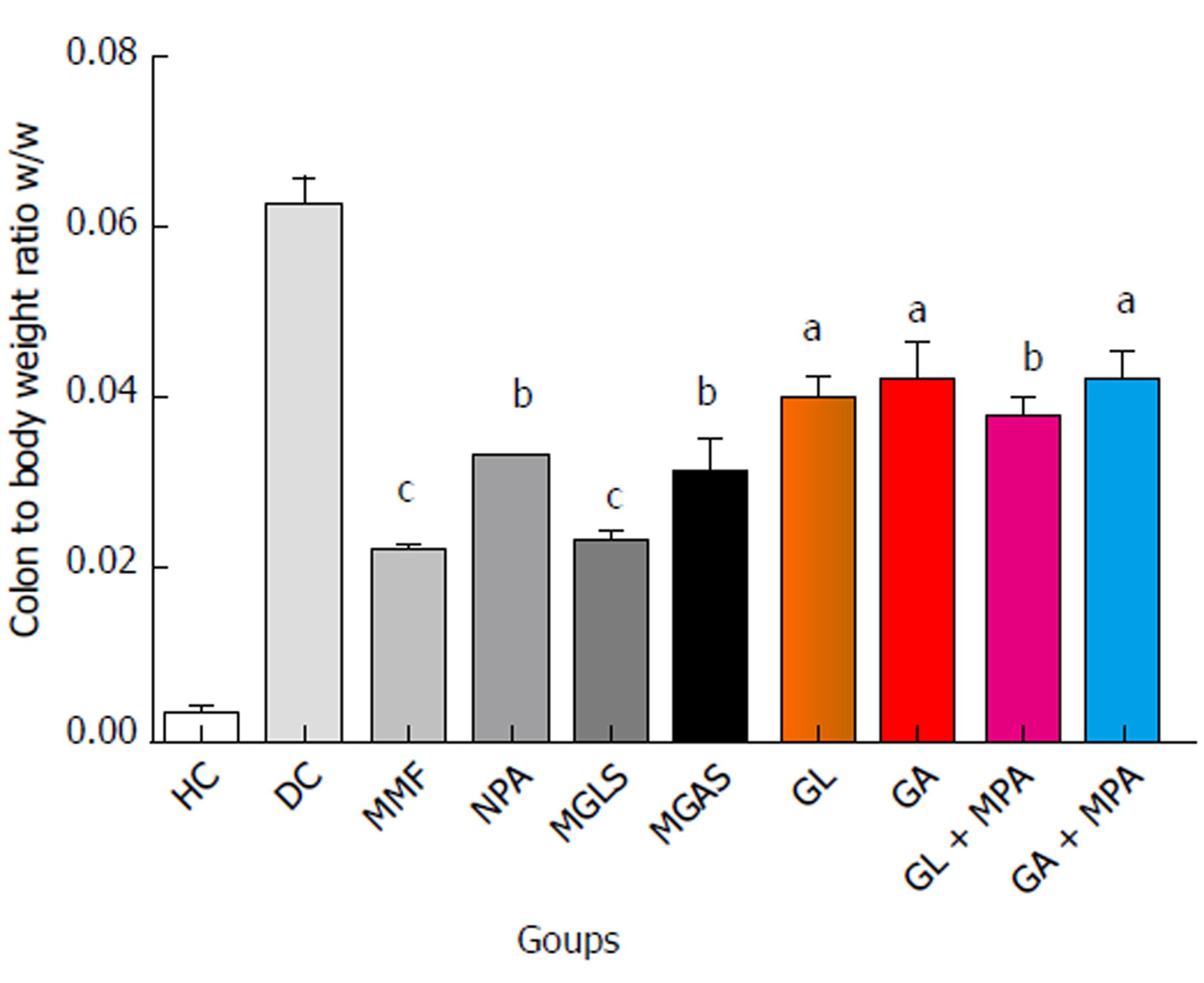
Figure 5 Colon to body weight ratio.
Average of six readings; One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test, statistical significance considered at aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Disease control. HC: Healthy control; DC: Disease control; MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil; MPA: Mycophenolic acid; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine; MGAS: Prodrug of MPA and D-galactosamine; GL: D-glucosamine; GA: D-galactosamine; GL + MPA: Physical mixture of D-glucosamine and MPA; GA + MPA oral: Physical mixture of D-galactosamine and MPA.
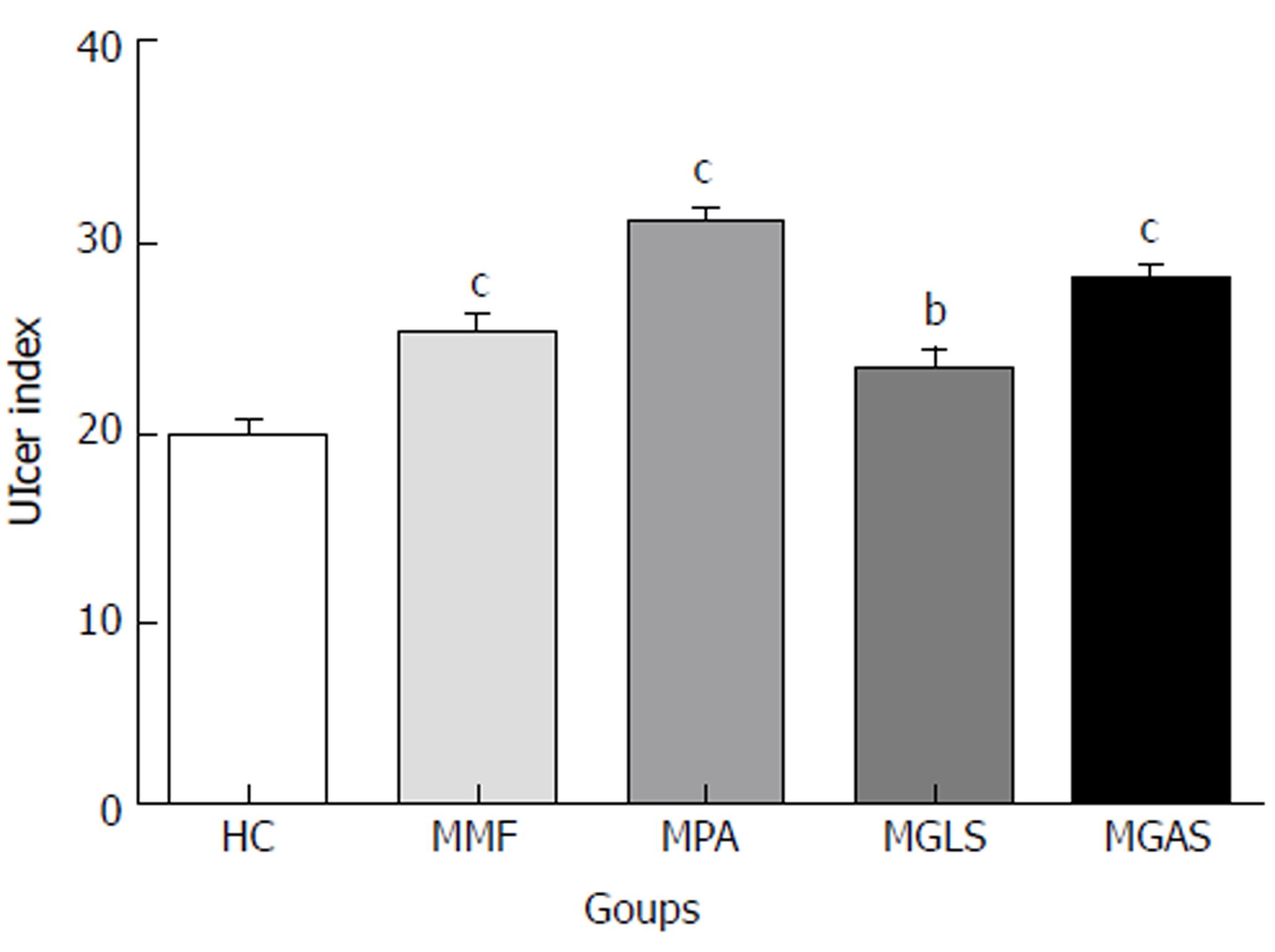
Figure 6 Results of ulcerogenic activity.
Average of six readings; One-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s Multiple Comparison Test, statistical significance considered at bP < 0.01, cP < 0.001 vs Healthy control. HC: Healthy control; MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil; MPA: Mycophenolic acid; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine; MGAS: Prodrug of MPA and D-galactosamine.
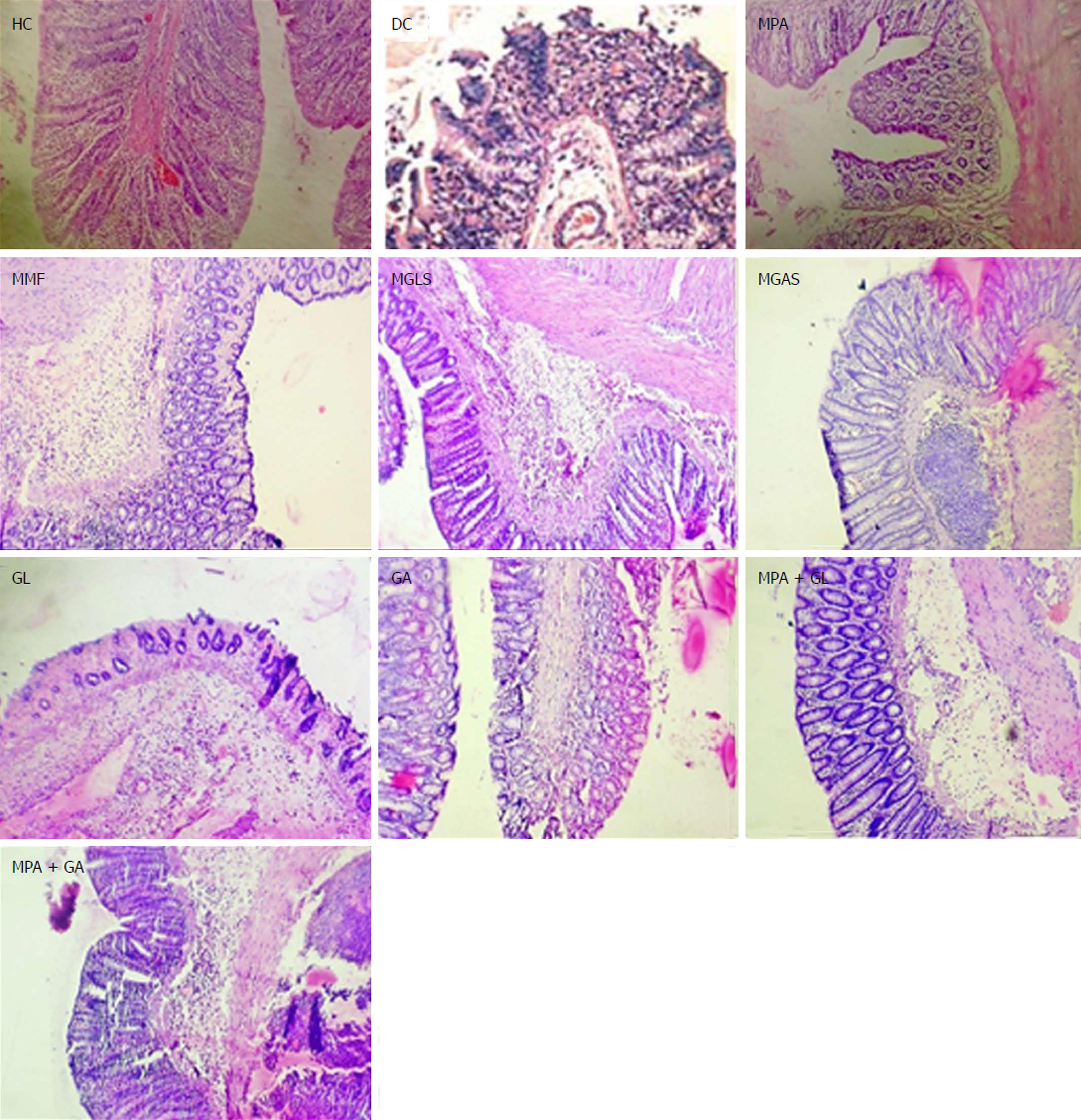
Figure 7 Photomicrographs of colon.
HC: Healthy control showing normal architecture of colon mucosa; DC: Disease control showing severe haemorrhage in submucosa with infiltration of inflammatory cells; MPA: MPA showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells and mild degeneration of epithelium lining; MMF: Showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells and mild degeneration of epithelium lining; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine; MGAS: Prodrug of MPA and D-galactosamine showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells; GL: D-glucosamine showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells; GA: D-galactosamine showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells; MPA + GL: Physical mixture of D-glucosamine and MPA showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells; MPA + GA: Physical mixture of D-galactosamine and MPA showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells and mild degeneration of epithelium lining.
Figure 8 Photomicrographs of pancreas.
HC: Healthy control; DC: Disease control; MMF: Mycophenolate mofetil; MPA: Mycophenolic acid; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine; MGAS: Prodrug of MPA and D-galactosamine; GL: D-glucosamine; GA: D-galactosamine; GL + MPA: Physical mixture of D-glucosamine and MPA; GA + MPA oral: Physical mixture of D-galactosamine and MPA. DC group showing reduced number and size of islets of Langerhans while all other groups showed normal pancreas architecture without evidence of pancreatitis.
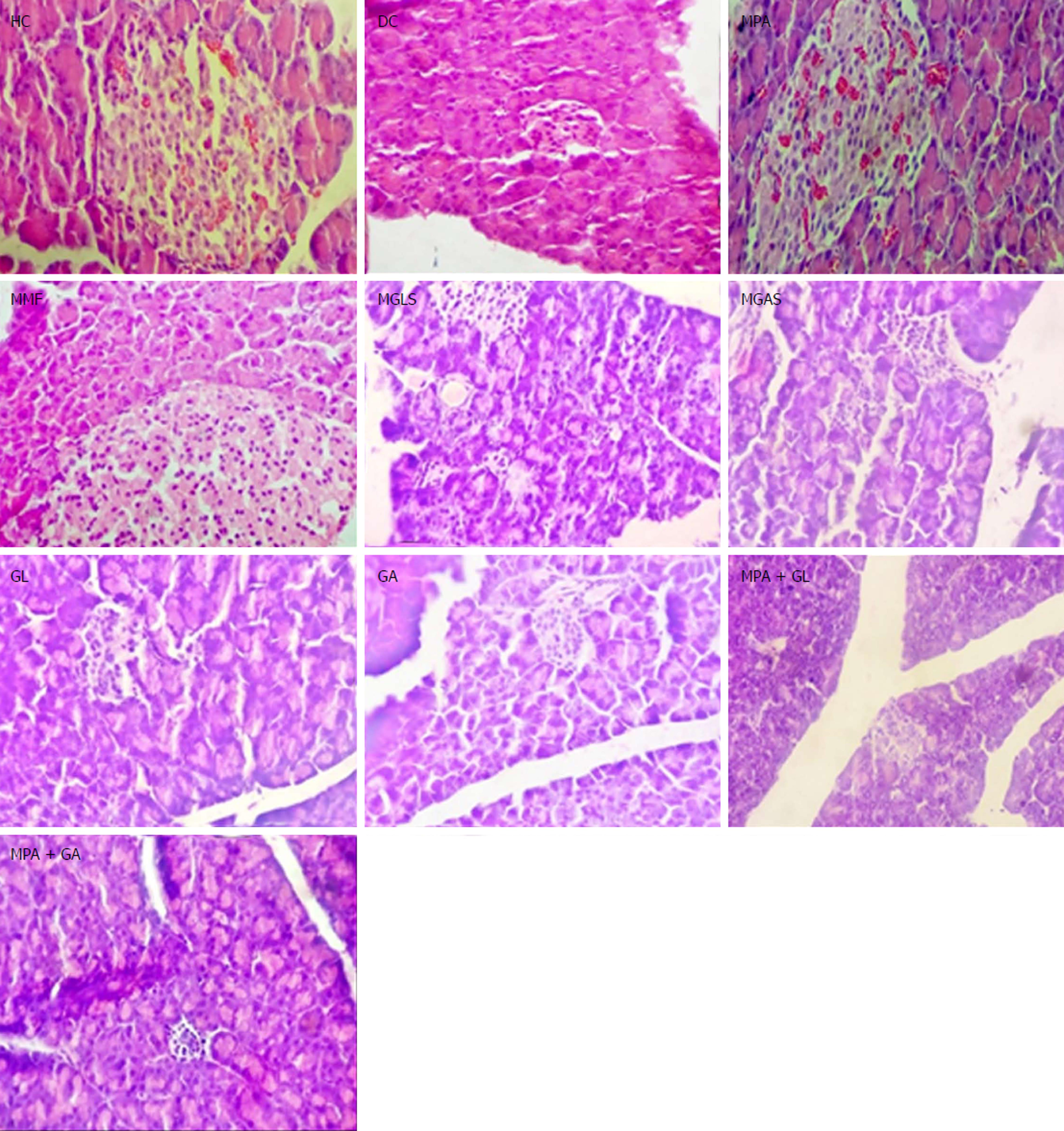
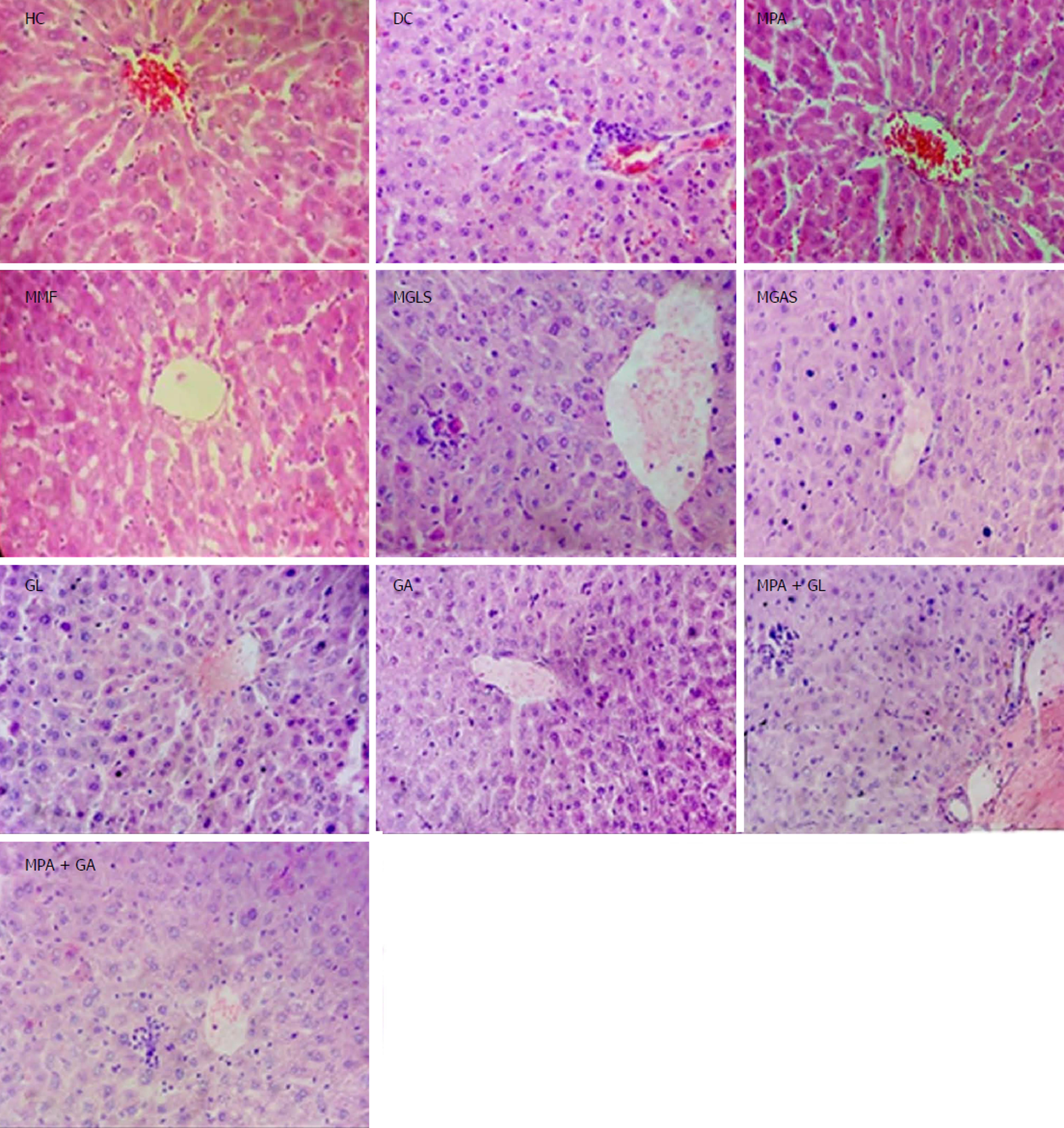
Figure 9 Photomicrographs of liver.
HC: Healthy control; DC: Disease control showing minimal degeneration of hepatocytes and congestion of blood vessels; MPA: MPA showing normal liver architecture; MMF: MMF Showing normal liver architecture; MGLS: Prodrug of MPA and D-glucosamine showing minimal infiltration of inflammatory cells; MGAS: Prodrug of MPA and D-galactosamine showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells; GL: D-Glucosamine showing minimal infiltration of inflammatory cells; GA: D-galactosamine showing minimal infiltration of inflammatory cells; MPA + GL: Physical mixture of D-glucosamine and MPA showing minimal infiltration of inflammatory cells; MPA + GA: Physical mixture of D-galactosamine and MPA showing mild infiltration of inflammatory cells.
- Citation: Chopade SS, Dhaneshwar SS. Determination of the mitigating effect of colon-specific bioreversible codrugs of mycophenolic acid and aminosugars in an experimental colitis model in Wistar rats. World J Gastroenterol 2018; 24(10): 1093-1106
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v24/i10/1093.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i10.1093