Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2017; 23(48): 8671-8678
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8671
Published online Dec 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8671
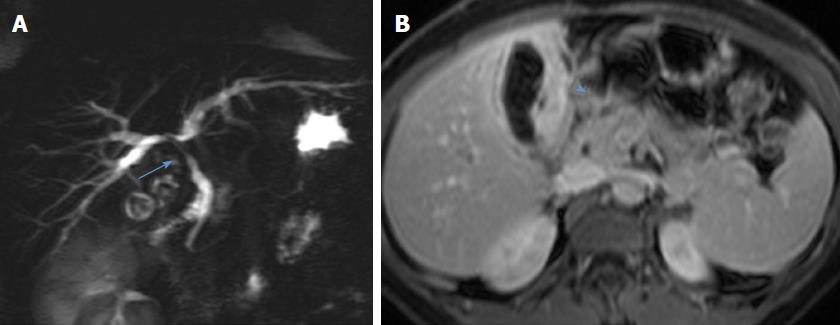
Figure 1 Preoperative magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography from case 1 demonstrates stenosis of the common bile duct and biliary confluence (arrow, A) and retrograde biliary dilatation.
The transverse section demonstrates diffuse asymmetrical gallbladder wall thickening (arrowhead, B) and contiguous hilar mass.
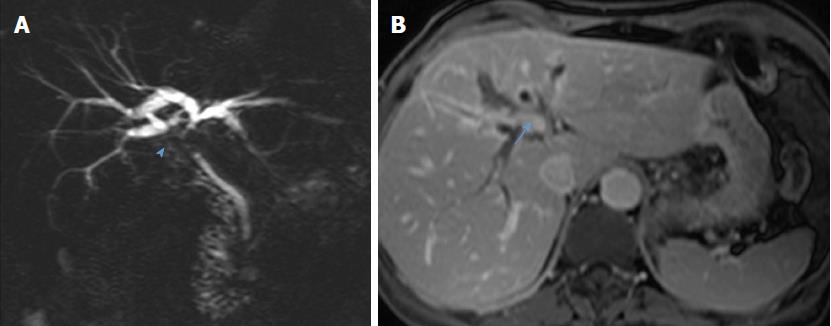
Figure 2 Preoperative magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography from case 2 demonstrates stenosis of the proximal and middle thirds of the common bile duct, biliary confluence (arrowhead, A), and right hepatic duct and second-order biliary radicals, with retrograde biliary dilatation; a suspicious-appearing spiculated hilar lymph node is seen on transverse section (arrow, B).
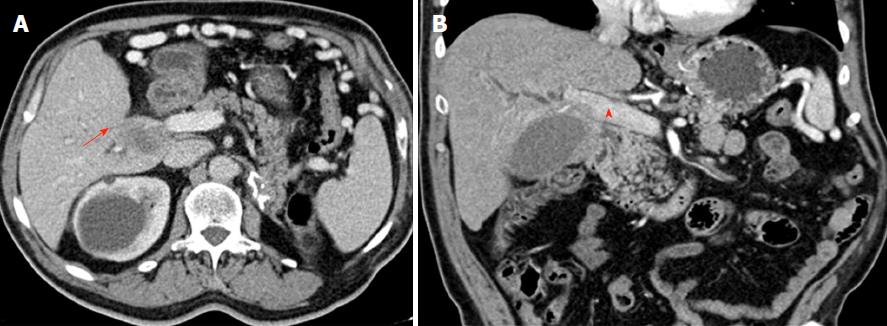
Figure 3 Preoperative CT images from case 3 demonstrating a dilated intrahepatic bile duct (arrow, A) that ends abruptly at the biliary confluence.
An ill-defined hilar mass is seen infiltrating the right hepatic artery (arrow, B) and bilateral hepatic ducts and contacting focally with the portal vein (arrowhead, B).
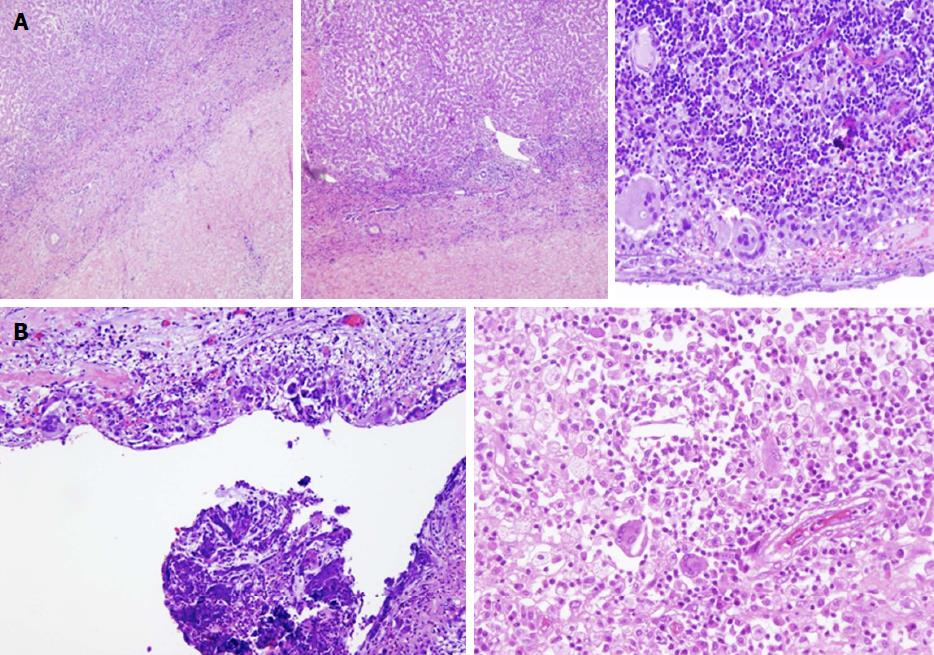
Figure 4 Histological examination of the surgical specimens from the three cases of xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis reveals findings of chronic cholecystitis and marked inflammatory infiltrate, including lymphocytes, plasma cells, foamy histiocytes, and spindle-shaped cells.
A: Focal formations of pseudocysts, with multinucleated foreign-body giant cells and cholesterol clefts, are also observed; B: Hyalinization and fibrosis of the gallbladder wall reflects chronic inflammation. Typically, the xanthogranulomatous reaction occupies a limited portion of the gallbladder wall, while the remainder shows signs of conventional chronic cholecystitis. Polymorphonuclear lymphocytes, reflecting acute inflammation, are also occasionally seen. The mucosa presents focal ulceration and erosion and reactive changes that consist in papillary hyperplasia and mucinous and cardial-type glandular metaplasia. Dysplastic changes and malignant features are absent in all three cases.
- Citation: Nacif LS, Hessheimer AJ, Rodríguez Gómez S, Montironi C, Fondevila C. Infiltrative xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis mimicking aggressive gallbladder carcinoma: A diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(48): 8671-8678
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i48/8671.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i48.8671