Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 28, 2017; 23(24): 4462-4466
Published online Jun 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i24.4462
Published online Jun 28, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i24.4462
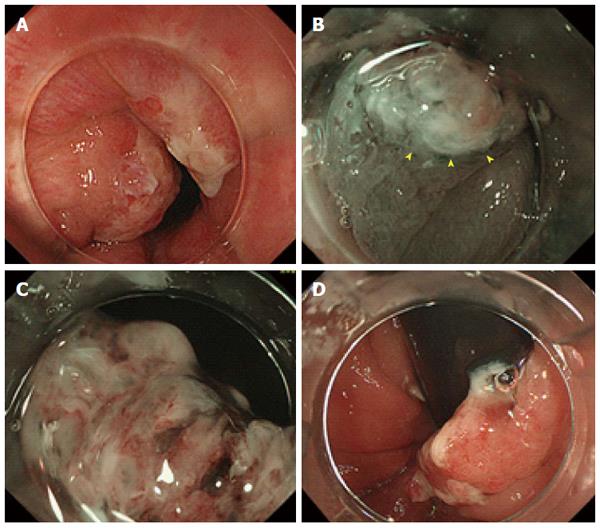
Figure 1 Findings on colonoscopy.
A: A single pine cone-shaped polyp with slightly reddish changes seen on a forward colonoscopic view of the lower rectum; B: Magnified narrow-band imaging shows whitish mucosal adhesions and slightly reddish villi (arrowheads) in the lesion; C: Magnified narrow-band imaging shows areas of abrasion and necrosis on the surface of the lesion but the detail is unclear; D: The lesion is seen to cover half of the circumference of the anal verge on a retroflex view.
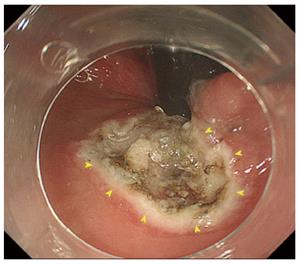
Figure 2 Intraoperative view.
Endoscopic submucosal dissection was performed to remove the polypoid lesion (arrowheads).
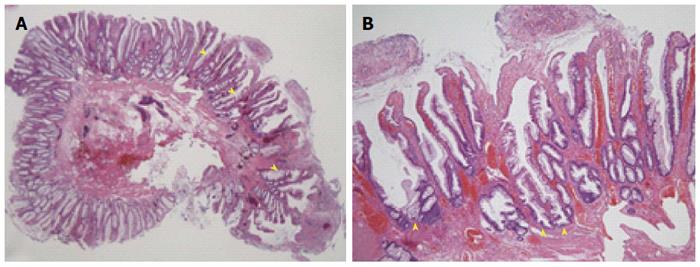
Figure 3 Histopathological findings.
A: Histopathological examination was performed with hematoxylin and eosin staining (× 10). The polyp contains serrated glands in its mucosal layer (arrowheads); B: Crypts and surface epithelial tissue showing dysplastic structural changes and an increased number of goblet cells (arrowheads) are seen on sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin (× 100).
- Citation: Kondo S, Mori H, Nishiyama N, Kondo T, Shimono R, Okada H, Kusaka T. Case of pediatric traditional serrated adenoma resected via endoscopic submucosal dissection. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(24): 4462-4466
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i24/4462.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i24.4462