Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 7, 2017; 23(21): 3825-3831
Published online Jun 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3825
Published online Jun 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3825
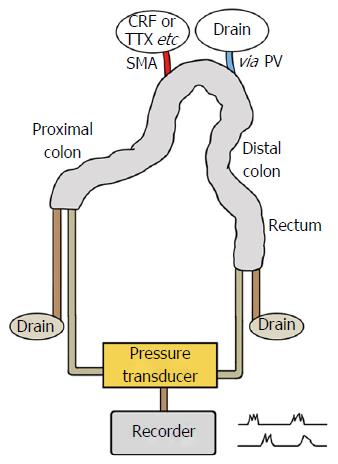
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the isolated vascularly-perfused rat colon.
The isolated whole rat colon was placed in a temperature-controlled water bath and vascularly perfused with Krebs solution via the superior mesenteric artery. Luminal pressure was monitored via microtip catheter pressure transducers at the proximal and distal ends of the colon. Pressure changes were recorded with a data acquisition system. AT: Atropine sulfate; CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; PV: Portal vein; SMA: Superior mesenteric artery; TTX: Tetrodotoxin.
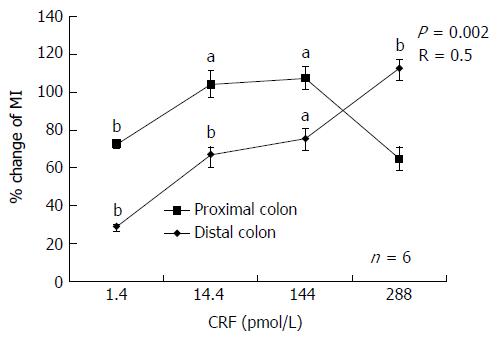
Figure 2 Concentration-response curves for corticotropin-releasing factor-induced contractility in isolated vascularly perfused rat colons.
CRF increased both proximal and distal colonic motility. Concentration-motility was observed only in the proximal colon. Data are expressed as percent change of MI over basal. Each data point represents the mean of 6 experiments. aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; MI: Motility index; R: Correlation coefficient.
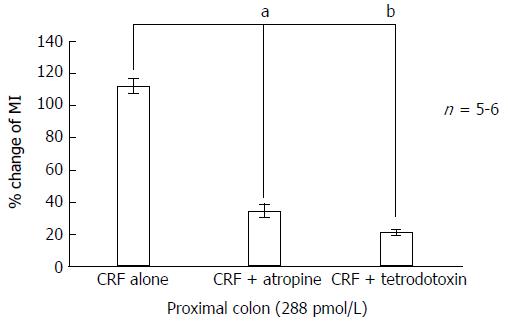
Figure 3 Effects of atropine and tetrodotoxin on corticotropin-releasing factor-induced colonic motility in the proximal colon.
Atropine (10-5 mol/L) reduced MI from 112.5% ± 22.0% to 34.3% ± 17.8% (P < 0.05). Administration of tetrodotoxin (10-6 mol/L) reduced MI from 112.5% ± 22.0% to 21.1% ± 9.8% (P < 0.01). aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01. CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; MI: Motility index.
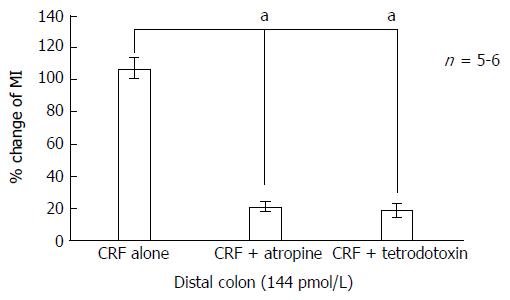
Figure 4 Effects of atropine and tetrodotoxin on corticotropin-releasing factor-induced colonic motility in the distal colon.
Atropine (10-5 mol/L) reduced MI from 112.5% ± 22.0% to 20.5% ± 15.2% (P < 0.05). Tetrodotoxin (10-6 mol/L) reduced MI from 112.5% ± 22.0% to 18.6% ± 18.6% (P < 0.05). aP < 0.05. CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; MI: Motility index.
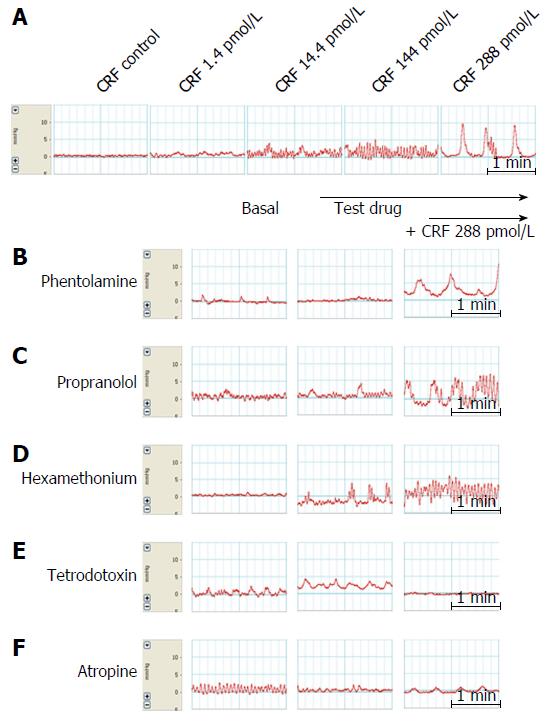
Figure 5 Representative tracings of the effects on proximal colonic motility of corticotropin-releasing factor alone (A), and of phentolamine (B), propranolol (C), hexamethonium (D), tetrodotoxin (E) and atropine (F).
Atropine and tetrodotoxin significantly inhibited CRF-induced colonic motility. CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; TTX: Tetrodotoxin.
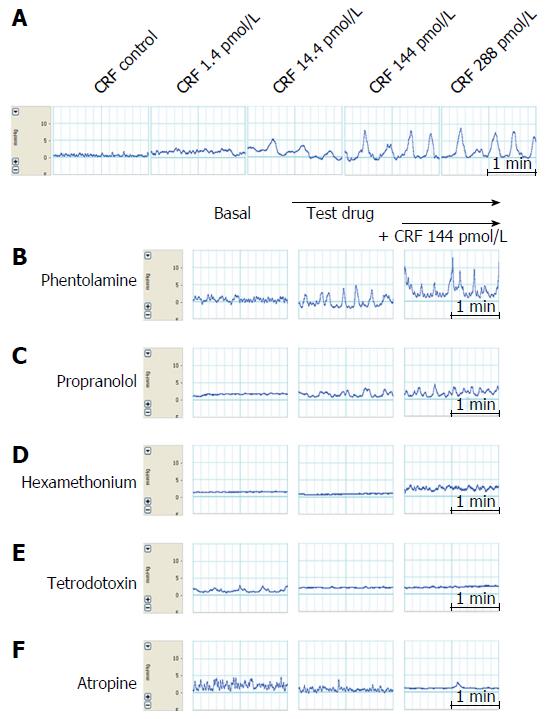
Figure 6 Representative tracings of the effects on distal colonic motility of corticotropin-releasing factor alone (A) and phentolamine (B), propranolol (C), hexamethonium (D), tetrodotoxin (E) and atropine (F).
Atropine and tetrodotoxin significantly inhibited CRF-induced colonic motility. CRF: Corticotropin-releasing factor; TTX: Tetrodotoxin.
- Citation: Kim KJ, Kim KB, Yoon SM, Han JH, Chae HB, Park SM, Youn SJ. Corticotropin-releasing factor stimulates colonic motility via muscarinic receptors in the rat. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(21): 3825-3831
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i21/3825.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i21.3825