Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 7, 2017; 23(1): 48-59
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.48
Published online Jan 7, 2017. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.48
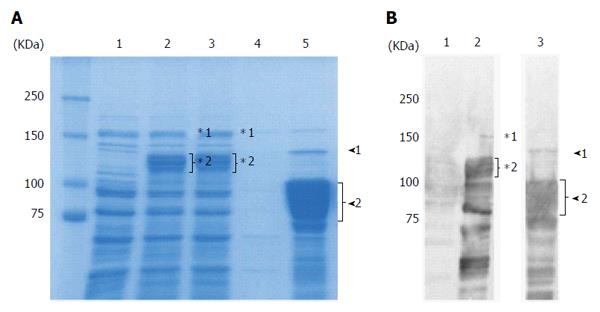
Figure 1 Purification of recombinant East Asian-type CagA.
A: CBB-stained 8% SDS-PAGE gel; 20 μg of protein were loaded per well. Lane 1: Uninduced lysate; 2: 0.4 mmol/L IPTG induced lysate; 3: Flow through; 4: Wash; 5: Elution. In the elution fraction (Lane 5), the 135 kDa band (arrowhead 1) is the full length rCagA. The 75-100 kDa rCagA cleavage product (arrowhead 2) comprised approximately 50% of the elution fraction; B: Western blot analysis with anti-CagA antibody. Lane 1: Uninduced lysate; 2: 0.4 mmol/L IPTG induced lysate; 3: Elution. Following induction (Lane 2), the full length GST-fused rCagA (*1) was expressed. However, it was subsequently cleaved (*2). In the elution fraction (Lane 3), the amount of full length rCagA was low (arrowhead 1) and various smaller-sized bands (arrowhead 2) were confirmed as rCagA fragments.
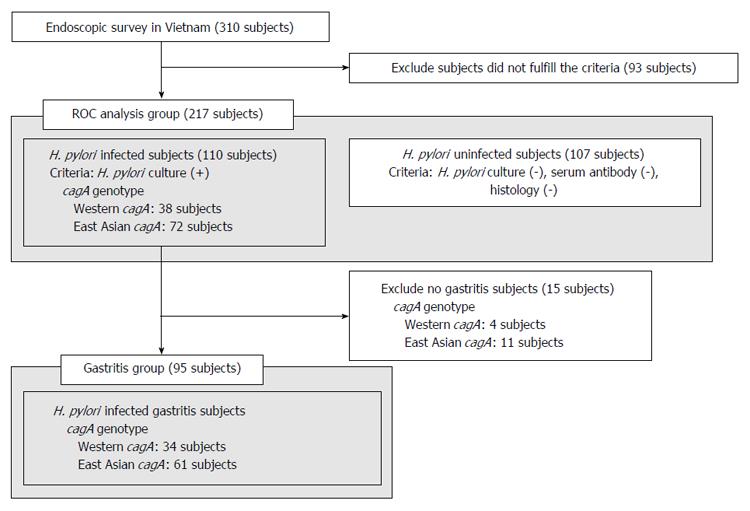
Figure 2 Subjects groups used in this study.
ROC analysis was performed to confirm the accuracy of East Asian-type CagA ELISA for subjects in the ROC analysis group. The correlation between CagA antibody titer and histological score was compared between subjects infected with either Western-type or East Asian-type cagA Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) in the gastritis group.
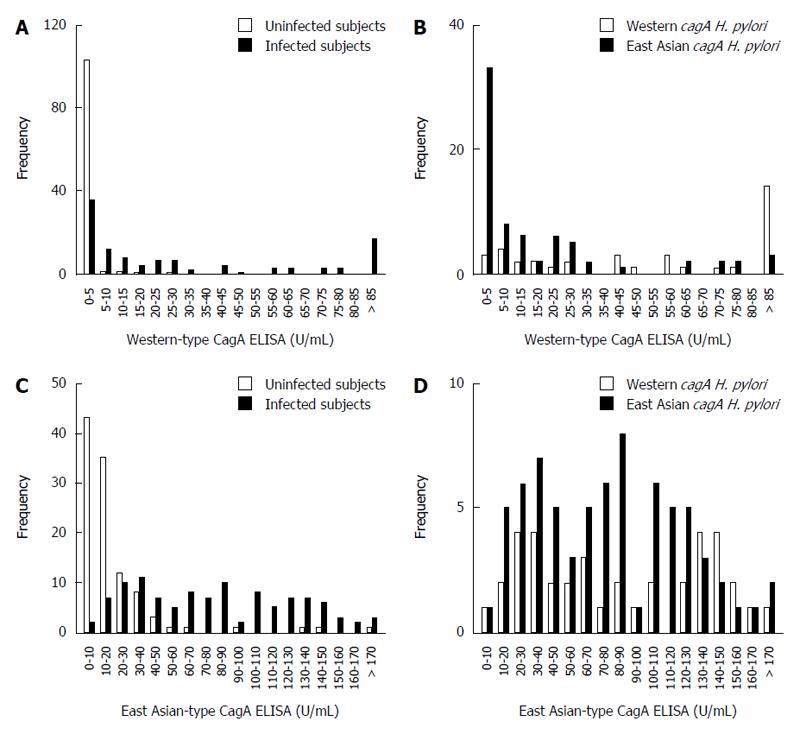
Figure 3 The distribution of CagA antibody ELISA titers is dependent on Helicobacter pylori infection status and Helicobacter pylori CagA-type.
A: Histogram of Western-type CagA ELISA titers of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori)-infected (gray bars) and uninfected subjects (white bars); B: Histogram of Western-type CagA ELISA titers of H. pylori infected subjects is dependent on cagA genotype; Western-type cagA H. pylori (white bars), East Asian-type cagA H. pylori (gray bars); C: Histogram of East Asian-type CagA ELISA titers of H. pylori infection and uninfected subjects. Bar coloring is the same as in (A); D: Histogram of East Asian-type CagA ELISA titers of H. pylori infected subjects is dependent on cagA genotype. Bar coloring is the same as in (B).
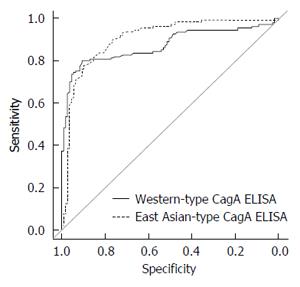
Figure 4 ROC curve analysis of Western-type and East Asian-type CagA ELISA.
The ROC curves of both types of CagA ELISA were analyzed using all 217 serum samples of the ROC analysis subjects group (Figure 2). The area under the curve (AUC) of the commercial Western-type CagA antibody ELISA was 0.87 and that of East Asian CagA antibody ELISA was 0.91. No significant difference was apparent.
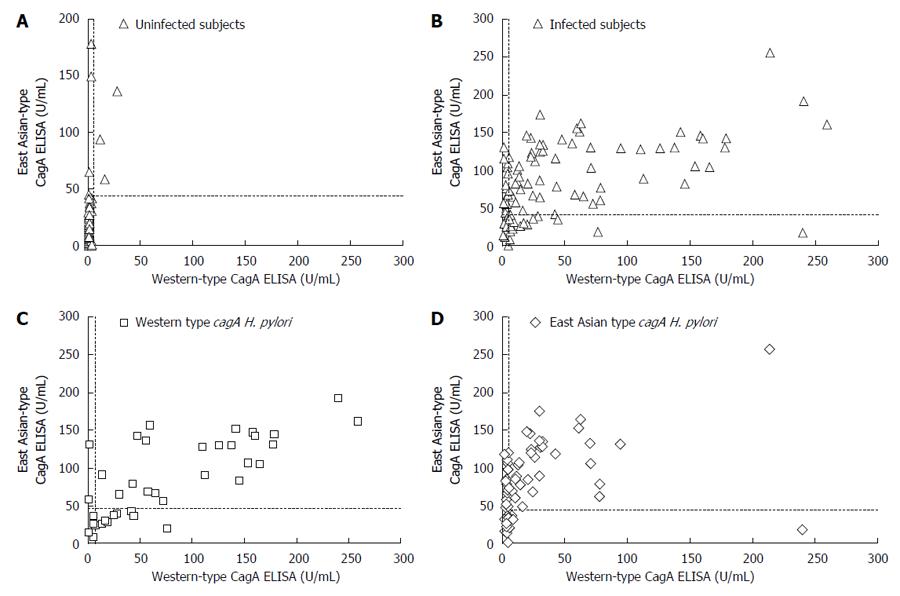
Figure 5 Relationship between the two types of CagA antibody ELISA titers.
Dotted lines indicate the cut off values (6.25 U/mL for Western-type CagA ELISA and 45.0 U/mL for East Asian-type CagA ELISA). A: Scatter plot of uninfected subjects. Of the 107 Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) uninfected subjects, 104 subjects (97.2%) were negative by Western-type CagA ELISA and 100 subjects (93.5%) by East Asian-type CagA ELISA; B: Scatter plots of infected subjects. Of the 110 H. pylori infected subjects, 69 (62.7%) subjects were positive by Western-type CagA ELISA and 78 (70.9%) by East Asian-type CagA ELISA; C: Scatter plot of Western-type cagA H. pylori infected subjects. Of the 38 subjects infected with western-type cagA H. pylori, 32 subjects (84.2%) were positive by Western-type CagA ELISA and 25 subjects (65.8%) were positive by East Asian-type CagA ELISA; D: Scatter plot of East Asian-type cagA H. pylori infected subjects. Of the 72 subjects infected with East Asian-type cagA H. pylori, 53 subjects (73.6%) were positive by East Asian-type CagA ELISA and 37 subjects (51.4%) were positive by Western-type CagA ELISA.
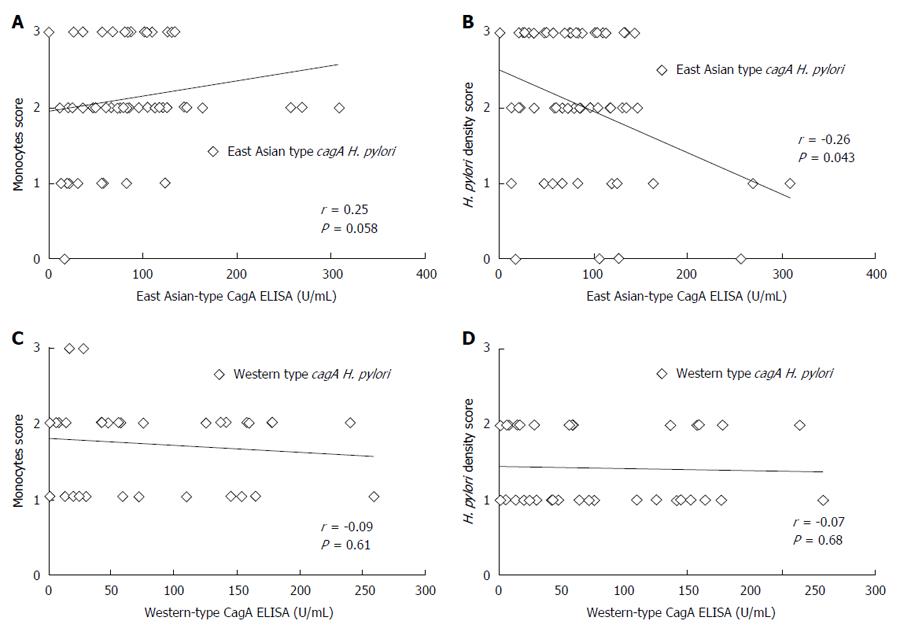
Figure 6 Correlation between CagA antibody ELISA titer and histological score.
A: Relationship between East Asian-type CagA ELISA titer and histological monocytes score. Among East Asian-type cagA possessed Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infected subjects diagnosed as gastritis (Gastritis group in Figure 1), East Asian-type CagA antibody titers tended to positive correlate with the infiltration of monocytes at antrum in stomach (r = 0.25, P = 0.058); B: Relationship between East Asian-type CagA ELISA titer and histological H. pylori density score. East Asian-type CagA antibody titers were negative correlated with the H. pylori density at an antrum in stomach (r = -0.26, P = 0.043); C: Relationship between Western-type CagA ELISA titer and histological monocytes score. There is no correlation (P = 0.61); D: No correlation was apparent for Western-type CagA ELISA titer and histological H. pylori density (P = 0.68).
- Citation: Matsuo Y, Kido Y, Akada J, Shiota S, Binh TT, Trang TTH, Dung HDQ, Tung PH, Tri TD, Thuan NPM, Tam LQ, Nam BC, Khien VV, Yamaoka Y. Novel CagA ELISA exhibits enhanced sensitivity of Helicobacter pylori CagA antibody. World J Gastroenterol 2017; 23(1): 48-59
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v23/i1/48.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v23.i1.48