Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 7, 2016; 22(5): 1779-1786
Published online Feb 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1779
Published online Feb 7, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1779
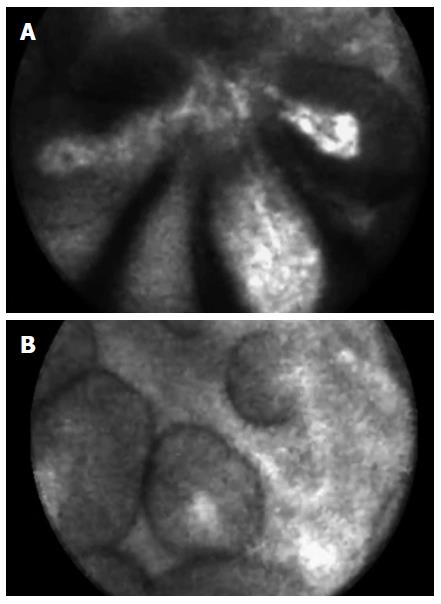
Figure 1 Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm: papillary projections (A) and, imaged in cross section, dark rings with a central core (B).
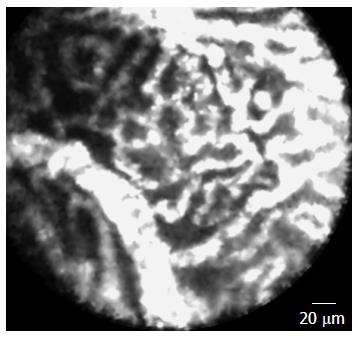
Figure 2 Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of a serous cystadenoma showing the typical vascular network.
Figure 3 Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of pancreatic adenocarcinoma: dark cells aggregates with pseudo-glandular aspects, irregular vessels with leakage of fluorescein (A) and histological correlations (B).
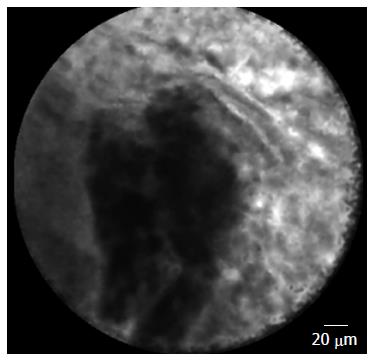
Figure 4 Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of normal pancreatic tissue: coffee bean aspect.
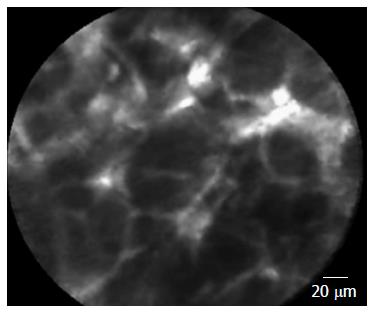
Figure 5 Needle-based confocal laser endomicroscopy of a malignant lymph node: glandular structures with dark cells and neo-vascularization with leakage of fluorescein.
- Citation: De Lisi S, Giovannini M. Endoscopic ultrasonography: Transition towards the future of gastro-intestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(5): 1779-1786
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i5/1779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i5.1779