Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2016; 22(46): 10166-10179
Published online Dec 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10166
Published online Dec 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10166
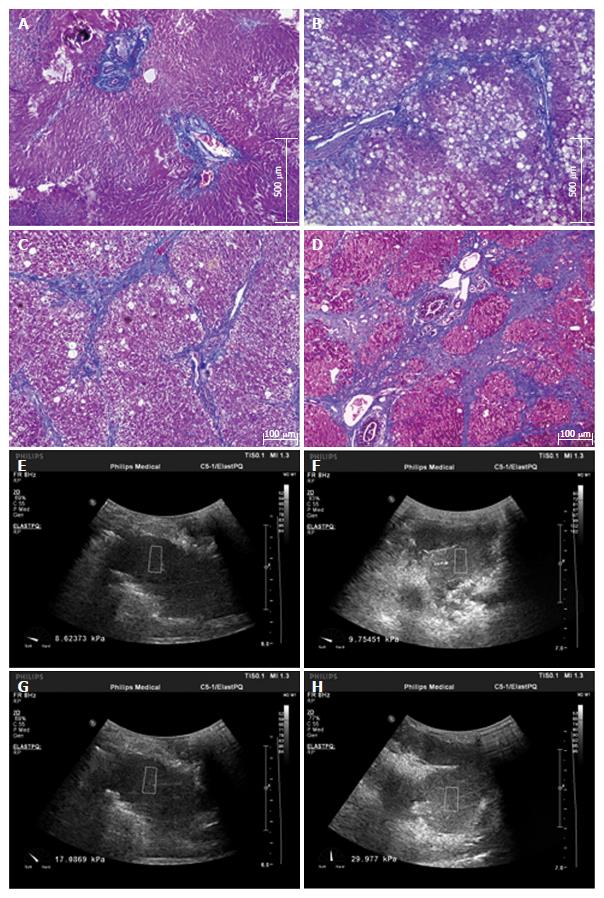
Figure 1 Masson trichrome staining for assessment of liver fibrosis stages according to METAVIR (A: F1, B: F2, C: F3, and D: F4; 100 ×) and the corresponding ElastPQ images (E: F1; F: F2; G: F3; and H: F4).
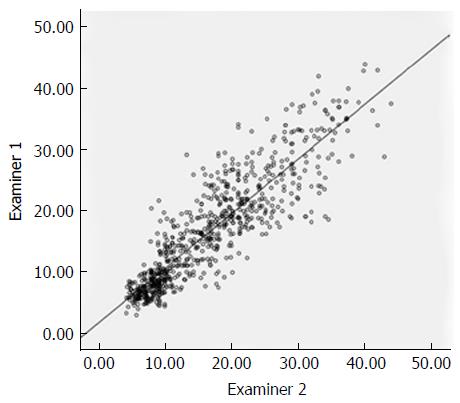
Figure 2 Graph shows correlation of elastography point quantification results between two examiners (ICC value of 0.
888, r2 = 0.788, P < 0.05).
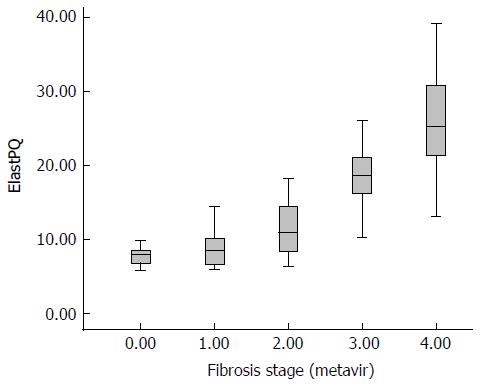
Figure 3 Boxplot shows the elastography point quantification results for each fibrosis stage.
The top and bottom of the boxes are the first and third quartiles, respectively. Accordingly, the length of the box plot represents the interquartile range within which 50% of the values were located. The lines through the middle of the boxes indicate the median values. ElastPQ: Elastography point quantification.
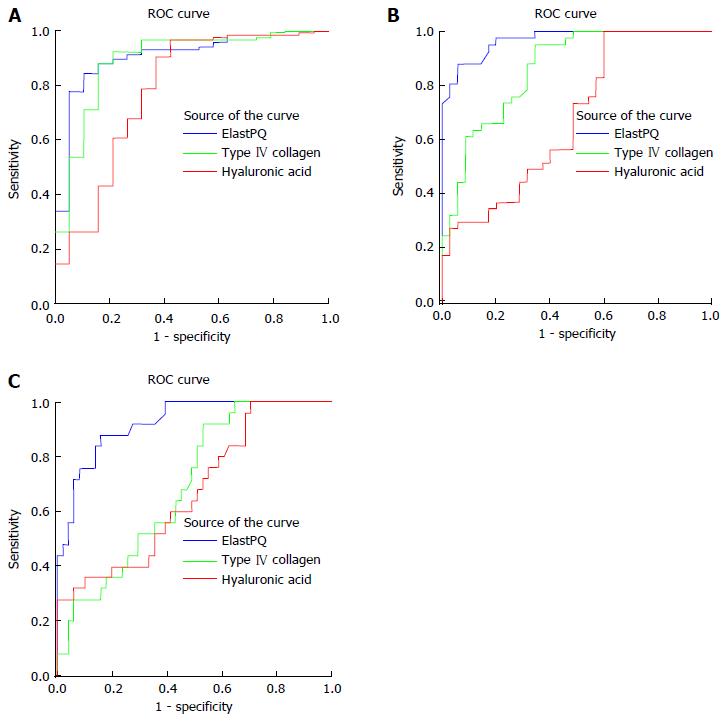
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic curves of elastography point quantification and serum fibrosis markers for diagnosis of (A) minimal fibrosis (F0-F1 vs F2-F4), (B) moderate fibrosis (F0-F2 vs F3-F4), and (C) cirrhosis (F0-F3 vs F4).
ElastPQ: Elastography point quantification.
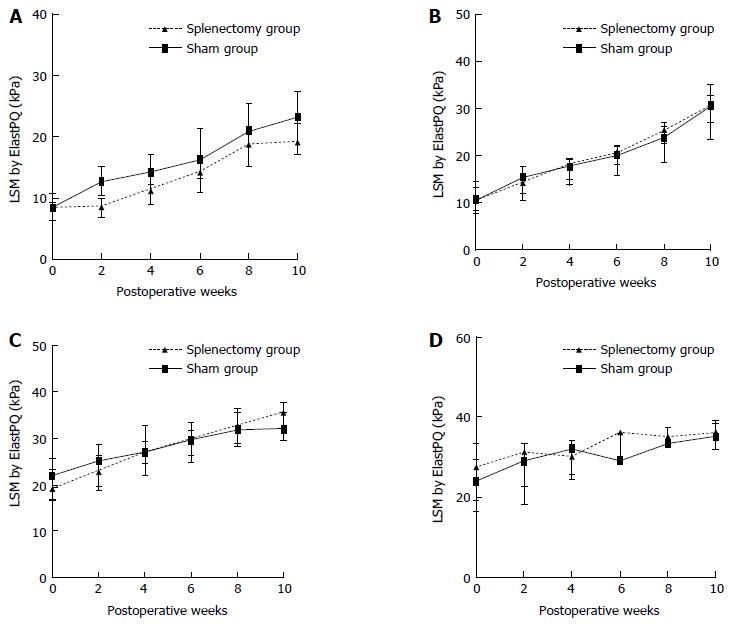
Figure 5 Dynamic changes in liver stiffness measurement by elastography point quantification after surgery in rabbits with F1 (A), F2 (B), F3 (C), and F4 (D) liver fibrosis (sham group vs splenectomy group).
LSM: Liver stiffness measurement; ElastPQ: Elastography point quantification.
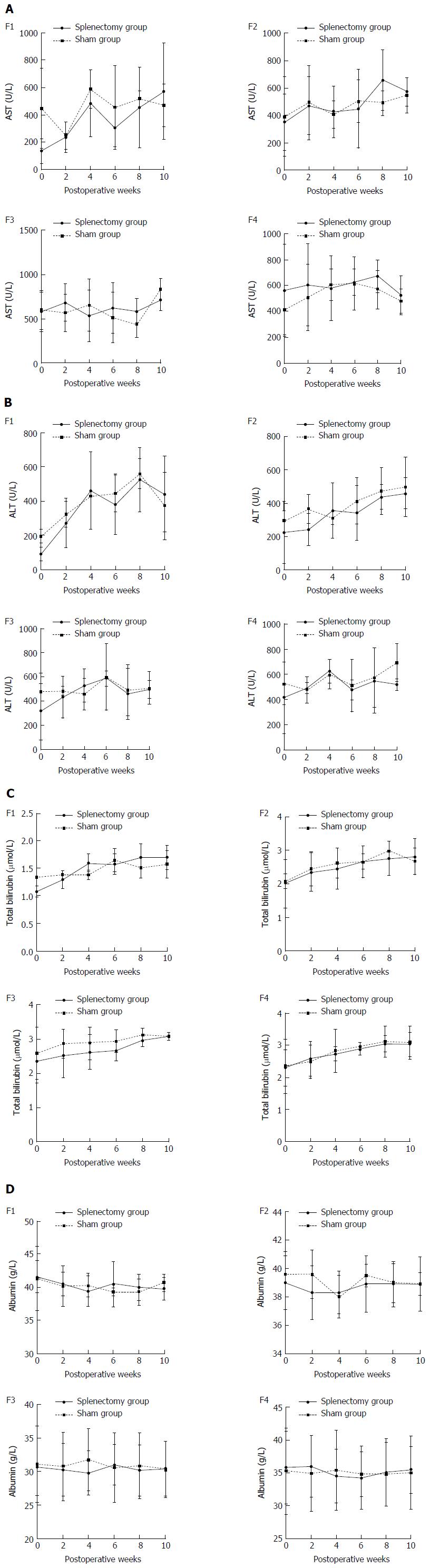
Figure 6 Longitudinal changes in liver function following splenectomy vs sham operation at different liver fibrosis stages.
A: Changes in AST for rabbits with F1-F4 liver fibrosis; B: Changes in ALT for rabbits with F1-F4 liver fibrosis; C: Changes in total bilirubin for rabbits with F1-F4 liver fibrosis; and D: Changes in albumin for rabbits with F1-F4 liver fibrosis. AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase.
- Citation: Wang MJ, Ling WW, Wang H, Meng LW, Cai H, Peng B. Non-invasive evaluation of liver stiffness after splenectomy in rabbits with CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(46): 10166-10179
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i46/10166.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10166