Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2016; 22(46): 10131-10139
Published online Dec 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10131
Published online Dec 14, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10131
Figure 1 Tissue-sampled sites.
Full-thickness tissue samples (2 cm × 1 cm size) were obtained from tumor-free sites in fundus, less curvature of corpus, and less curvature of antrum.
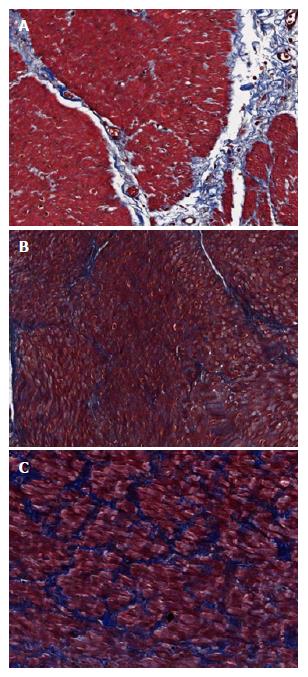
Figure 2 Degree of intercellular fibrosis.
A: Mild fibrosis means minimal fibrosis without bridging; B: Moderate fibrosis means bridging fibrosis without encirclement; C: Severe fibrosis means muscle fiber-encircling fibrosis. Masson’s Trichrome stain (× 200).
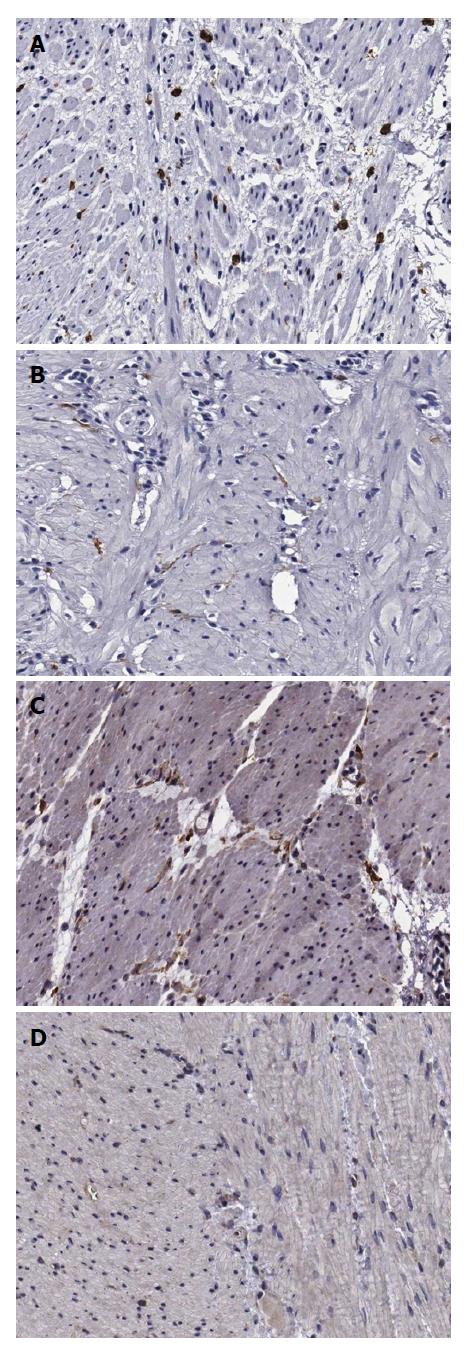
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining of interstitial cells of Cajal (upper panel) and platelet-derived growth factor receptor α-positive fibroblast-like cells (lower panel) in the human gastric corpus (× 200).
Cellularity of ICC is higher in the control group (A) than in the DM group (B). Cellularity of FLCs is higher in the control group (C) than in the DM group (D). DM: Diabetes mellitus; FLCs: Fibroblast-like cells.
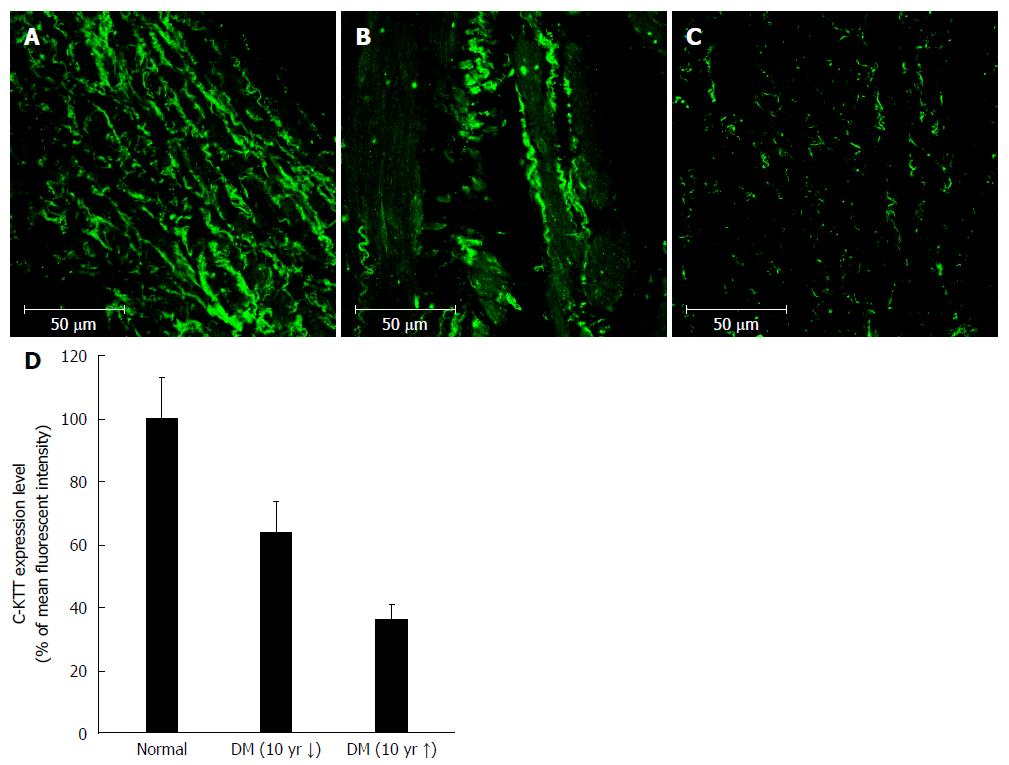
Figure 4 Immunofluorescent staining of interstitial cells of Cajal in the human gastric corpus.
Panels (A), (B), and (C) show representative images from the control, DM of < 10 years’ duration, and DM of > 10 years’ groups, respectively. Cellularity of ICC decreases with increasing duration of DM (D). DM: Diabetes mellitus; ICC: Interstitial cells of Cajal.
- Citation: Park KS, Cho KB, Hwang IS, Park JH, Jang BI, Kim KO, Jeon SW, Kim ES, Park CS, Kwon JG. Characterization of smooth muscle, enteric nerve, interstitial cells of Cajal, and fibroblast-like cells in the gastric musculature of patients with diabetes mellitus. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(46): 10131-10139
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i46/10131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i46.10131