Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Gastroenterol. Jan 21, 2016; 22(3): 1179-1189
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1179
Published online Jan 21, 2016. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1179
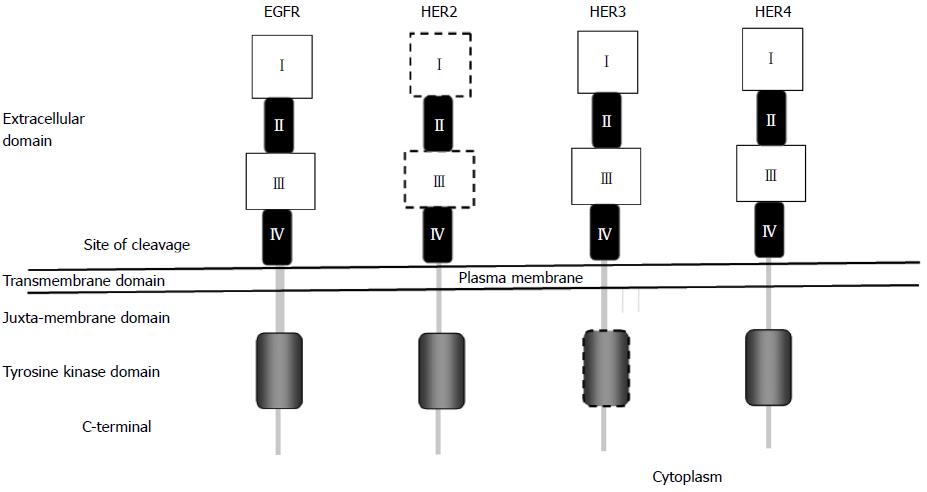
Figure 1 Structure of ERBB family of receptors.
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; HER: Human EGFR.
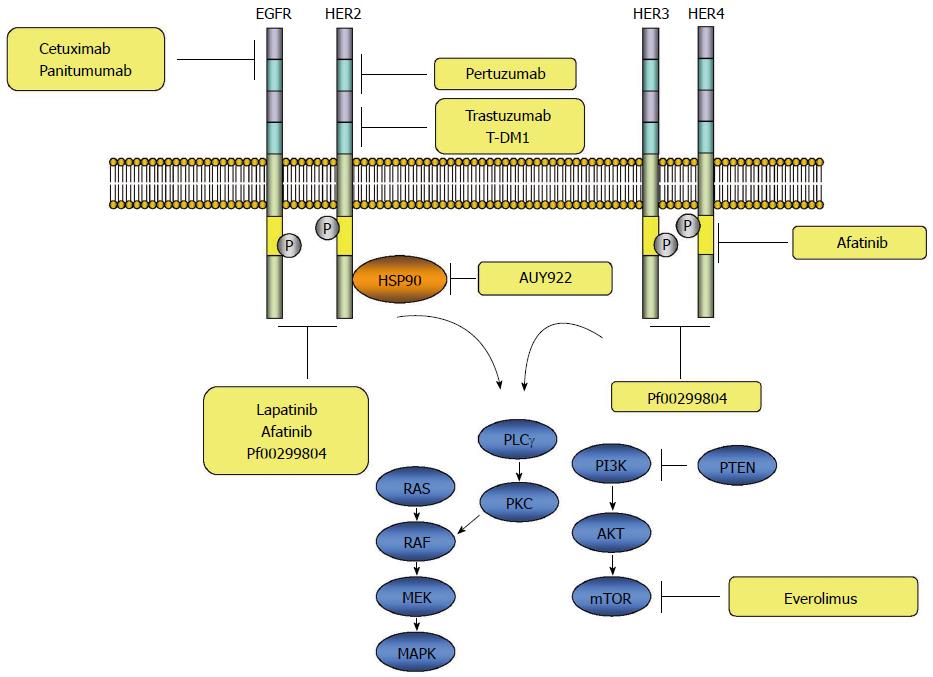
Figure 2 Signal transduction cascade through activation of ERBB receptors and schematic diagram of molecular targeting agents where they work.
EGFR: Epidermal growth factor receptor; HER: Human EGFR; PLC-γ: Phospholipase C-γ; PKC: Protein kinase C; MEK: Protein kinase kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
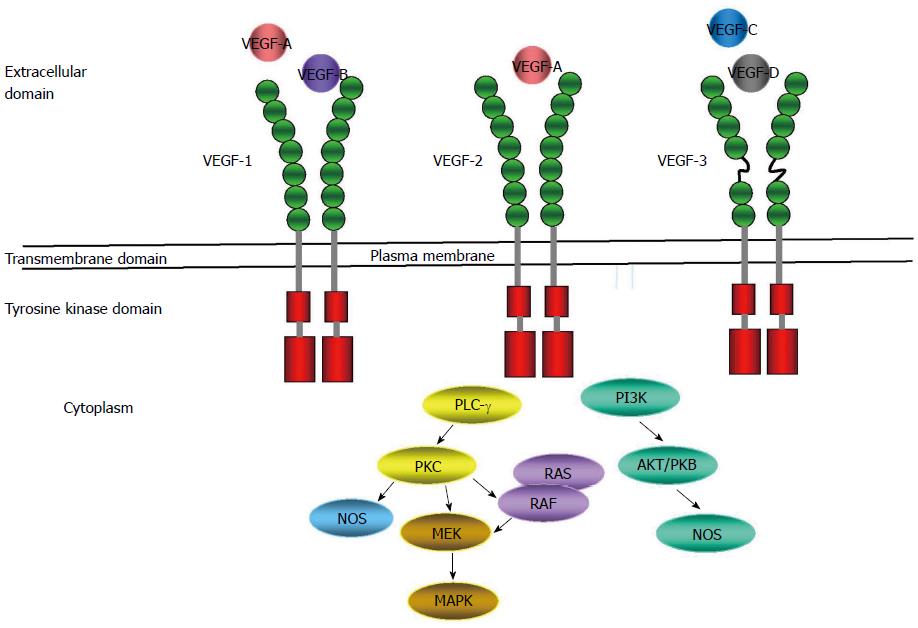
Figure 3 Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor and signal transduction.
Binding of ligands to receptors leads to phosphorylation of the receptors by activation of receptor-kinase activity, which leads to subsequent signal transduction. VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; PLC-γ: Phospholipase C-γ; PKC: Protein kinase C; MEK: Protein kinase kinase; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase.
- Citation: Lee SY, Oh SC. Changing strategies for target therapy in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2016; 22(3): 1179-1189
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v22/i3/1179.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1179