Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 7, 2015; 21(33): 9707-9716
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9707
Published online Sep 7, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9707
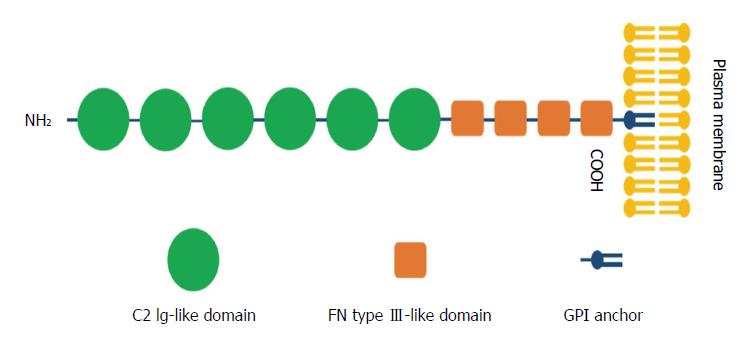
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the structure of contactin 1.
Contactin 1 (CNTN1) is composed of an N-terminal signal peptide, six C2 immunoglobulin (Ig)-like repeats, four fibronectin type III-like domains and a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchor at the carboxy-terminus linked to the plasma membrane.
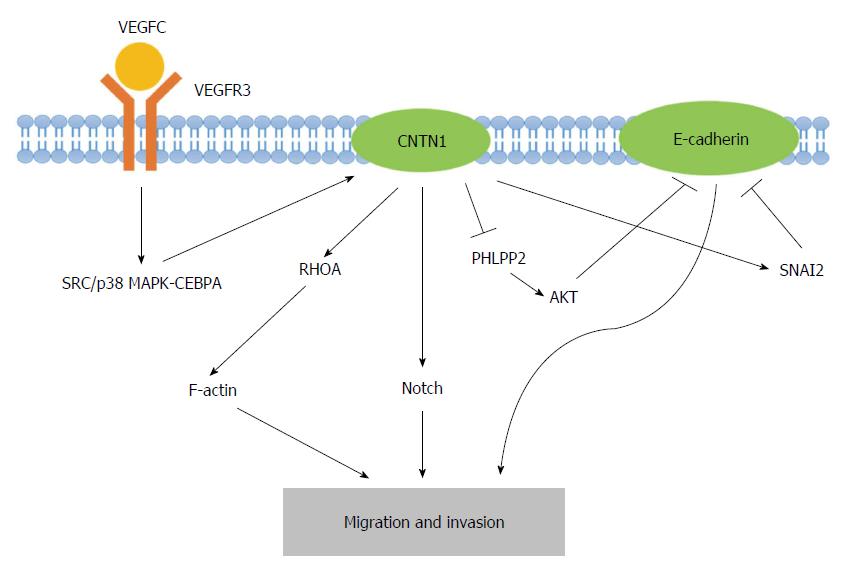
Figure 2 Graphic representation of the molecular mechanisms underlying the contactin 1-induced migration and invasion of cancer cells.
Contactin 1 (CNTN1) serves as a downstream effector of the vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC)/FLT4 axis, which activates SRC/p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-CEBPA signaling. CNTN1 regulates F-actin rearrangement with the aid of RhoA and activates Notch signaling. Furthermore, CNTN1 inhibits E-cadherin through the activation of SNAI2 as well as the upregulation of AKT, which result from the CNTN1-induced inhibition of PHLPP2. These mechanisms of CNTN1 contribute to the migration and invasion of cancer cells. PHLPP2: PH domain and leucine rich repeat protein phosphatase 2.
- Citation: Chen DH, Yu JW, Jiang BJ. Contactin 1: A potential therapeutic target and biomarker in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(33): 9707-9716
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i33/9707.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i33.9707