Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 14, 2015; 21(14): 4391-4396
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4391
Published online Apr 14, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4391
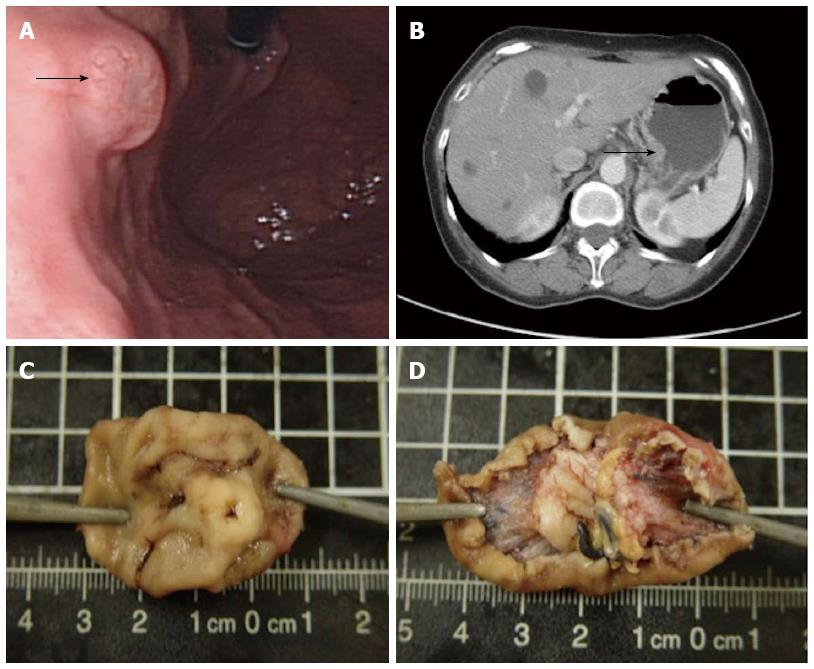
Figure 1 Endoscopy reveals a polypoid mass (arrow) (A); an isolated mural lesion was seen in computed tomography scan (arrow) (B); and grossly, a polypoid submucosal tumor is noted (C, D).
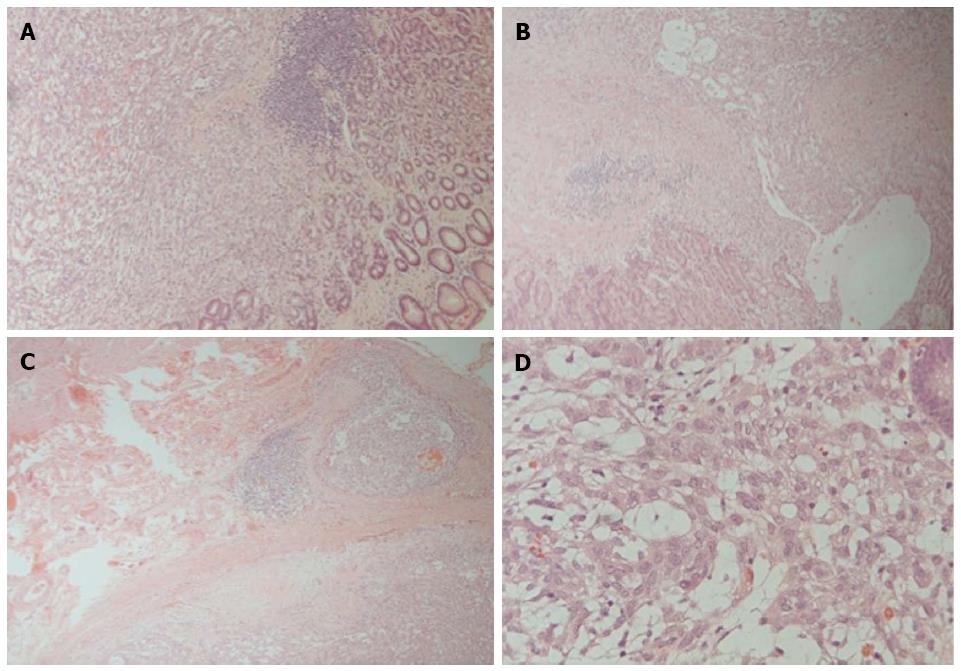
Figure 2 A submucosal biphasic tumor with lymphoid cuffing noted (Magnification × 40) (A); the tumor involves mucosa (Magnification × 100) (B); some infiltrative nests penetrate through the fibrous capsule (Magnification × 40) (C); and the epitheloid cells bearing low-grade pleomorphism and visible nucleoli are arranged in reticular pattern (Magnification × 400) (D).
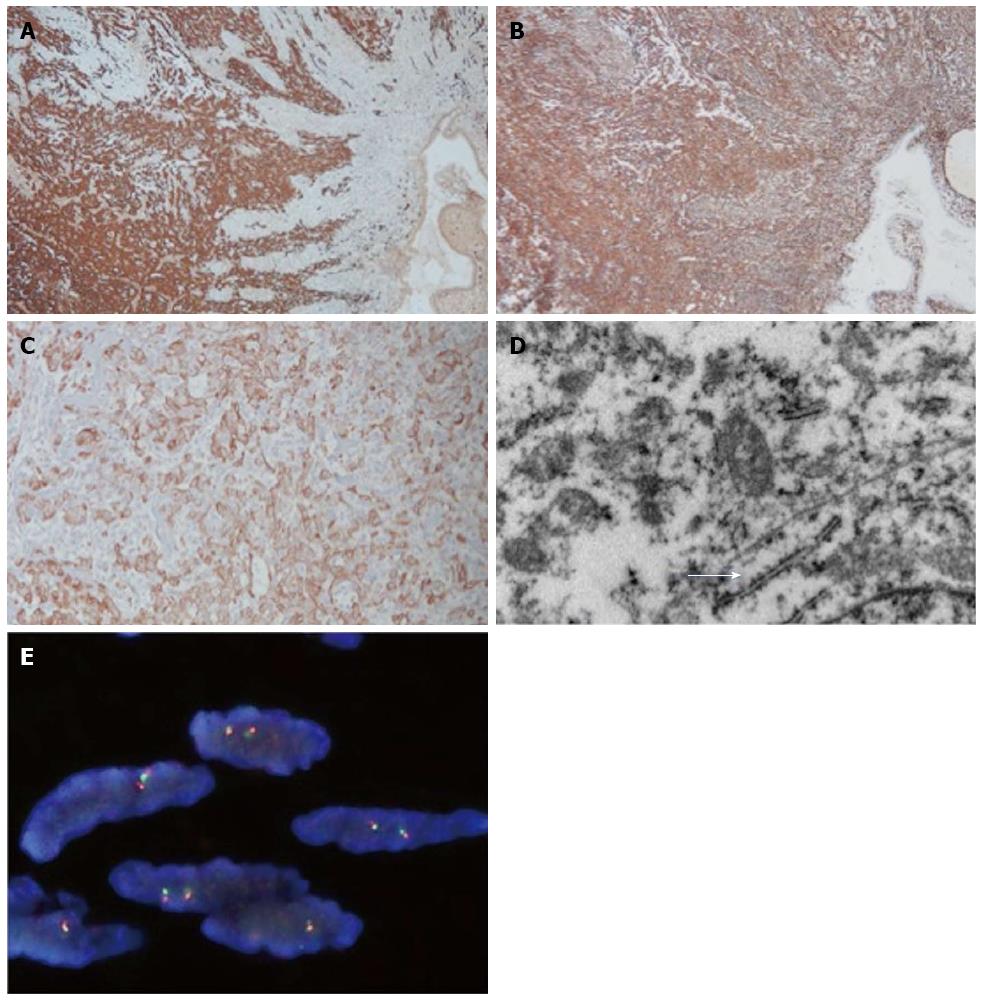
Figure 3 The tumor cells are diffusely positive for S-100 protein (Magnification × 40) (A); Vimentin is expressed by both components (Magnification × 40) (B); the tumor cells express AE1/AE3 (Magnification × 200) (C); and presence of cell junctions (arrow) indicates the epithelial differentiation (D); No break-apart signals observed by FISH (E).
- Citation: Tseng CE, Hsieh YH, Wei CK, Huang HY, Chi CL. Myoepithelial carcinoma of the stomach: A diagnostic pitfall. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(14): 4391-4396
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i14/4391.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4391