Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2015; 21(11): 3380-3387
Published online Mar 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3380
Published online Mar 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3380
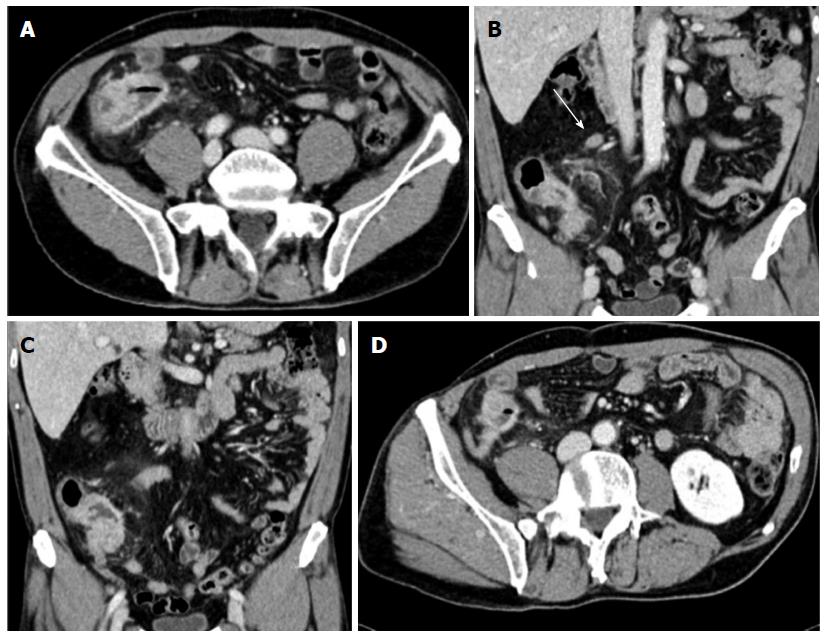
Figure 1 Abdominal computed tomography performed after colonoscopy.
A: Transverse image of the cecum-ascending colon; B and C: Coronal images showing symmetric concentric wall thickening of the cecum-ascending colon mimicking a tumor lesion; heterogeneous hyperdensity of perivisceral fat tissue is also seen. Satellite lymphadenopathy (arrow) is observed along the ileocolic vessels; D: Enlarged appendix with a thickened wall and marked contrast enhancement.
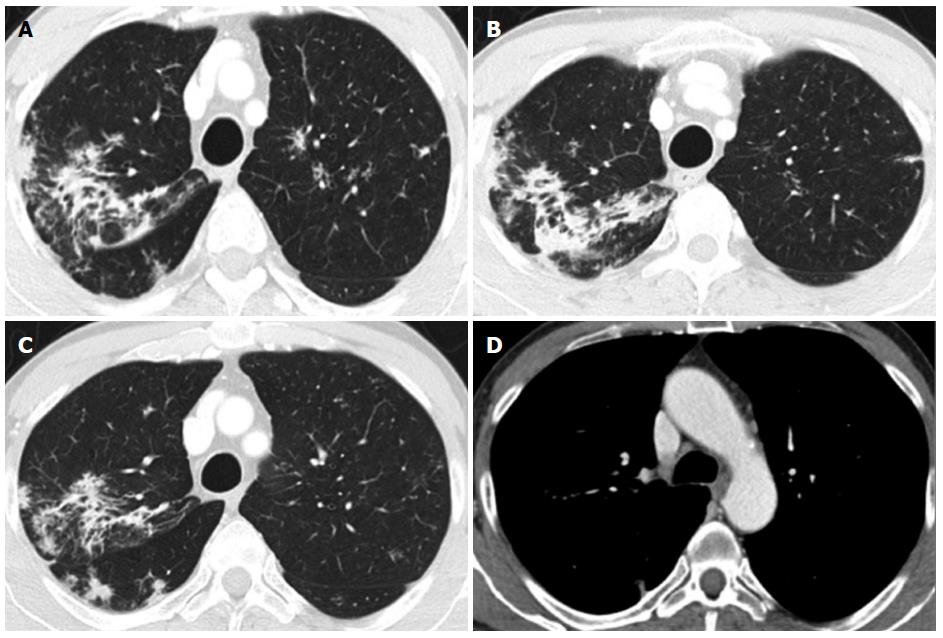
Figure 2 Chest computed tomography performed after colonoscopy for whole-body staging.
A and B: Asymmetric discrete airspace consolidation with air bronchograms in the right upper lobe; C: Numerous micronodular opacities are present in both upper pulmonary lobes (also seen in panel A) with distribution in the peribronchovascular interstitium. These findings showed no significant change after four weeks of antibiotic therapy; D: No pathologic hilar or mediastinal lymph node enlargement was observed.
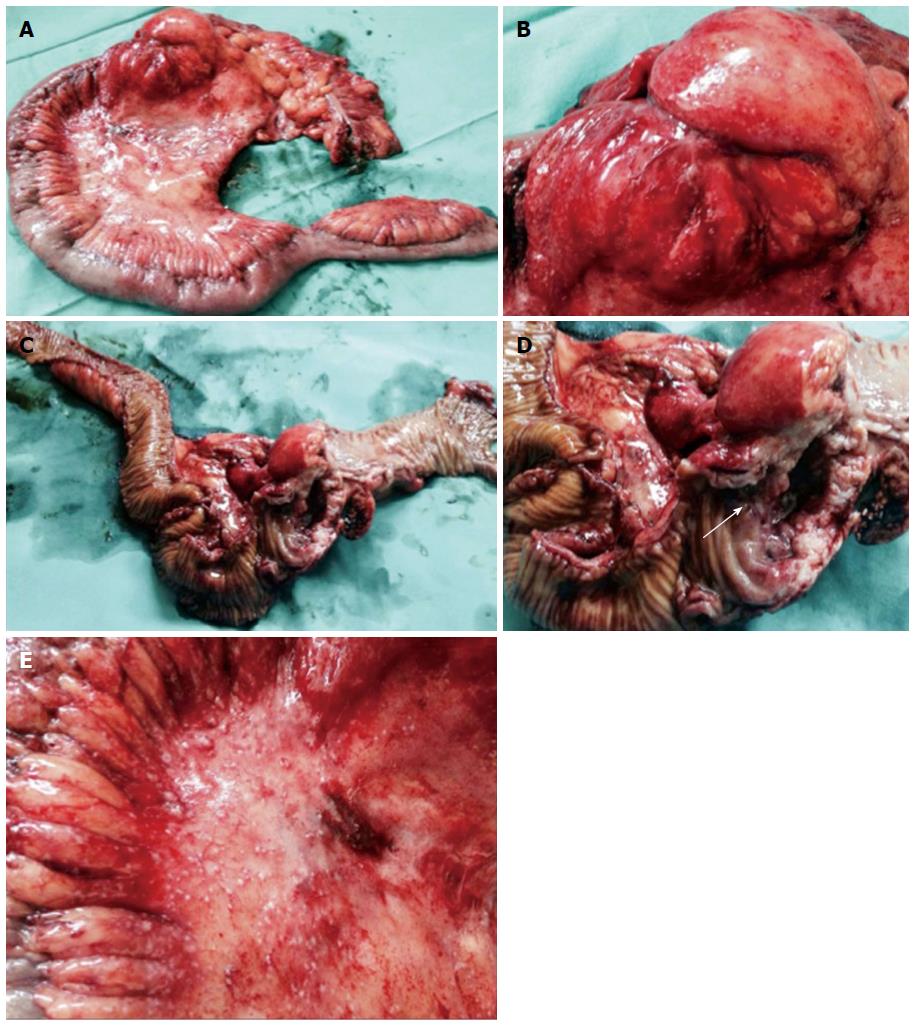
Figure 3 Resected specimen after laparotomy.
A: Right hemicolectomy was performed; B-D: A voluminous stenotic ulcerated lesion of the colonic wall in proximity to the ileocecal valve (arrow in D) was observed; E: Numerous peritoneal micronodules near the colonic lesion are shown.
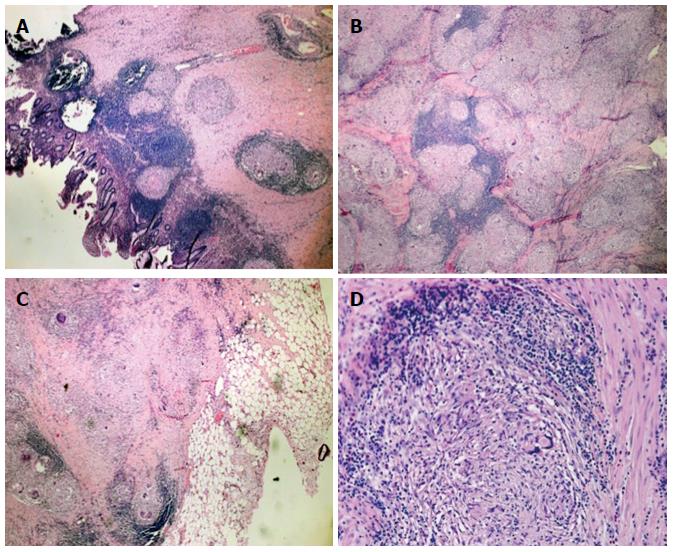
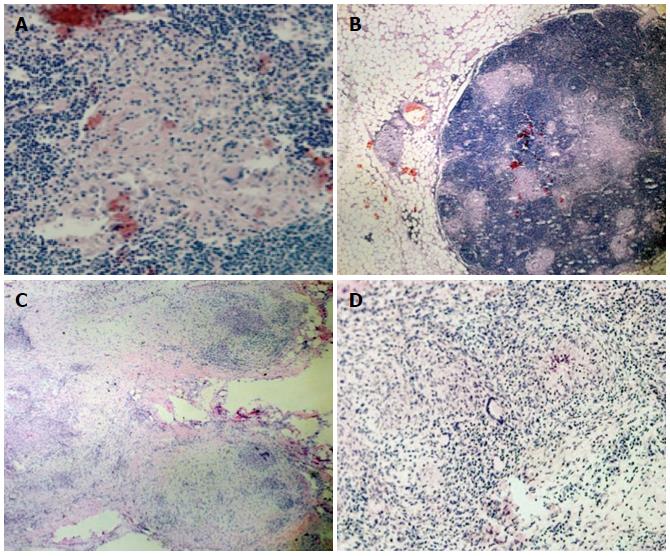
Figure 4 Histologic examination of the intraoperative specimen.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining showed A: Noncaseating epithelioid granulomas in the colonic wall (magnification × 5); B: Confluent granulomata in the colonic wall (magnification × 10); C: Perivisceral involvement (magnification × 5); D: Microscopic aspects of the sarcoidotic granulomas (magnification × 20).
Figure 5 Extracolonic sarcoidosis involvement.
Hematoxylin and eosin staining revealed: Sarcoidotic involvement of locoregional lymphadenopathy (A, B) (A: × 10; B: magnification × 40); Sarcoidotic granulomas in the parietal peritoneum adjacent to the colonic lesion (C, D) (C: magnification × 2; D: magnification × 20).
- Citation: Erra P, Crusco S, Nugnes L, Pollio AM, Di Pilla G, Biondi G, Vigliardi G. Colonic sarcoidosis: Unusual onset of a systemic disease. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(11): 3380-3387
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i11/3380.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3380