Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 21, 2015; 21(11): 3256-3265
Published online Mar 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3256
Published online Mar 21, 2015. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3256
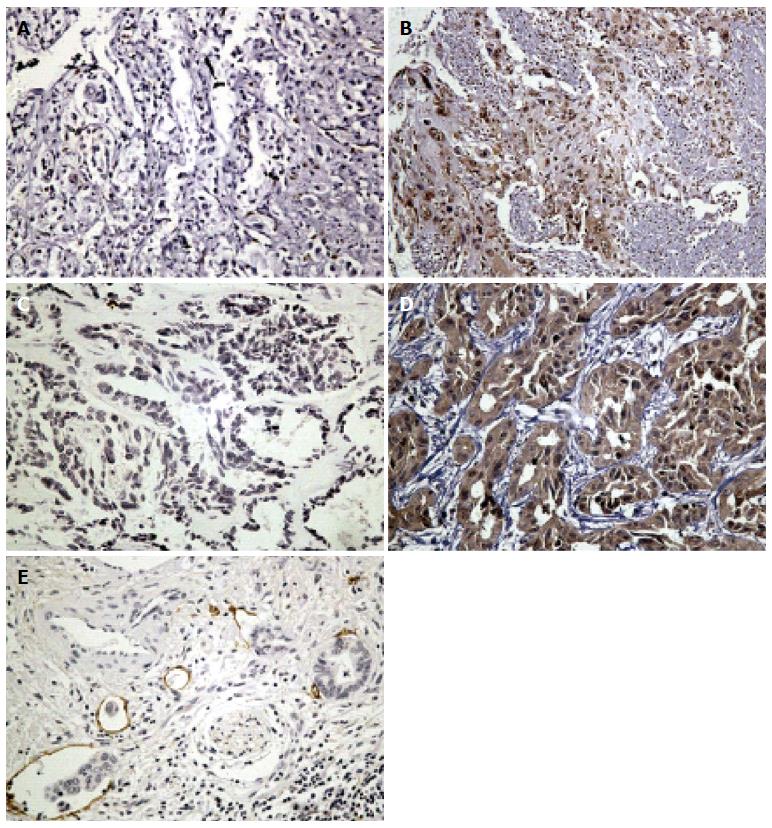
Figure 1 Representative immunohistochemistry in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
A: Negative staining for high-mobility group box 1; B: Strong staining for high-mobility group box 1 was mainly localized in the nucleus, and effused to cytoplasm and extra milieu in inflamed or necrotic areas; C: Negative staining for vascular endothelial growth factor C; D: Strong staining for vascular endothelial growth factor C in cytoplasm; E: Representative staining for D2-40 in lymphatic endothelial cells. A cancer embolus in lymph-vessel is shown; magnification, × 200.
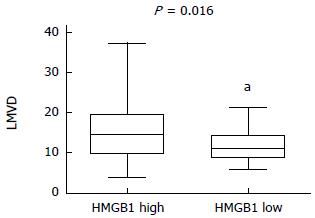
Figure 2 Distribution of lymphatic microvessel density categorized by high-mobility group box 1 expression.
aP < 0.05 vs high expression. LMVD: Lymphatic microvessel density; HMGB1: High-mobility group box 1.
Figure 3 Survival curves of high-mobility group box 1 and vascular endothelial growth factor C in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Kaplan-Meier method univariate analyses of HMGB1 (A); VEGF-C (B); Survival curves of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma patients with and without expression of HMGB1 and VEGF-C co-expression (C). VEGF-C: Vascular endothelial growth factor C; HMGB1: High-mobility group box 1.
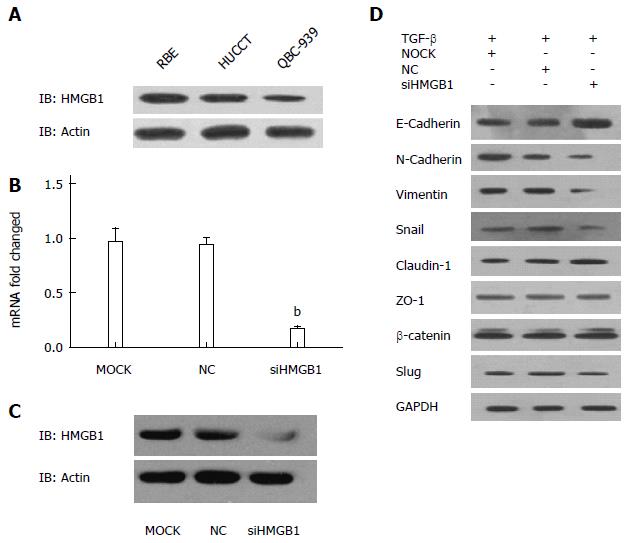
Figure 4 High-mobility group box 1 overexpression promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in RBE cell line.
A: HMGB1 protein expression level in RBE, HUCCT-1, and QBC939 cell lines; B: mRNA expression level of HMGB1; C: Western blot; D: HMGB1 siRNA knockdown in RBE cells; bP < 0.01 vs control. HMGB1: High-mobility group box 1.
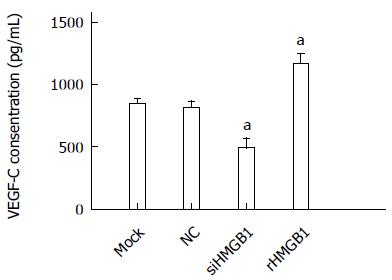
Figure 5 Vascular endothelial growth factor C levels in different groups.
NC: Negative control; rHMGB1: Human recombinant high-mobility group box 1; siHMGB1: short interfering microRNA to high-mobility group box 1; aP < 0.05 vs control. VEGF-C: Vascular endothelial growth factor C.
- Citation: Xu YF, Ge FJ, Han B, Yang XQ, Su H, Zhao AC, Zhao MH, Yang YB, Yang J. High-mobility group box 1 expression and lymph node metastasis in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2015; 21(11): 3256-3265
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v21/i11/3256.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v21.i11.3256