Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2014; 20(47): 17894-17904
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17894
Published online Dec 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17894
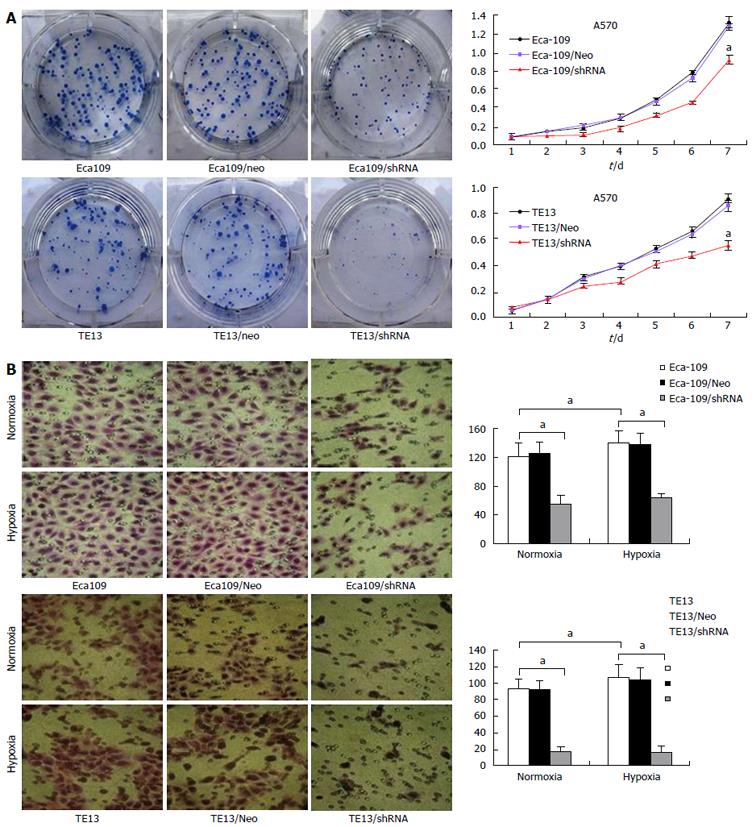
Figure 1 Effects of hypoxia inducible factor-1α knockdown on regulation of esophageal cancer cell viability and migration.
A: MTT assay demonstrated that Eca109/HIF-1α shRNA and TE13/HIF-1α shRNA cells proliferated slower than normal Eca109 and TE13 cells or Eca109 HIF-1α Neo and TE13 HIF-1α Neo cells; B: Transwell migration assay demonstrated that Eca109/HIF-1α shRNA and TE13/HIF-1α shRNA cells invaded slower than normal Eca109 and TE13 cells or Eca109 HIF-1α Neo and TE13 HIF-1α Neo cells. Expression of HIF-1α and the four VM-related genes in TE13/shHIF and Eca109/shHIF cells under hypoxia vs under normoxia, aP < 0.05. HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor.
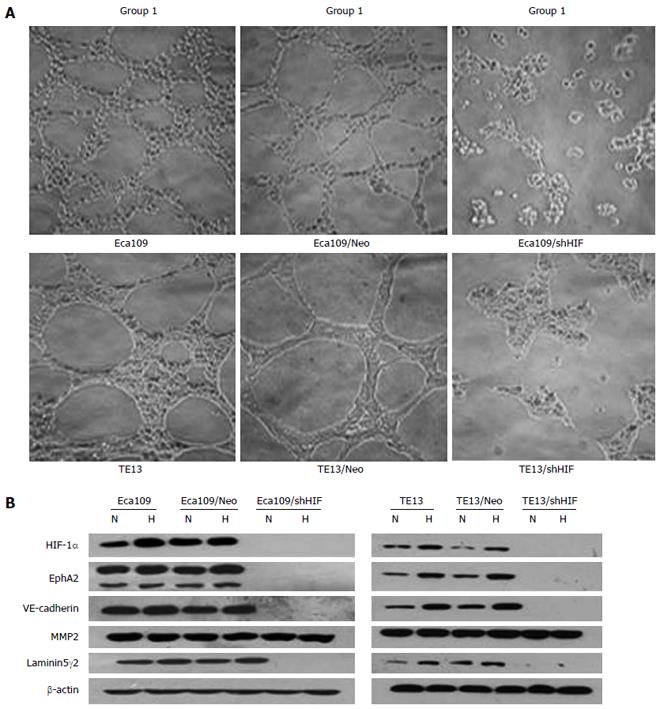
Figure 2 Knockdown of hypoxia inducible factor-1α inhibits vasculogenic mimicry formation and expression of vasculogenic mimicry-related genes in vitro.
A: Effect of silencing HIF-1α on the formation of VM in ESCC cells (magnification × 200) (Group 1: Untransfected cells; Group 2: Cells transfected with empty vector; Group 3: Cells transfected with pGCsi-HIF3); Control group vs parental cells, P < 0.05; B: Expression of HIF-1α protein and VM-related genes in esophageal squamous cancer cells. Expression of HIF-1α and the four VM-related genes in TE13/shHIF and Eca109/shHIF cells under hypoxia vs under normoxia, P < 0.05. HPF: High-power field; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor; VM: Vasculogenic mimicry; ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. N: Normoxia; H: Hypoxia.
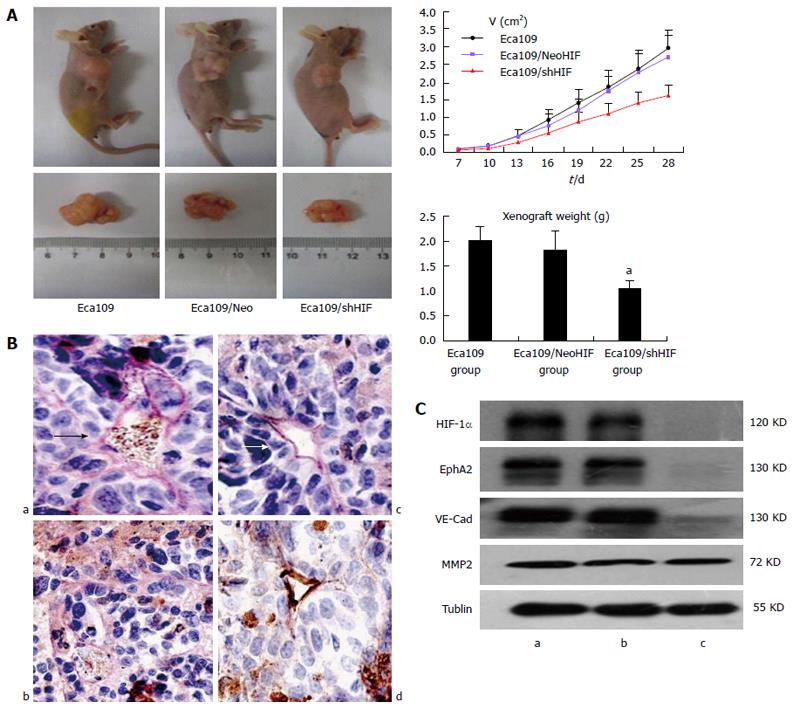
Figure 3 In vivo effects of hypoxia inducible factor-1α knockdown on regulation of esophageal cancer cell xenograft formation and gene expression.
A: Tumor size curve and weight of xenograft (Eca109/shHIF-1α cells vs Eca109 cells and Eca109/HIF-1α Neo cells, aP < 0.05); B: VM structure (arrow) in xenografts of three groups (a: Eca109 group; b: Eca109/shHIF group; c: Eca109/NeoHIF group; d: Normal vessels; arrow, VM structure); C: Western blot detected HIF-1α and EphA2, VE-cadherin and MMP2 expression (a: Eca109 group; b: Eca109/NeoHIF group; c: Eca109/shHIF group; Eca109/shHIF-1α cells vs Eca109 and Eca109 HIF-1α Neo control cells, P < 0.05). HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor; VM: Vasculogenic mimicry.
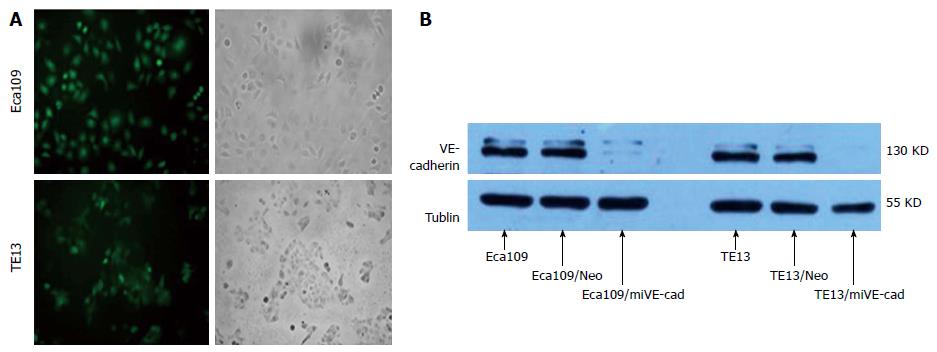
Figure 4 Identification of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells stably transfected with pGCsi-VE-cadherin.
A: Expression of green fluorescent protein in two stably transfected ESCC cell lines (magnification × 200); B: Expression of VE-cadherin protein in the two ESCC cell lines. ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
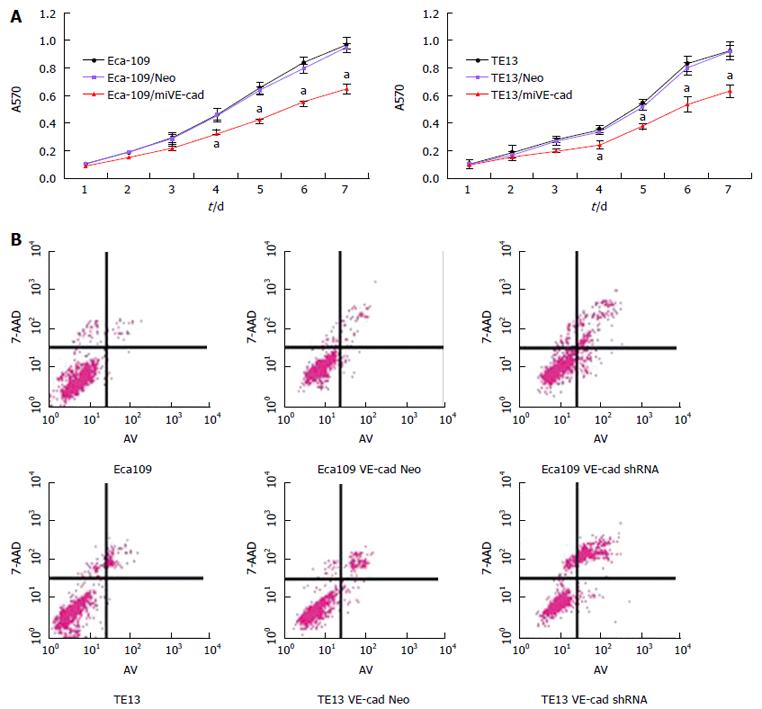
Figure 5 Knockdown of VE-cadherin inhibits proliferation and promotes apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.
A: shRNA-mediated VE-cadherin knockdown inhibits the proliferation of ESCC cells. Eca109, TE13 and their derived stable cells were cultured under normoxic conditions and proliferation was determined by MTT assay; aP < 0.05; B: shRNA-mediated VE-cadherin knockdown promoted apoptosis of ESCC cells. Eca109, TE13 and their derived stable cells were cultured under normoxic or hypoxic conditions and apoptosis was detected by Annexin V staining. ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
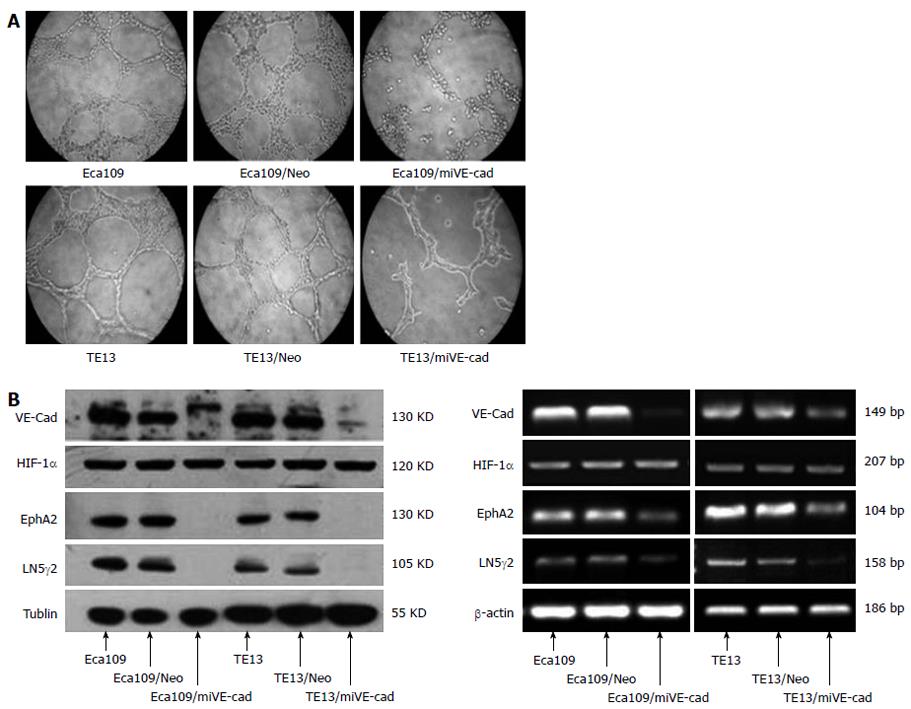
Figure 6 shRNA against VE-cadherin inhibits vasculogenic mimicry formation and expression of vasculogenic mimicry-related genes in vitro.
A: Effect of silencing VE-cadherin on the formation of VM in ESCCs (magnification × 400); B: Protein and mRNA expression of VE-cadherin and VM-related genes in esophageal squamous cancer cells. ESCC: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; VM: Vasculogenic mimicry; VE-cad: VE-cadherin; LN5γ2: Laminin 5γ2; HIF: Hypoxia inducible factor; EphA2: EphrinA2.
- Citation: Tang NN, Zhu H, Zhang HJ, Zhang WF, Jin HL, Wang L, Wang P, He GJ, Hao B, Shi RH. HIF-1α induces VE-cadherin expression and modulates vasculogenic mimicry in esophageal carcinoma cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(47): 17894-17904
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i47/17894.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i47.17894