Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 21, 2014; 20(43): 16306-16310
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16306
Published online Nov 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16306
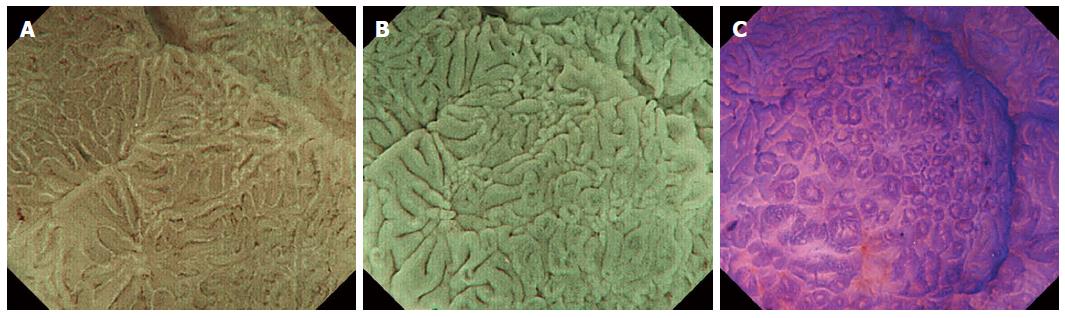
Figure 1 Magnifying endoscopy of early colorectal adenocarcinoma.
A: M-NBI shows the vascular pattern and the surface pattern; however, the surface pattern is obscure; B: MA-NBI effaces the vascular pattern and accentuates the surface pattern; C: M-CV provides a clear pit pattern. M-NBI: Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging; MA-NBI: Magnifying endoscopy with acetic acid spray and narrow-band imaging; M-CV: Magnifying endoscopy with crystal violet dye.
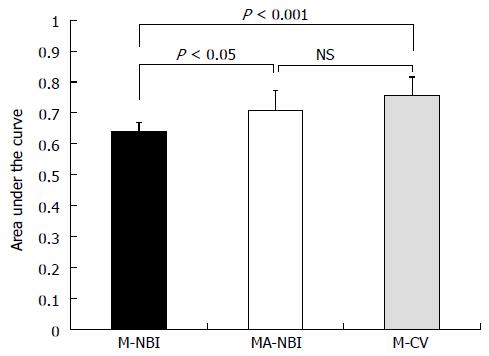
Figure 2 Comparison of the areas under the receiver operating characteristic curves of 10 colonoscopists for differentiating early colorectal adenocarcinomas from adenomas.
M-NBI: Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging; MA-NBI: Magnifying endoscopy with acetic acid spray and narrow-band imaging; M-CV: Magnifying endoscopy with crystal violet dye; NS: Not significant.
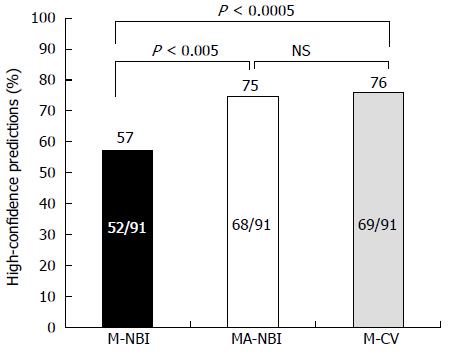
Figure 3 Comparison of the proportions in which predictions were made with high confidence.
M-NBI: Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging; MA-NBI: Magnifying endoscopy with acetic acid spray and narrow-band imaging; M-CV: Magnifying endoscopy with crystal violet dye; NS: Not significant.
- Citation: Goto N, Kusaka T, Tomita Y, Tanaka H, Itokawa Y, Koshikawa Y, Yamaguchi D, Nakai Y, Fujii S, Kokuryu H. Magnifying narrow-band imaging with acetic acid to diagnose early colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(43): 16306-16310
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i43/16306.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i43.16306