Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 21, 2014; 20(31): 10729-10739
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10729
Published online Aug 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10729
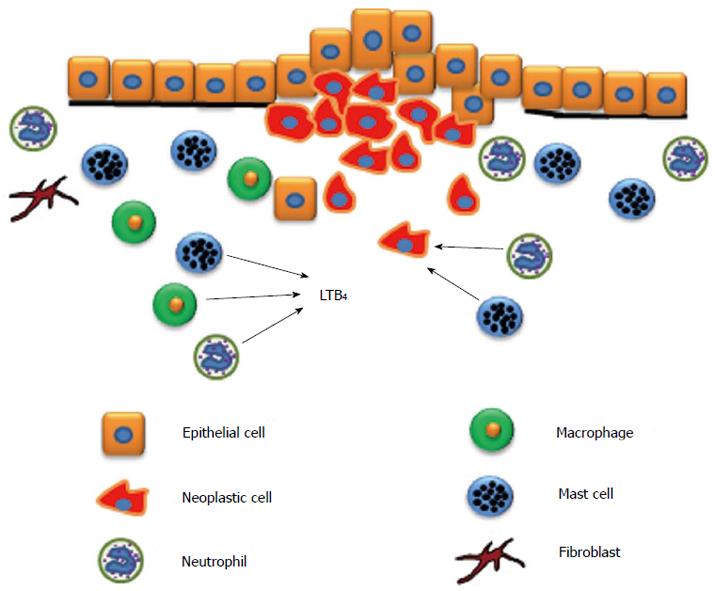
Figure 1 Inflammatory cell infiltration into the tumor microenvironment.
As pancreatic adenocarcinoma progresses, inflammatory cells such as mast cells, neutrophils, and macrophages are attracted to the tumor microenvironment and enhance tumor growth. Leukotriene B4 (LTB4) is a chemotactic factor for macrophages, neutrophils, and mast cells. Fibroblasts are also activated and enhance collagen production.
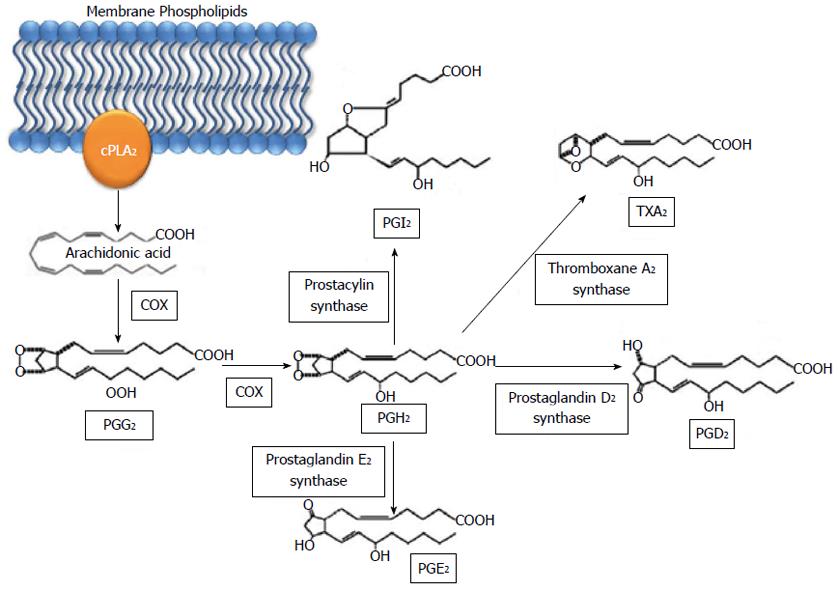
Figure 2 Metabolic pathway of prostaglandins via cyclooxygenase.
Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2 and converted to PGG2 and subsequently PGH2 by COX. PGH2 is then converted to PGI2, TXA2, PGD2, and PGE2. cPLA2: Cytosolic phospholipase A2; COX: Cyclooxygenase; PG: Prostaglandin; TX: Thromboxane.
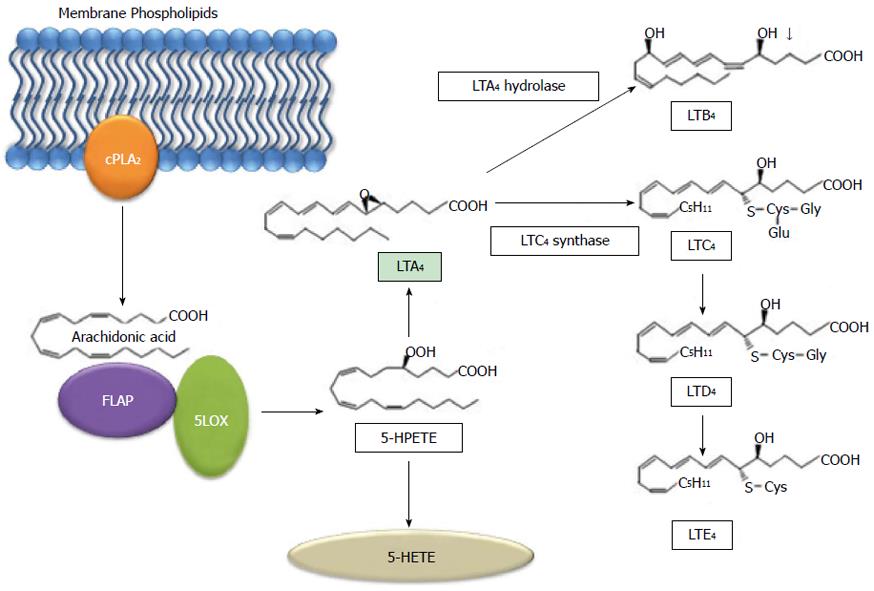
Figure 3 Metabolic pathway of arachidonic acid via 5- lipoxygenase.
Arachidonic acid is released from membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2 and converted to 5-HPETE by 5-LOX and 5-LOX activating protein (FLAP). 5-HPETE can then form either 5-HETE or LTA4. LTA4 then becomes LTB4 or LTC4. LTC4 can then form LTD4 and subsequently LTE4. cPLA2: Cytosolic phospholipase A2; LOX: Lipoxygenase; FLAP: 5-LOX activating protein; HPETE: Hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid; HETE: Hydroxyl 6 trans 8, 11, 14 cis eicosatetraenoic acid; LT: Leukotriene.
- Citation: Knab LM, Grippo PJ, Bentrem DJ. Involvement of eicosanoids in the pathogenesis of pancreatic cancer: The roles of cyclooxygenase-2 and 5-lipoxygenase. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(31): 10729-10739
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i31/10729.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i31.10729