Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2014; 20(30): 10440-10448
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10440
Published online Aug 14, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10440
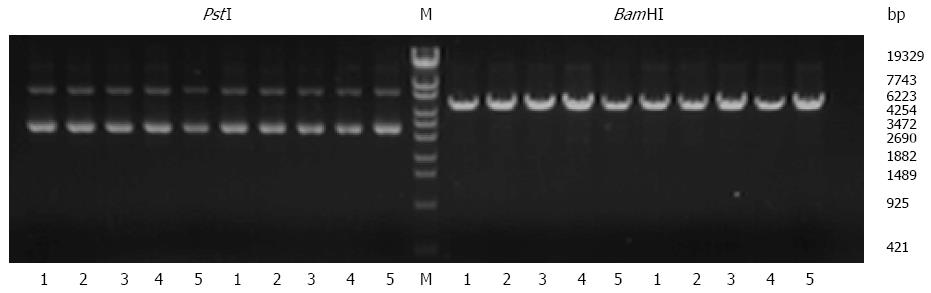
Figure 1 Identification of recombinant vectors.
BamHI and PstI were used to digest and identify the recombinant plasmids. The results show that all plasmids were positive for the recombinant vector; M: Marker; 1: p-OPN-siRNA-1; 2: p-OPN-siRNA-2; 3: p-OPN-siRNA-3; 4: p-OPN-siRNA-4; 5: p-NC-siRNA.
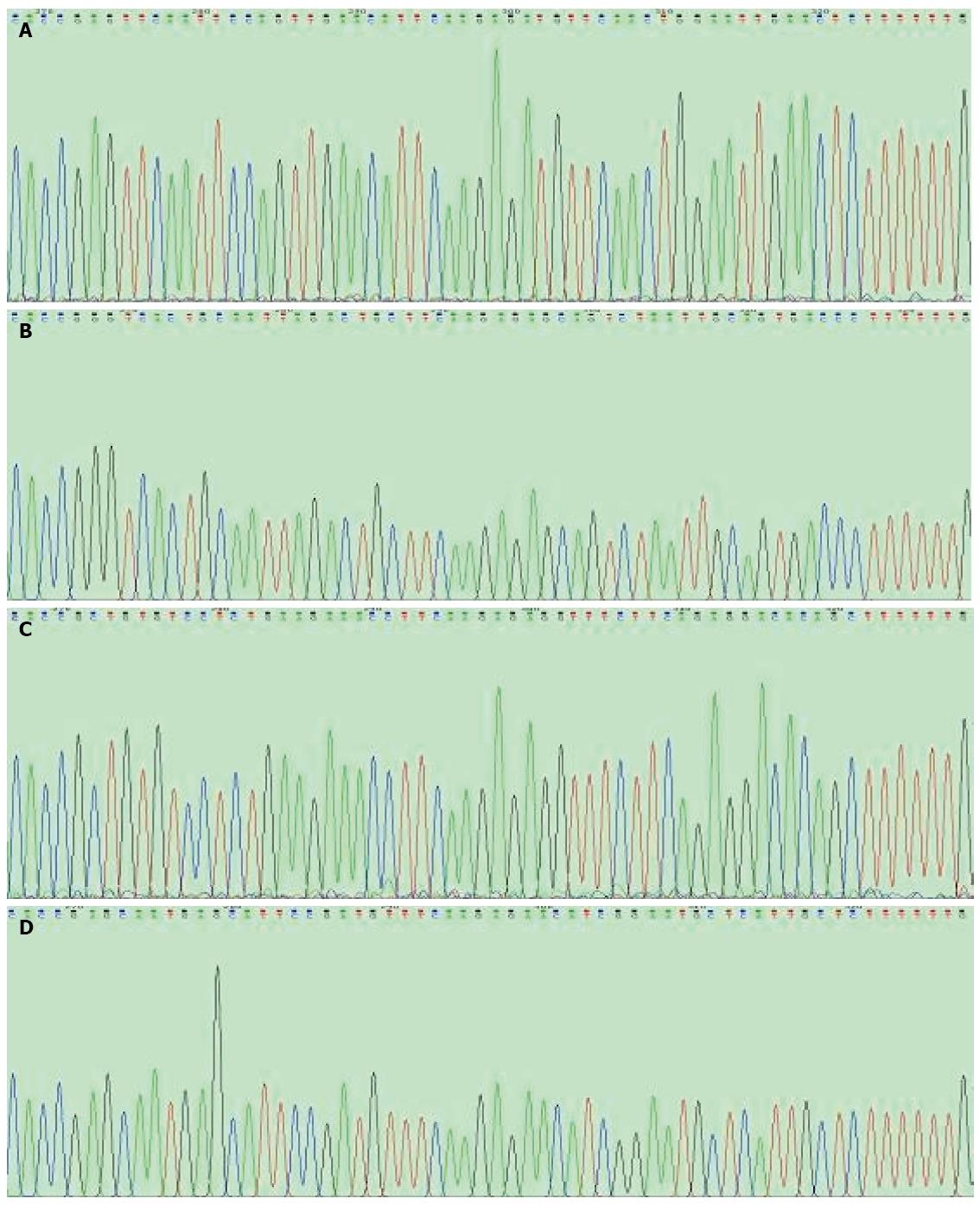
Figure 2 Verification of the recombinant vectors.
Sequencing of the recombinant vectors (performed by Sangon Co.) showed that all coding sequences were inserted correctly with no mutations; A: p-OPN-siRNA-1; B: p-OPN-siRNA-2; C: p-OPN-siRNA-3; D: p-OPN-siRNA-4.
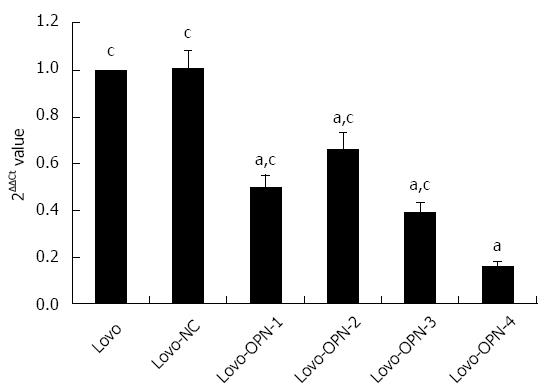
Figure 3 Confirmation of osteopontin knockdown by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction.
The expression of OPN mRNA was significantly decreased in Lovo cells by p-OPN-siRNA-1, -2, -3, and -4 (aP < 0.05 vs Lovo), with the largest reduction observed with p-OPN-siRNA-4 (cP < 0.05 vs Lovo-OPN-4). OPN: Osteopontin.
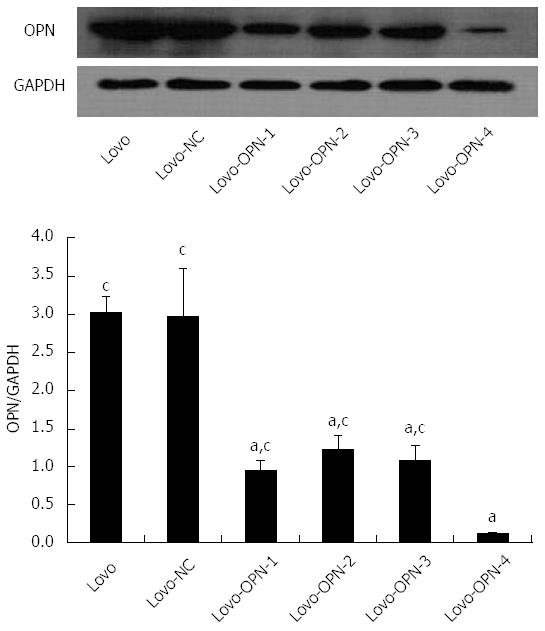
Figure 4 Confirmation of osteopontin knockdown by western blot.
The expression of OPN protein was significantly decreased in Lovo cells by p-OPN-siRNA-1, -2, -3, and -4 (aP < 0.05 vs Lovo), with the largest reduction observed with p-OPN-siRNA-4 (cP < 0.05 vs Lovo-OPN-4). OPN: Osteopontin.
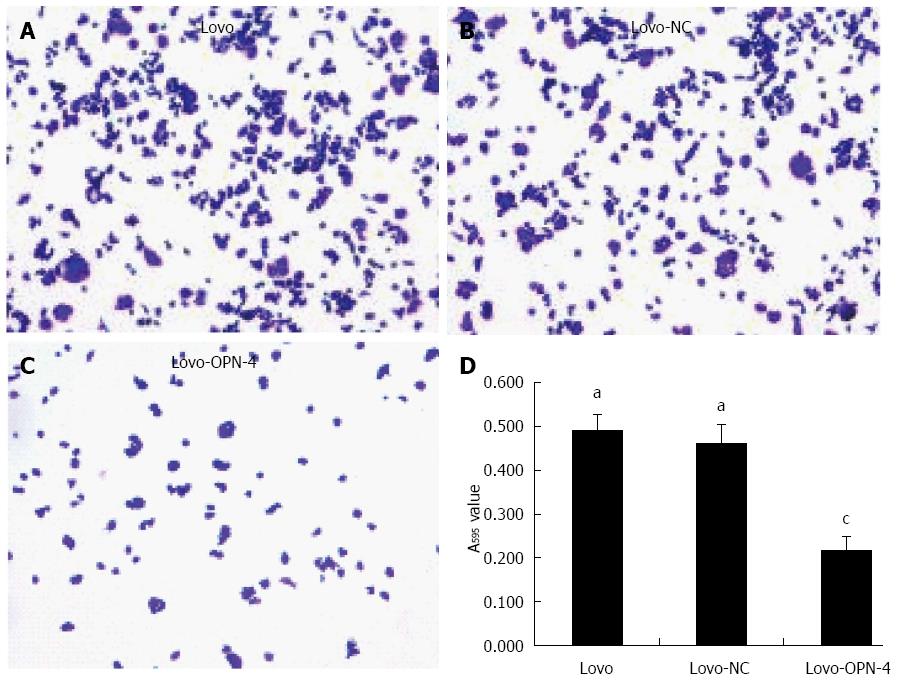
Figure 5 Cell adhesion assay.
Staining with 0.1% crystal violet (magnification × 100) revealed reduced adhesion in cells expressing Lovo-OPN-4 (A-C); Quantification of adhesion, obtained by absorbance at 595 nm (D) (n = 15; aP < 0.05 vs Lovo-OPN-4; cP < 0.05 vs Lovo). OPN: Osteopontin.
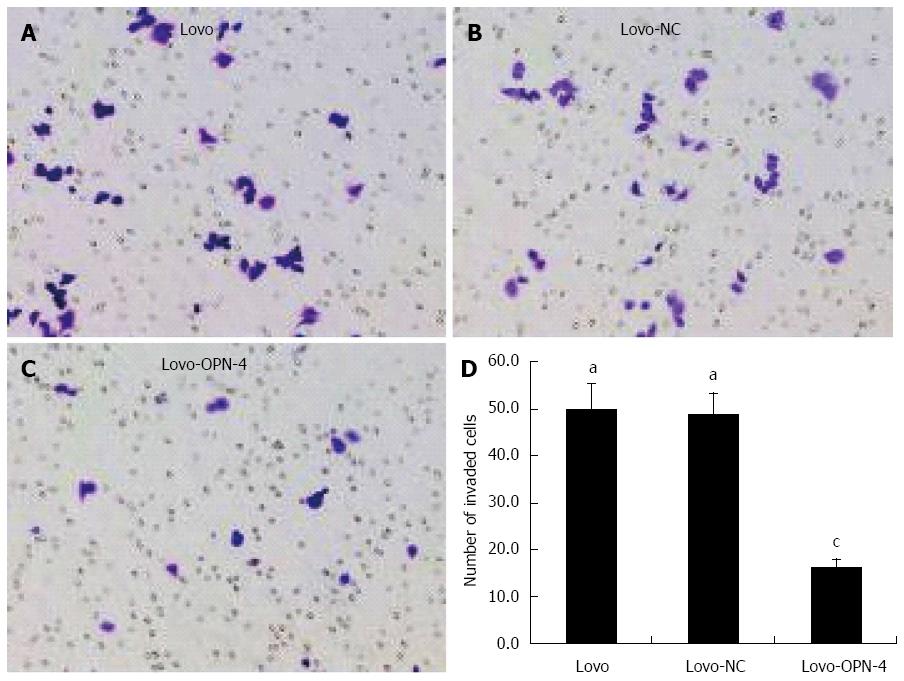
Figure 6 Cell invasion assay.
Staining with 0.1% crystal violet (magnification × 200) revealed a reduced number of invasive Lovo-OPN-4 cells (A-C); Quantification of invasion (D) (n = 15; aP < 0.05 vs Lovo-OPN-4; cP < 0.05 vs Lovo). OPN: Osteopontin.
- Citation: Wu XL, Lin KJ, Bai AP, Wang WX, Meng XK, Su XL, Hou MX, Dong PD, Zhang JJ, Wang ZY, Shi L. Osteopontin knockdown suppresses the growth and angiogenesis of colon cancer cells. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(30): 10440-10448
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i30/10440.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10440