Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2014; 20(28): 9578-9584
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9578
Published online Jul 28, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9578
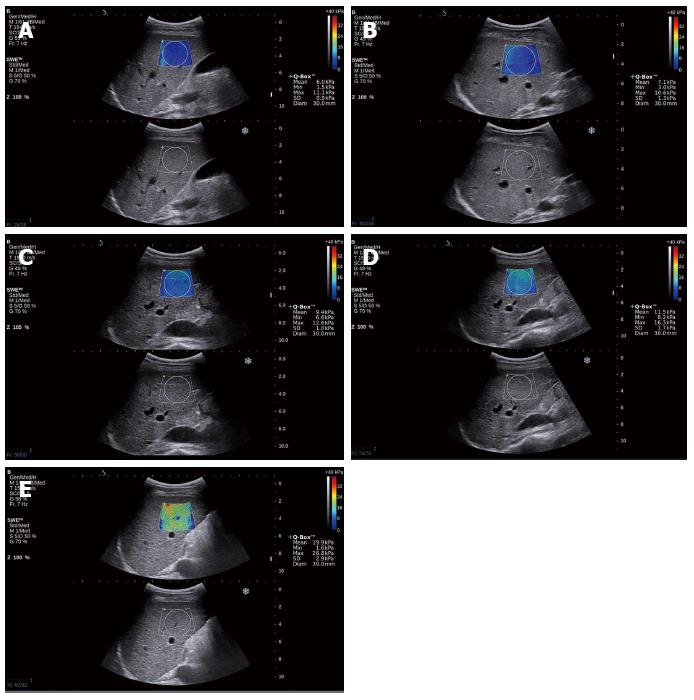
Figure 1 Liver elasticity maps assessed using the shear wave elastography technique.
The liver stiffness is changed in colour by different fibrosis levels. A: Fibrosis levels F0; B: Fibrosis levels F1; C: Fibrosis levels F2; D: Fibrosis levels F3; E: Fibrosis levels F4.
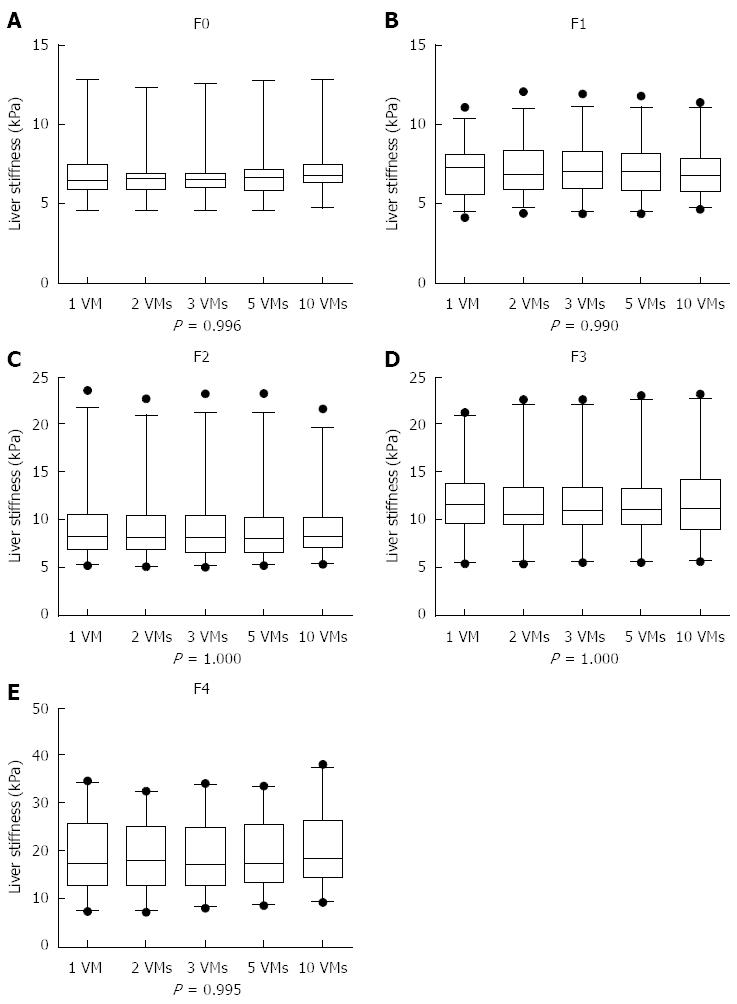
Figure 2 Box-plot showing liver stiffness measurement at different stages of fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B.
Box plots show 25%-75% interquartile range (box), median (middle line), 5%-95% range (two outer lines), and outliers (black dots). LSM: liver stiffness measurement; CHB: Chronic hepatitis B; VMs: Valid measurements.
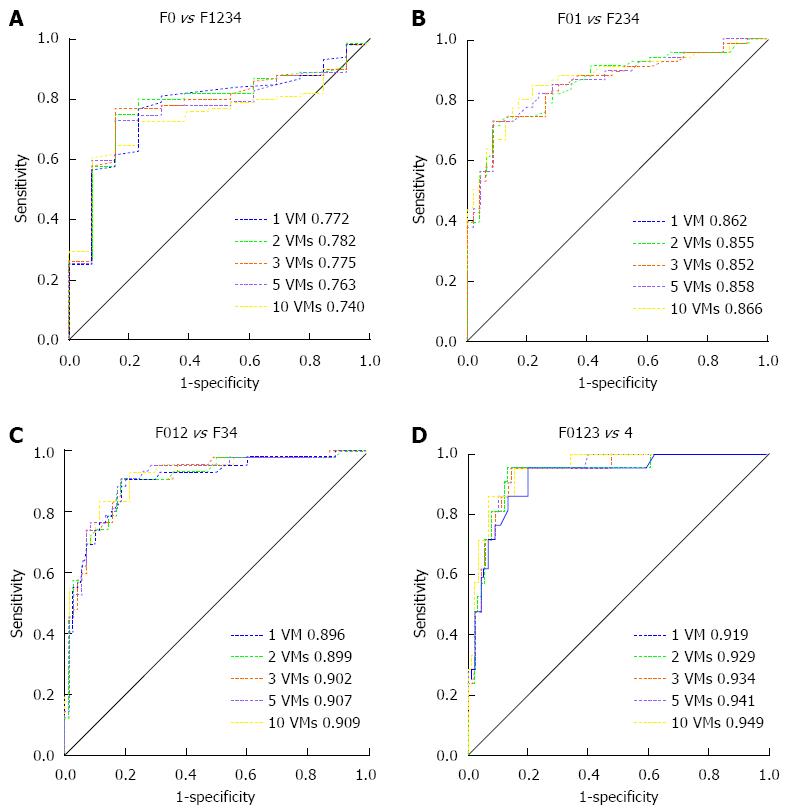
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curves of all groups showed that the diagnostic performance of 1 VM, 2 VMs, 3 VMs, 5 VMs and 10 VMs of detection in distinguishing degree of liver fibrosis was equivalent.
The receiver operating characteristic curves using these different VMs for predicting significant fibrosis (≥ F0) (A), (≥ F1) (B), (≥ F2) (C) and cirrhosis (F4) (D) in chronic hepatitis B. AUROC values among 1, 2, 3, 5 and all 10 VMs taken did not differ significantly (P > 0.05 for all). VMs: Valid measurements.
- Citation: Huang ZP, Zhang XL, Zeng J, Zheng J, Wang P, Zheng RQ. Study of detection times for liver stiffness evaluation by shear wave elastography. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(28): 9578-9584
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i28/9578.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i28.9578