Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 21, 2014; 20(15): 4421-4427
Published online Apr 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4421
Published online Apr 21, 2014. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4421
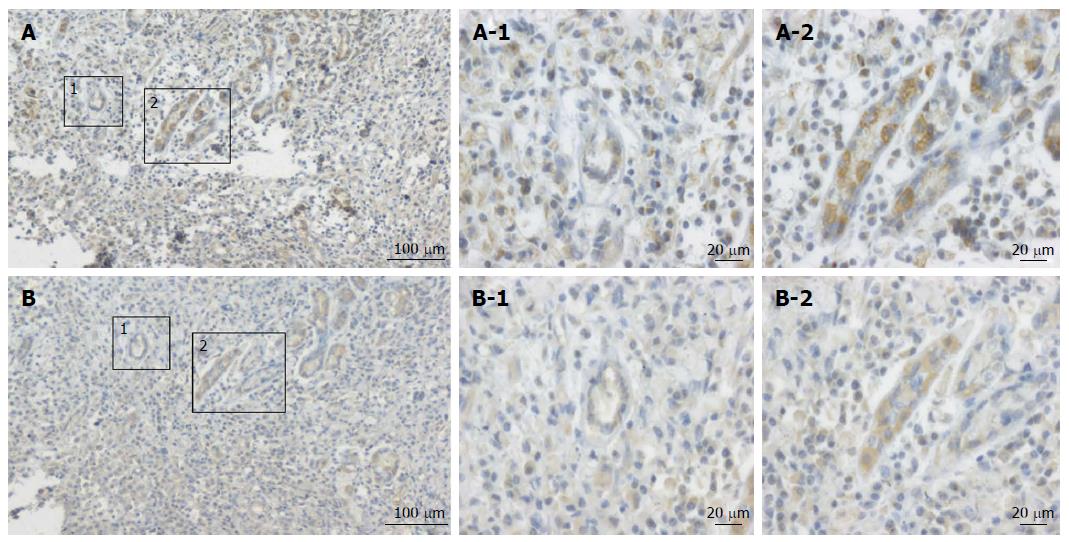
Figure 1 The expression patterns of CCL2 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α were detected in consecutive human gastric cancer tissues sections.
A: Expression pattern of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha (HIF-1α) in human gastric cancer tissues (100 ×); B: Expression pattern of CCL2 in the human gastric cancer tissues (400 ×). The spatial distribution of HIF-1α expression was consistent with that of CCL2 in tumor sections. (A-1 vs B-1, A-2 vs B-2).
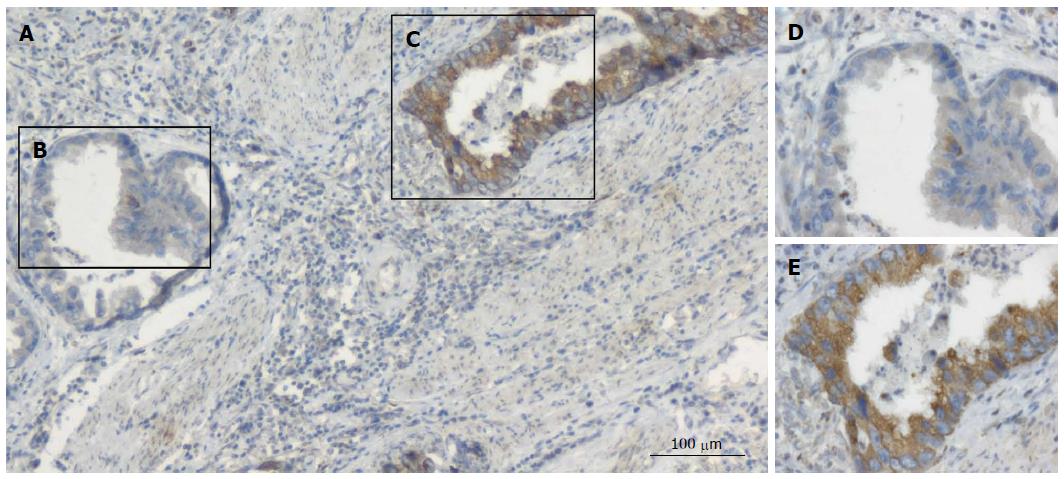
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical detection of the expression pattern of CCL2 in human gastric cancer tissue.
A: Expression pattern of CCL2 in gastric cancer (100 ×); C, E: Positive staining for CCL2; D, E: Expression pattern of CCL2 in gastric cancer (400 ×); The images in D and E are the amplified sections corresponding to B and C. B, D: Negative staining for CCL2.
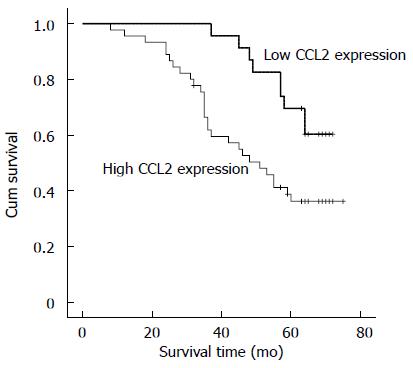
Figure 3 Relationship between the expression of CCL2 and overall survival time in gastric cancer patients.
Patients with high CCL2 expression had a poor overall survival [50.6 mo (95%CI: 44.44-56.93) vs 64.6 mo (95%CI: 60.27-68.94), P = 0.013].
- Citation: Tao LL, Shi SJ, Chen LB, Huang GC. Expression of monocyte chemotactic protein-1/CCL2 in gastric cancer and its relationship with tumor hypoxia. World J Gastroenterol 2014; 20(15): 4421-4427
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v20/i15/4421.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i15.4421